Chaque année qui passe, il devient de plus en plus évident qu'être une entreprise « axée sur les données » n'est plus optionnel.
Les données peuvent révéler beaucoup de choses sur les utilisateurs, les bases de clients, les marchés, et plus encore. Des modèles et des tendances peuvent même être extraits des données qui résident dans les bases de données internes. Être capable d'analyser les données et de les mettre en action peut faire une grande différence pour de nombreuses industries.
Bien sûr, pour interpréter les données et les appliquer efficacement, une entreprise devra considérer quel logiciel d'analyse est le plus adapté pour elle.
Dans cet article, nous allons décomposer les quatre principaux types d'analyses de données que les entreprises devraient s'attendre à rencontrer dans leur recherche de logiciels.
Types d'analyses de données
Les entreprises cherchant à obtenir un avantage concurrentiel en utilisant les données à l'intérieur et à l'extérieur de leurs systèmes devraient se familiariser avec les quatre types d'analyses de données.
Quels sont les différents types d'analyses de données ?
- L'analyse descriptive répond à la question « que s'est-il passé ? »
- L'analyse diagnostique cherche à savoir « pourquoi cela s'est-il passé ? »
- L'analyse prédictive indique ce qui est susceptible de se produire ensuite.
- L'analyse prescriptive fournit les actions à entreprendre ensuite.
Maintenant que vous avez une compréhension de base de chaque type d'analyse de données, plongeons plus profondément dans les caractéristiques, les défis et les exemples de chacun.
Analyse descriptive
L'analyse descriptive est introductive, rétrospective, et répond à la question « que s'est-il passé ? » Elle représente environ 80 % des analyses commerciales aujourd'hui, ce qui en fait le type d'analyse de données le plus courant.
Aperçu de l'analyse descriptive
L'analyse descriptive introduit un problème à une entreprise en analysant les données historiques qui résident dans les bases de données et systèmes internes. Cette analyse est peu complexe avec peu de barrières à l'entrée pour les analystes de données.
L'analyse descriptive est généralement visualisée dans des rapports simples, des tableaux de bord et des tableaux de bord de performance à l'aide de logiciels de visualisation de données. Il est courant de présenter ces informations aux décideurs en utilisant des outils de business intelligence.
Pour que l'analyse de données apporte une réelle valeur, un problème doit d'abord être identifié. C'est peut-être le plus grand avantage de l'analyse descriptive et comment elle ouvre la porte à des solutions plus avancées, dont certaines seront discutées plus tard dans l'article.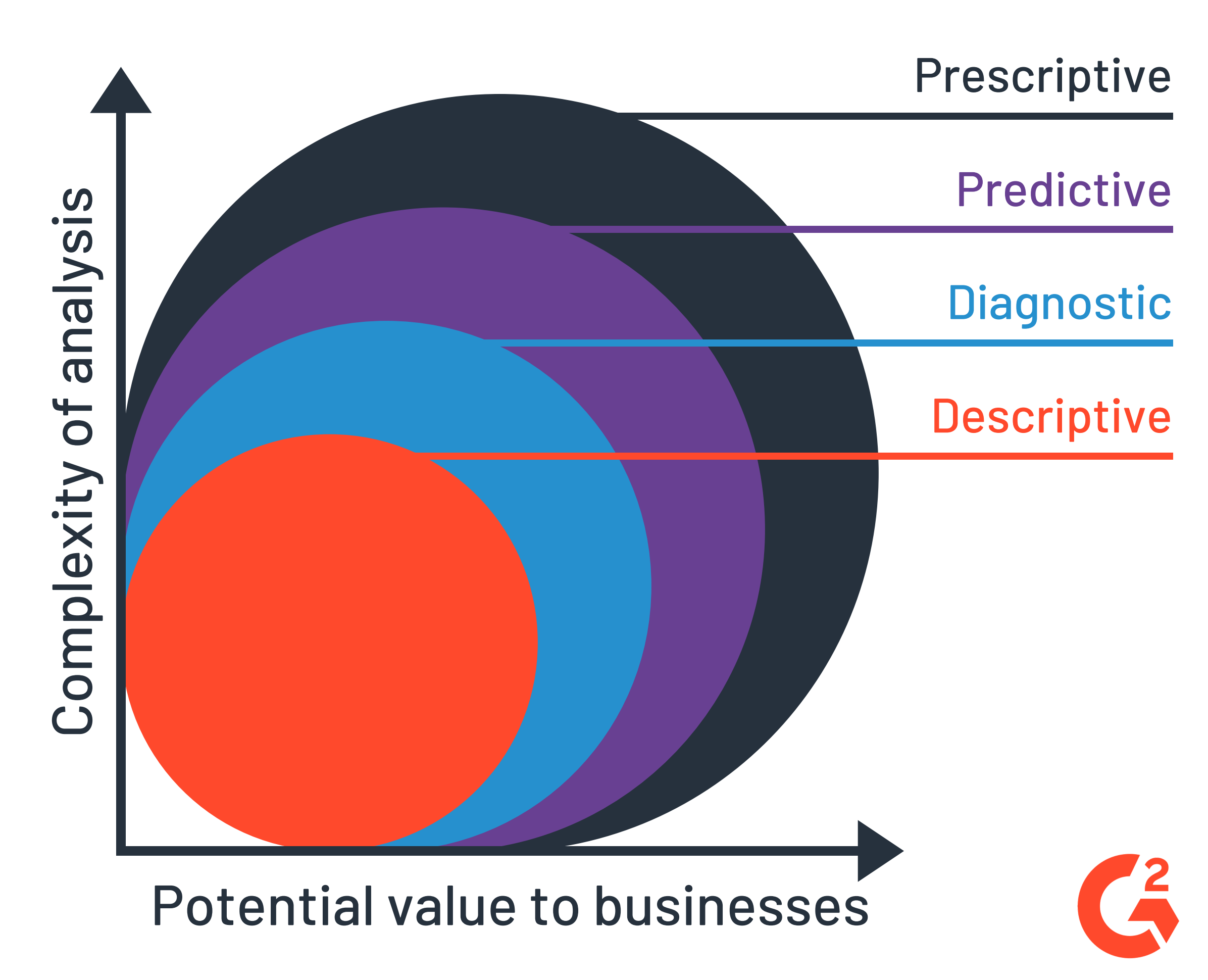
Défis de l'analyse descriptive
L'analyse descriptive, cependant, a ses limites. Alors que d'autres analyses vont plus en profondeur sur des problèmes spécifiques et tracent les prochaines étapes possibles qu'une entreprise devrait prendre, l'analyse descriptive se contente d'introduire le problème.
Pour de nombreuses entreprises qui se considèrent comme « axées sur les données », l'analyse descriptive n'est que la première de nombreuses étapes.
Exemple d'analyse descriptive
Disons que les chiffres de trafic du site web ont légèrement échoué à atteindre leur objectif en 2018. C'est une raison suffisante pour effectuer une analyse descriptive pour voir ce qui a mal tourné.

