Making computers learn the ABC of a human brain.
People often assume artificial intelligence means robots are coming to life to interact with humans. However, this notion misconstrues the meaning of AI.
Artificial intelligence is highly multifaceted, with subcomponents that extend far beyond the “robot-human relationship” misconception. The hype of AI doesn't live up to its name yet. While many call it a stepping stone of automation, there is more if you look at it through your magnifier.
AI is a superset containing different data analysis and visualization techniques. A few techniques are robotic process automation, natural language processing, deep learning, or machine learning. The difference lies in how vastly each process improves when merged. Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning operationalization software with your tech stack is a great way to experiment with your data and see where it leads you.
Before pitching AI as a solution in your next project plan, go through these quick artificial intelligence terms to back your statements with proof.
Artificial intelligence terms A to Z
As Stephen Hawking had clearly projected, "AI is humanity's gigantic step into a robotic future. It can design improvements to itself and conquer mankind before we know it. But before we bow down to the will of robots, we need to know how they are constructed.
Each term of AI centers around the concept of human-computer interaction. To know how the human brain functions, systems are fed with algorithmic expressions. These systems then translate human commands and detect external objects. Let's see what terms contribute to self-assist properties like these.
Want to learn more about MLOps Platforms? Explore MLOps Platforms products.
Relevant artificial intelligence terminology
While browsing the internet, you've probably heard terms like "data mining" and "machine learning" but never could find a concise definition to help you understand what you read. Now? You don't have to look far. Below are brief definitions of words and phrases related to AI.
Note: not all letters of the alphabet are listed if they do not contain relevant enough terms.
AI terms, A through E
AGI, ANI, ANN...what do they all mean? Though the first letter of each stands for "artificial," the meaning of successive letters isn't implicated.
A
Algorithm: a formula or a set of instructions given to a computer in order for it to complete a task (i.e., a set of rules for a computer). It represents the relationship between input and resultant variables through a mathematical or conditional expression.
Artificial intelligence: a subset of computer science that deals with computer systems performing tasks with similar, equal, or superior intelligence to that of a human (e.g. decision-making, object recognition and classification, speech recognition and translation)
Artificial general intelligence (AGI): also known as strong AI, AGI is a type of artificial intelligence that is considered human-like and still in its preliminary stages (more of a hypothetical existence in the present day)
Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI): weak AI, ANI is an artificial intelligence that can only focus on one task or problem at a given time (e.g., playing a game against a human competitor). This is the current existing form of AI. This artificial intelligence algorithm is programmed to solve a limited number of data problems.
Artificial neural network (ANN): a network modeled after the human brain by creating an artificial neural system via a pattern-recognizing computer algorithm that learns from, interprets, and classifies sensory data
Activation function: It is the main calculative layer of a neural network. The activation function triggers the right decision node within the neural network and displays the node as an output. It converts a series of inputs into singular or multiple output classes.
Artificial immune system: A technique of intelligent, fuzzy neural networks or rule-based machine learning systems used for the vernacular immune system. The logic is built using reactive expressions to solve a particular problem, just like the immune system.
Autonomous cars: Self-drive cars that work on the principle of computer vision to detect, identify, and categorize external obstacles and drive right around them.
B
Backpropagation: shorthand for “backward propagation of errors,” is a method of training neural networks where the system’s initial output is compared to the desired output, then adjusted until the difference (between outputs) becomes minimal
Bag of words: This algorithm is used for document classification and information retrieval. It extracts the text from a document and stores it in a bag of words without the grammar and sentence order. The frequency of words is used as a feature to train the algorithm and classify the document.
Bag of words (computer vision): This algorithm extracts features or characteristics from images and feeds similar-looking features to the algorithm to classify the image.
Bayesian network: also known as the Bayes network, Bayes model, belief network, and decision network, is a graph-based model representing a set of variables and their dependencies.
Big data: large amounts of structured and unstructured data that are too complex to be handled by standard data-processing software
Batch normalization: Batch normalization is used to adjust input variables in neural networks. It unloads a neural network by adjusting weights and biases and pushing them in batches to come at a stable output.
Binary tree: Binary tree is a deep-rooted tree where each node has two children, namely the left child and a right child. A rooted tree generally imparts levels (distance from the roots). Thus for every node, the notions are defined as the nodes connected to it.
