Years of trust can crumble in minutes with a cyber attack.
A single breach can leave a company scrambling to recover, not just from financial losses but from the shattered confidence of its customers. With sensitive information exposed, customer trust will become a question mark, making cybersecurity indispensable for your business.
Implementing robust solutions like identity and access management (IAM) software is crucial for protecting your organization and its valuable assets against cyber attacks. These solutions offer features like permission control, multi-factor authentication, and user lifecycle management.
What is a cyber attack?
A cyber attack is an offensive and unethical attempt to gain unauthorized access to computer systems or networks. It's launched from one or more computers to expose, alter, disable, or steal an organization's assets.
Cyber attacks have become increasingly sophisticated. Therefore, it's also advisable to have a centralized security program in your organization equipped with advanced technologies like security information and event management (SIEM), user provisioning solutions, and vulnerability management tools.
The entity responsible for conducting the attack is the attacker. An attacker can be sovereign states, specific groups, individuals within society, or organizations. It can also be a part of cyberwarfare or cyberterrorism, where the product facilitating a cyber attack is called a cyber weapon.
$10.5 trillion
is the projected amount of damage costs associated with cybercrime by 2025.
Source: eSentire
Why do cyber attacks happen?
A cyber attack aims to access the device by hacking into a susceptible system. The intent can range from installing spyware on a personal device to destroying an entire company's or even a nation's digital infrastructure.
The increase in such instances every year hints at a few common motives. Some of the most reported reasons include:
- Ransom: Cyber attacks are aimed at extracting ransom from the owner of the device or network.
- Accessing financial details: The aim of such attacks can be to access the financial details of the clients of a company or the company itself. This information can be publicized or used for personal monetary benefits. It can also be used to hack one's bank account and drain out the cash.
- Accessing intellectual property: The motive can be to hack into a company's device or network to access product design or trade secrets to implement them in one's organization or publicize them.
- Terrorism: A common trend is seen among terrorist groups that hack into personal devices to install spyware or use encrypted services for communication. It is a potential threat to the safety of an entire nation.
Types of cyber attacks
Due to the highly developed hacking mechanisms, now cyber attacks have evolved into different types and can pose a greater threat to your device or network security. Here's a list of the most common types of cyber attacks:
1. Malware
Malware is malicious software, commonly a trojan, that interrupts the normal functioning of your system or restricts your access to the information stored in it.
Such software includes spyware, ransomware, viruses, and worms. In most cases, the user clicks on an unsafe link or email attachment that installs malware in the computer system.
Risks of malware
Once installed, the malware can pose the following risks:
- Ransomware: Blocks the user's access to the system or information and demands a ransom to unlock access.
- Spyware: Obtains device data by transmitting from the hard drive.
- Virus: Disrupts the components of the device or renders the system inoperable.
2. Phishing
Phishing includes fraudulent communication that seems to be coming from a legitimate company or individual. The means of communication can be emails or text messages.
It aims to steal data, mainly private information like the victim’s address, credit card details, or electronic healthcare records. While sometimes the attacker is satisfied with the stolen data, it can also be the first step to more massive cyber attacks. It can also install the malware on the victim's device.
Attackers use emotions like fear, urgency, or greed to make the recipient click on links or email attachments. Once you are redirected to the link, you compromise any data that the attacker is looking for. Following the initial attack, you might be susceptible to losing corporate funds, damaging your company's reputation, or even making sensitive files open to access.
Types of phishing attacks
There are six types of phishing:
- Spear phishing: Targeted toward specific individuals rather than a broad group.
- Sms-phishing or smishing: Tricks people to give away their private information via text or SMS messages.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Impersonating a company's executive supplier.
- Whaling: The malicious actor attacks the executive of a company, such as the CEO or MD.
- Social media phishing: Attackers use social media to obtain information about the victim.
- Voice phishing: Also known as vishing, this attack involves a phone call indicating an emergency to obtain sensitive information.
3. Man-in-the-Middle attack
A man-in-the-middle attack (MITM) is a type of cyber attack in which the hacker relays or modifies communication between two parties who believe to be communicating directly.
Eavesdropping is one example of an MITM attack, in which the attacker establishes independent connections with two victims. The attacker controls the entire conversation and can intercept communications between two victims, inject new messages, or make modifications as needed.