L'analyse nous dit :
- Le trafic du site web a chuté drastiquement au T3.
- Il a repris au début du T4.
- Il est resté stable tout au long de l'année.
Analyse diagnostique
L'analyse diagnostique est également rétrospective, mais elle cherche à savoir « pourquoi » le problème qui a été exposé dans l'analyse descriptive s'est produit.
Aperçu de l'analyse diagnostique
L'analyse diagnostique est l'étape essentielle « suivante » après qu'une entreprise ait effectué une analyse descriptive. L'analyse diagnostique exploite également les données historiques d'une entreprise à travers de nombreuses sources internes.
Cette analyse est plus complexe et nécessite que les analystes de données approfondissent les analyses pour trouver des modèles, des tendances et des corrélations. Cela peut être fait en utilisant des techniques de fouille de données telles que l'analyse de régression, la détection d'anomalies, l'analyse de regroupement, et d'autres.
Le plus grand avantage de l'analyse diagnostique est de pouvoir fournir un contexte à un problème commercial à travers un certain nombre de modèles de données.
Défis de l'analyse diagnostique
Bien que les analyses diagnostiques reposent sur la rapidité et la précision des machines, il est important que les analystes humains ne confondent pas les modèles avec la « causalité » d'un problème commercial. Au lieu de cela, ces informations devraient être utilisées pour soutenir la prise de décision.
Pour de nombreuses entreprises, comprendre « ce qu'était » le problème et « pourquoi » il s'est produit peut suffire, mais pour certaines, se tourner vers l'avenir offre des réponses plus précieuses. C'est là que l'analyse prédictive entre en jeu.
Exemple d'analyse diagnostique
En utilisant notre exemple précédent, nous comprenons maintenant où le problème s'est produit, mais pourquoi exactement le trafic du site web a-t-il chuté si brusquement ?