Brute force search: A generative algorithm that proposes all the solutions to a problem and nitpicks the best solution.
C
Chatbots: a chat robot that can converse with a human user through text or voice commands. Utilized by e-commerce, education, health, and business industries for easy communication and to answer user questions.
 Image courtesy of IBM
Image courtesy of IBM
Classification: algorithm technique that allows machines to assign categories to data points
Cloud robotics: Cloud robotics enables machines or robots to access cloud storage. These machines are equipped with a cloud-hosted provider over a converged infrastructure to access content, respond faster, and display accurate results.
Clustering: An algorithm technique that allows machines to group similar data into larger data categories.
Cognitive computing: a computerized model that mimics human thought processes by data mining, NLP, and pattern recognition
Cognitive science: The broader form of AI ties back to linguistics, philosophy, and the meta-existence of computers. It enables machines to simulate human thought and action.
Computer vision: when a machine processes visual input from image files (JPEGs) or camera feeds
Computational intelligence: The ability of a computer to learn from an experimental situation and use learnings for future predictions.
Convolutional neural network (CNN): a type of neural network specifically created for analyzing, classifying, and clustering visual imagery by using multilayer perceptrons
D
Data mining: the process of sorting through large sets of data in order to identify recurring patterns while establishing problem-solving relationships
Data science: A catchall term for database management, analysis, and visualization encompassing all techniques of artificial intelligence and machine learning. It describes different methods, algorithms, knowledge, and systems to draw insights from datasets, train models, and create co-relations. It is based on mathematics, statistics, geometry, and matrices and determinants.
Data set: A dataset is a representation of data. It can be a singleton database or multiple matrices containing several rows and columns. Each dataset has a defined list of variables and underlying values that best describe the problem. A dataset is refined and cleaned before it is fed to a machine-learning algorithm.
Data warehouse: It is a central repository that holds data from one or more than one sources. It stores and versions old and new data in a centralized platform.
Decision tree learning: A supervised learning algorithm where the nodes individually vote to predict the class of the input. It is also used for predictive modeling or statistical modeling.
Dimensionality reduction: The process of reducing random variables to adjust the accuracy of output. In facial recognition, DR is used during principal component analysis to reduce the size of the input image set to adjust output and eliminate noise.
Deep learning: a machine learning technique that teaches computers how to learn by rote (i.e., machines mimic learning as a human mind would by using classification techniques)
Digital ecosystem: several software platforms or cloud services that work in tandem across a network
AI terms, F through J
This section should be of particular interest if you enjoy experimental AI!
F
Feature extraction: In machine learning, computer vision, or pattern recognition, feature extraction starts with dividing the image or data into bounding boxes and extracting one single feature out of the boxes. The features are extracted, pooled, and fed to a supervised vector machine to predict the output.
Feedforward neural network: It is the simplest artificial neural network where information exits through the output node and doesn't come back for analysis. Data only flows in the forward direction and doesn't form a loop.
Fuzzy logic: A conditional logic where variables can exhibit any degree of truthfulness, ranging from 0 to 1. The value 0 depicts "false," and the value 1 depicts "truth." In contrast to boolean expressions, which only display output as 0 (true) or 1(false), fuzzy logic can display partial truth in decimal values.
G
Generative adversarial networks (GAN): a type of neural network that can generate seemingly authentic photographs on a superficial scale to human eyes. GAN-generated images take elements of photographic data and shape them into realistic-looking images of people, animals, and places.