The two common entry point for MITM attacks are:
- Unsecured public Wi-Fi: The attacker can insert itself between the user's device and the Wi-Fi network. This way, the attacker can access all the data transferring via the network on the user's device. Unknowingly, the user passes all information to the attacker.
- Malware: Once the attacker has successfully infiltrated a user's device, they can install malware to intercept their communication.
4. Denial-of-Service (or DoS) attack
DoS, or Distributed Denial of Service Attack (DDoS), is a force method for stopping a digital service from functioning correctly. It occurs when the attacker blocks access to a server or website connected to the Internet.
This attack is processed using several automated systems that flood a network to exhaust the limited bandwidth. This makes the target incapable of fulfilling legitimate requests or responding to queries.
5. Structured Query Language (SQL) injection
SQL injection interferes with an application's query to its database, allowing the attacker to view generally concealed information.
In some cases, hackers can escalate a SQL injection to perform a DDoS attack that may compromise the server or other critical infrastructure.
6. Zero-day exploitation
Zero-day attacks happen when a vulnerability is discovered recently but not fixed. Once a patch is released, the users start downloading the security updates, reducing the number of vulnerable devices. The attackers target the vulnerability in this window of time between the declaration of the issue and its patch's optimum implementation.
Techniques for exploiting such vulnerabilities are usually sold on the dark web and are often discovered by government agencies.
7. Cryptojacking
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and others have become increasingly popular and beneficial in recent times. The cryptojacking attack uses someone else's device for 'mining' or generating cryptocurrency for the attacker.
It is a specialized attack that involves installing malware on the victim's machine to perform the necessary calculations or run codes in JavaScript and execute them on the host browser.
8. DNS tunneling
While the DNS tunneling process has several ethical uses in the information technology industry, it can also be used to perform cyber attacks. During the attack, HTTP and other protocol traffic are sent over DNS. They can be used to disguise outbound traffic as DNS, concealing data that is usually shared via the internet.
For unethical use, DNS requests are altered to extract data from a susceptible device to the attacker's network. This attack can also be used to command and control callbacks from the attacker's network to the compromised system.
7 phases of cyber attacks
There are seven phases in which cyberattacks are performed. Let's take a deep dive into them.
1. Reconnaissance
Before the launch of any cyber attack, the attackers first identify the target and find the best possible way to exploit it. The attackers need merely one point of entrance to commence the process. Phishing is a common starting point in this step.
The aim of this first phase is to get to know the target. Some of the common questions answered in this stage include:
-
Who are the executives or important stakeholders in the company?
The company's website or LinkedIn profile is an excellent place to start looking for this answer. -
Who are their business partners?
Attackers can use social engineering by making classic 'sales calls' to the company and extracting such information. -
What information is available about the company?
A thorough web search on the company is useful for finding basic information. The rest of the information, such as software and hardware used by the company, can be found by running scans with the IP address or checking the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) web registry database.
After the attackers identify the target, they can exploit it through various methods. To proactively identify suspicious activity on your network, consider implementing a security information and event management (SIEM) solution.
2. Weaponization
Now that the attackers have the necessary information with them, it is time to create the equipment to penetrate the network. With the gathered data, attackers can craft malware to infiltrate your system. This could be coded for malware or creating phishing emails that should look legitimately like emails sent by professional vendors or business contacts. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) can help detect and block such malware before it can be deployed.
The next step is to create fake landing pages or web pages. These might look like a duplicate of the vendor's original website or even the bank page. The aim of this website is to solely capture the username and password, a download link, or something enticing the visitor to click on it.
The final step in this phase is to collect the tool to be used when the attacker achieves unauthorized access to a device.
3. Delivery
In this phase, the attacking equipment is launched. Phishing emails are sent, and the pseudo-web pages are posted online. If the email contains a weaponized attachment, the user will quickly have malware installed on their device.
Stay vigilant and implement email security solutions to filter out malicious messages.
4. Exploitation
The most sadistic and dangerous part of the process begins now. Once the data is fed through the weaponized web page, the attacker uses it against web-based email systems or VPN connections of the company network. If malware has been installed on the victim's device, the attacker can also access the device remotely.
The attacker uses this access to find the flow of traffic on the network, connected systems, and further exploitation possibilities.
5. Installation
Now, the attackers can remain on the network for as long as they need to. To ensure uninterrupted access, they might install a persistent backdoor to the network, create an admin account, disable firewall rules, or even activate remote desktop access on servers.