L'analyse nous dit :
- Le trafic du site web a chuté lors d'une mise à jour de l'algorithme du moteur de recherche.
- Il y a eu une diminution de 25 % du contenu web publié.
- Un nombre record de backlinks ont été perdus au T3.
Analyse prédictive
L'analyse prédictive, contrairement aux deux analyses précédentes, se tourne vers l'avenir et est un peu plus proactive avec ses conclusions. Elle tente de prévoir ce qui est susceptible de se produire ensuite, et constitue la moitié de ce qui est considéré comme des « analyses avancées ».
Aperçu de l'analyse prédictive
L'analyse prédictive considère le « quoi » et le « pourquoi » entourant les problèmes commerciaux clés, et fournit des prédictions calculées de ce qu'une entreprise pourrait attendre ensuite. Bien sûr, pour exploiter l'analyse prédictive, un data scientist devra d'abord passer au crible et nettoyer les données historiques.
Cette analyse est très complexe et est rendue possible grâce à des technologies avancées comme l'apprentissage automatique, la fouille de données, et la modélisation prédictive.
Avec les bonnes données et algorithmes, les entreprises ne devraient pas commettre deux fois la même erreur en utilisant l'analyse prédictive. Son utilité transcende également de nombreuses industries. Par exemple, les fabricants pouvant prévoir les futures pannes d'équipement avec la maintenance prédictive.
Défis de l'analyse prédictive
L'analyse prédictive, bien que formidable, peut présenter certains inconvénients. Tout d'abord, il est important de comprendre que des données inexactes conduisent toujours à des analyses inexactes. Les modèles prédictifs construits avec des informations inexactes ne feront qu'ajouter à la confusion pour une entreprise.
De plus, les modèles doivent être constamment surveillés, ajustés et affinés par des analystes et des scientifiques des données pour s'assurer qu'ils génèrent les bons résultats.
Exemple d'analyse prédictive
L'analyse diagnostique nous a montré une variété de problèmes, il est maintenant temps de prédire les prochaines étapes afin qu'un chiffre de trafic de site web précis puisse être généré pour les prochains trimestres. Voici à quoi pourrait ressembler cette estimation :

Analyse prescriptive
L'analyse prescriptive est le dernier type d'analyse avancée. Elle prend les informations qui ont été prédites et prescrit les prochaines étapes calculées à suivre.
Aperçu de l'analyse prescriptive
L'analyse prescriptive utilise à la fois des données historiques et des informations externes pour la prévision la plus précise possible. Elle dépend de règles codifiées.
Cette analyse est extrêmement complexe et nécessite un data scientist ou des scientifiques ayant une connaissance préalable des modèles prescriptifs. L'analyse prescriptive nécessite généralement une utilisation intensive de l'apprentissage automatique pour surveiller et identifier de nouvelles règles.
Défis de l'analyse prescriptive
Le défi le plus évident de l'analyse prescriptive est sa très haute barrière à l'entrée pour de nombreuses entreprises. Ces types d'analyses peuvent être coûteux à générer et nécessitent l'assistance de scientifiques des données – un domaine avec une demande écrasante.
L'analyse prescriptive n'est en aucun cas largement incorporée aujourd'hui, mais à mesure que la science des données devient plus courante, nous devrions voir des options prescriptives plus abordables.
Exemple d'analyse prescriptive
Maintenant que nous avons une idée de la direction que devrait prendre le trafic du site web, quelles sont les actions concrètes à entreprendre pour y parvenir ? Les modèles prescriptifs devraient révéler une variété de réponses.

L'analyse nous dit :
- Publier le double de contenu web pour atteindre les objectifs de trafic.
- Le contenu de vente générera le plus de trafic.
- Le contenu de marketing par e-mail est le gain de backlink le plus facile.
Quelle analyse est la bonne pour vous ?
De l'identification et de l'approfondissement du problème aux prédictions et à la génération d'étapes concrètes à suivre, les quatre types d'analyses de données apportent une valeur évidente à toute entreprise.
Cependant, une entreprise devrait faire un peu de planification au préalable pour envisager une solution d'analyse de données qui lui convient. Considérez des questions telles que : « Jusqu'où devons-nous plonger dans les données ? » « Les réponses à nos problèmes sont-elles évidentes ? » et « Avons-nous les ressources nécessaires pour effectuer cette analyse ? »
Si vous pensez tout savoir sur les données, détrompez-vous. Découvrez la différence entre les données structurées et non structurées et comment cela peut impacter vos décisions commerciales axées sur les données.
Vous voulez en savoir plus sur Plateformes d'analyse ? Découvrez les produits Plateformes d'analyse.

Devin Pickell
Devin is a former senior content specialist at G2. Prior to G2, he helped scale early-stage startups out of Chicago's booming tech scene. Outside of work, he enjoys watching his beloved Cubs, playing baseball, and gaming. (he/him/his)