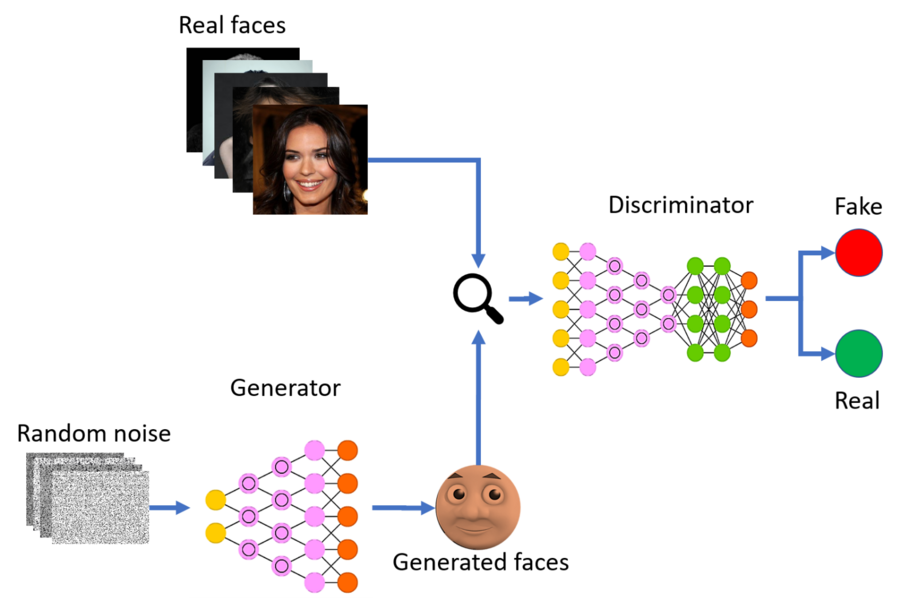 Source: Medium.com
Source: Medium.com
Genetic algorithm: an algorithm based on principles of genetics that is used to efficiently and quickly find solutions to difficult problems
H
Heuristic: a computer science technique designed for quick, optimal, solution-based problem-solving. A heuristic technique stops the algorithm at every step during analysis and searches for the different hypotheses of solutions before arriving at a suitable solution.
I
Image recognition: the process of identifying or detecting an object or feature of an object in an image or video
Intelligent agents: Agents that observe a particular environment through sensors and work to achieve a goal for the algorithm. It is mostly used in reinforcement learning and deep-Q networks to learn or use knowledge to perform an action.
Independent component analysis: ICA is a powerful machine learning technique that extracts trends from the observed data and uses it to process and categorize new data independently. It separates a multivariate into independent, non-Gaussian components to form a linear transformation.
Now is the time to get SaaS-y news and entertainment with our 5-minute newsletter, G2 Tea, featuring inspiring leaders, hot takes, and bold predictions. Subscribe below!
AI terms, K through O
Some of the most used terms lie between K-O in the AI glossary!
K
Kernel method: In artificial intelligence, the kernel method is a bootstrap method used for pattern analysis and classification. It is the most known method of supervised vector machine and studies different relations within the input to predict a category.
Knowledge extractions: The extraction of knowledge from technical documentation, XML, unstructured datasets, or relational databases. Knowledge elements are extracted by running specific queries that represent the data best.
K-nearest neighbor: It is an unsupervised algorithm where the data class is determined by looking at the nearest data points. The most number of data points in a particular direction means that current data also belongs to the same category.
L
Limited memory: systems with short-term memory limited to a given timeframe. Limited memory AI derives knowledge from real-time experiences or events and stores it in the database. When a problem occurs, it gives out redundant results.
M
Machine learning (ML): focuses on developing programs that access and use data on their own, leading machines to learn for themselves and improve from learned experiences
Machine learning models: It is a program trained on old data to make predictions for fresh data. There are three types of machine learning models, namely supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised.
Machine intelligence: It is an advanced form of human intelligence where machines learn from their own mistakes, prioritize automation tasks in a sequential manner, and achieve goals.
Machine consciousness: Machine consciousness, or artificial consciousness, is an awareness state attained by machines after a specific period of time to decipher human emotions and expressions. It's being experimented on in the robotics industry.
Machine translation: an application of NLP for language translation (human-to-human) in text- and speech-based conversations.
N
Natural language processing (NLP): helps computers process, interpret, and analyze human language and its characteristics by using natural language data
Naive Bayes classifier: It is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification problems. It is either a single algorithm or a group of algorithms with distinguishing features (all variables of the dataset are independent of each other).
Nanobots: Nanobots are molecular-sized robots measured on a nanoscale and programmed to accomplish a specific task within the human body. The concept is used to create smart vaccines, cancer therapy, and immunotherapy through painless methods of medication.
Neural networks: Neural networks is a deep learning technique that resembles the structure of a human brain. The structure of a neural network constitutes several layers that perform calculations on the input and decide the correct output class. A neural network requires large datasets and high GPU to work. However, the output is processed much faster as compared to a machine learning algorithm.