6. Command and control
At this stage, the attacker has complete remote access to the network or device and administrator account, and all required tools are now positioned for the next move. The attacker has access to the digitized aspect of the enterprise.
They can imitate users, make changes, and even send emails from the company's highest executives to the employees. Here, the company becomes the most vulnerable since the threat might still be undercover and unnoticed, yet highly potent.
Network detection and response (NDR) solutions can help identify and stop such malicious activity.
7. Action on the objective
In the last stage, attackers can do absolutely everything through your company's network. As discussed above, attackers now have motives other than monetary benefits.
Depending on their objective, the attacker may maneuver your company networks and act according to their wish. If they want to extract money, of course, they'll let you know.
Cyber attack examples
The increased sophistication in cyber scams has become traumatic to each victim. While cyber attacks’ intensity is almost subjective, some attacks have been on an extreme scale or hinted at the beginning of a new trend in the cyber attack realm.
Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack
In May 2021, hackers launched a ransomware attack against Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel pipeline on the east coast of the US. The attack forced the pipeline to shut down for several days, causing widespread fuel shortages and price hikes. This incident demonstrates the disruptive potential of ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure, disrupting essential services and causing economic damage.
Kaseya supply chain attack
In July 2021, hackers exploited a vulnerability in software from Kaseya, a popular IT management platform, to launch a global ransomware attack. The attack impacted thousands of businesses worldwide, disrupting operations and causing data loss. This incident underscores the importance of software vendors prioritizing security and promptly addressing vulnerabilities.
Lapsus$ ransomware group
This prolific cybercrime group gained notoriety for targeting major companies like Microsoft, Nvidia, T-Mobile, and Okta. Lapsus$ employed a variety of tactics, including social engineering and exploiting vulnerabilities, to steal sensitive data and extort victims for millions. This incident highlights the increasing risk posed by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups that target high-value organizations.
Ransomware attack on the Costa Rican government
In April 2022, the Conti ransomware group crippled Costa Rica's government systems, disrupting essential services like tax collection and customs operations. This attack demonstrates the disruptive potential of ransomware on government functions and highlights the need for robust cyber defenses in the public sector.
Cryptocurrency exchange hacks
Since 2022, several cryptocurrency exchanges have been targeted by sophisticated cyberattacks, resulting in the theft of millions of dollars worth of digital assets. These attacks highlight the vulnerabilities of cryptocurrency platforms and the need for robust security protocols to protect user funds.
How to protect your business against cyber attacks
Mitigating the cyber threats of an attack calls for more than an anti-virus installation. It needs constant vigilance and awareness. However, it can be simplified by following some cybersecurity best practices.
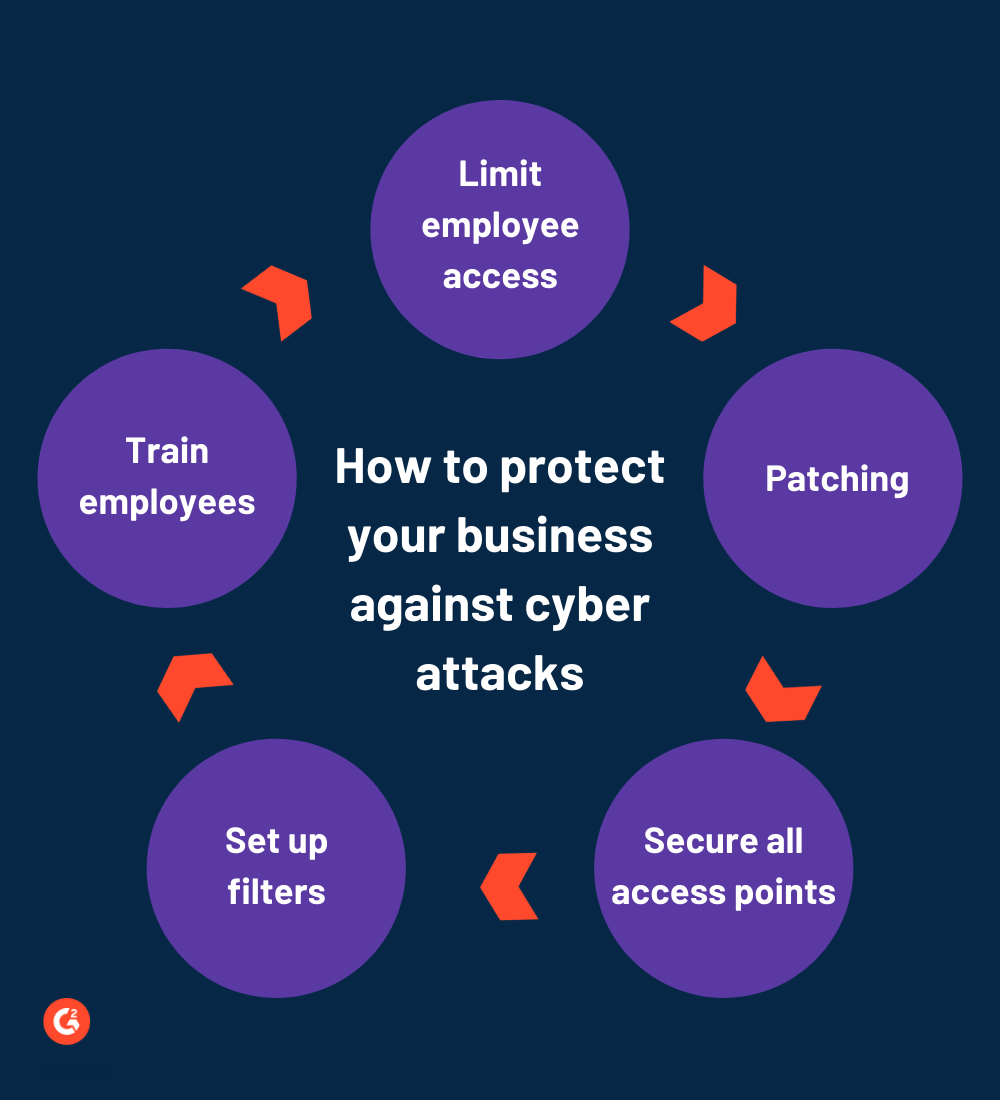
Disclaimer: These recommendations follow the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework and do not constitute legal advice. If you have legal questions, consult a licensed attorney.
Here's how you can protect your corporate networks from cyber attacks.
- Limit employee access: Reducing human error chances can be highly beneficial in protecting the remote cases of a data breach. Allow your employees to access only the information that they require for their tasks. If an employee leaves the company or transfers elsewhere, remove all of their information from the systems.
- Patch management: It is crucial to patch and update every piece of software on every device used by your employees. Do not delay downloading OS updates, as they usually have enhanced security features.
- Secure all networks and access points: Optimize each network and wireless access point for your company's use. Change the administrative password on new devices, set WAP to avoid broadcasting to SSID, and avoid using WEP.
- Set up filters: Detect hackers and prevent spam by using email anti-spam software on your devices. Download blacklist services to block users from accessing potentially risky websites.
- Train employees: The most crucial element for maintaining cybersecurity is to teach the best cybersecurity practices to the users. Every employee should be aware of the business and personal use of emails, treating work information at home, handling cybersecurity risks, etc.
Tip: Consider using user provisioning tools to regulate user access controls.
Cyber attack trends
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, making it crucial for businesses and individuals to stay informed about the latest cyber attack trends.
- Mobile malware: With the increasing use of mobile devices for work and personal activities, cybercriminals are targeting them more frequently with malware designed to steal data, track location, or launch phishing attacks. Businesses should enforce strong mobile security policies for employees.
- Weaponization of artificial intelligence (AI): Attackers are increasingly using AI-powered tools to automate social engineering attacks, analyze vast amounts of data to identify vulnerabilities, and even develop new malware strains. Organizations need to be aware of these potential threats and implement AI-powered security solutions to counter them.
- Internet of Things (IoT) security concerns: The expansion of internet-connected devices (IoT) creates new attack surfaces. Many IoT devices have weak security protocols, making them vulnerable to exploitation. Businesses and consumers need to be cautious about the security of the IoT devices they use.
Protect your digital doorstep
Ever since information technology evolved as a basic necessity, cyber attacks have become a growing threat. With attackers developing ever-more sophisticated tactics, nobody is entirely safe from their impending danger.
However, there is hope. By staying informed about the latest threats, implementing robust cybersecurity measures, and fostering a culture of security awareness within organizations, we can significantly reduce the risk of being victims of a cyber attack.
Take the first step to protecting yourself from cyber attacks. Check out the top security solutions you need in 2024.
This article was originally published in 2020. It has been updated with new information.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.