Node: A basic unit of a data structure, like a stack or a linked list, or a queue, that represents an underlying value or a variable.
O
Optical Character Recognition (OCR): conversion of images of text (typed, handwritten, or printed), either electronically or mechanically, into machine-encoded text. An OCR software parses the characters of a pdf document and formats it into a new destination file in the exact same way they had been written.
Source: YouTube
OpenAI: A for-profit technological company that conducts scientific research in artificial intelligence and machine learning. ChatGPT, a conversational AI platform, is their latest invention. Developed on the principle of reinforcement learning, ChatGPT is equipped with advanced AI capabilities to complete human-dependent tasks.
Open source software: It is a type of computer software under an open license where the developer (copyright holder) gives users the rights to exchange data, code, and information through the platform.
AI terms, P through T
Robots, robots, robots. You'll finally find some robot-centric definitions here!
P
Pattern recognition: It is a data science method that is used to detect, analyze and label patterns or regularities in data.
Predictive analytics: Statistical interpretation techniques from data mining, machine learning, and deep learning are used to predict outcomes of events.
Principal component analysis: A statistical process in which a set of unrelated observations are converted into related variables. The related variables encompass one or more than one feature of the original dataset, where each variable is orthogonal to its preceding variables.
R
Reactive machines: can analyze, perceive, and make predictions about experiences, but do not store data; they react to situations and act based on the given moment
Recurrent neural network (RNN): a type of neural network that makes sense of and creates outputs based on sequential information and pattern recognition
Reinforcement learning: a machine learning method where the reinforcement algorithm learns by interacting with its environment and is then penalized or rewarded based on the decisions it makes.
Robotics: focused on the design and manufacturing of robots that exhibit and/or replicate human intelligence and actions
Robotic process automation (RPA): uses software with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to perform repetitive tasks once completed by humans.
R: A statistical data modeling technique used to create data co-relations and create a good fit model to predict an event possibility.
S
Strong AI or ASI is the highest awareness stage attained by a machine to translate human emotions and expressions. It includes techniques like reactive AI, self-aware AI, and theory of mind. The sensory responses of a human are analyzed and read by computers to frame a biological response. It almost appears as if an actual human is interacting with a computer. Framing a consciousness streak in computers isn't easy and requires high-level expertise and programmable units (GPU).
Structured data: clearly defined data with easily searchable patterns
Supervised learning: a type of machine learning where output datasets teach machines to generate desired outcomes or algorithms (akin to a teacher-student relationship)
T
Transfer learning: a system that uses previously-learned data and applies it to a new set of tasks
Turing Test: a test created by computer scientist Alan Turing (1950) to see if machines could exhibit intelligence equal to or indistinguishable from that of a human
AI terms U, through Z
Fewer AI terms fall between U-Z, but the most important ones are displayed.
U
Unstructured data: data without easily searchable patterns (e.g., audio, video, social media content)
Unsupervised learning: a type of machine learning where an algorithm is trained with information that is neither classified nor labeled, thus allowing the algorithm to act without guidance (or supervision)
V
Voice recognition: Also known as speech recognition, it is a human-computer interaction technique that allows computers to understand, interpret human dictation, and produce written output in accordance with speech commands.
W
Weak AI: see artificial narrow intelligence (ANI)
On the road to expertise
With these frequently-searched terms fresh in your mind, you’re ready to tackle AI head-on and continue your knowledge exploration adventure! Investing in artificial intelligence requires deep-diving into current informational trends and gauging the correct solution for your business.
Has this glossary piqued your curiosity about learning more about artificial intelligence? If so, check out different types of AI and how they impact worldwide inventions.
This article was originally published in 2019. The content has been updated with new information.

Rebecca Reynoso
Rebecca Reynoso is the former Sr. Editor and Guest Post Program Manager at G2. She holds two degrees in English, a BA from the University of Illinois-Chicago and an MA from DePaul University. Prior to working in tech, Rebecca taught English composition at a few colleges and universities in Chicago. Outside of G2, Rebecca freelance edits sales blogs and writes tech content. She has been editing professionally since 2013 and is a member of the American Copy Editors Society (ACES).