What are hypervisors?
Hypervisors, sometimes called virtual machine monitors (VMM), are software platforms that create and run virtual machines (VMs). A hypervisor enables one host computer to support multiple guest VMs, and as a result, expands operations and access without the need for purchasing additional physical hardware. Hypervisors make supporting guest VMs possible by sharing critical resources like Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, and storage.
Hypervisors are also known as server virtualization software. Organizations use server virtualization software products to separate their dedicated servers into multiple scalable virtual instances. These tools offer easy management and centralized control of virtual servers.
How do hypervisors work?
Hypervisors abstract and manage a computer’s physical hardware resources, including components like memory, storage, and CPUs. The resources then get distributed to virtual machines where each operates as its own isolated and independent instance. In essence, the hypervisor creates a pool of shared resources to share among VMs.
Hypervisors then become responsible for monitoring and allocating resources to make sure VMs have what they need to operate efficiently. The provisioning process keeps VMs from conflicting with one another when using resources from the host. Virtual machines run their own programs with the resources they require.
Types of hypervisors
Two main types of hypervisors are available. Businesses should consider their infrastructure, business growth strategy, equipment, and costs when deciding which one to use.
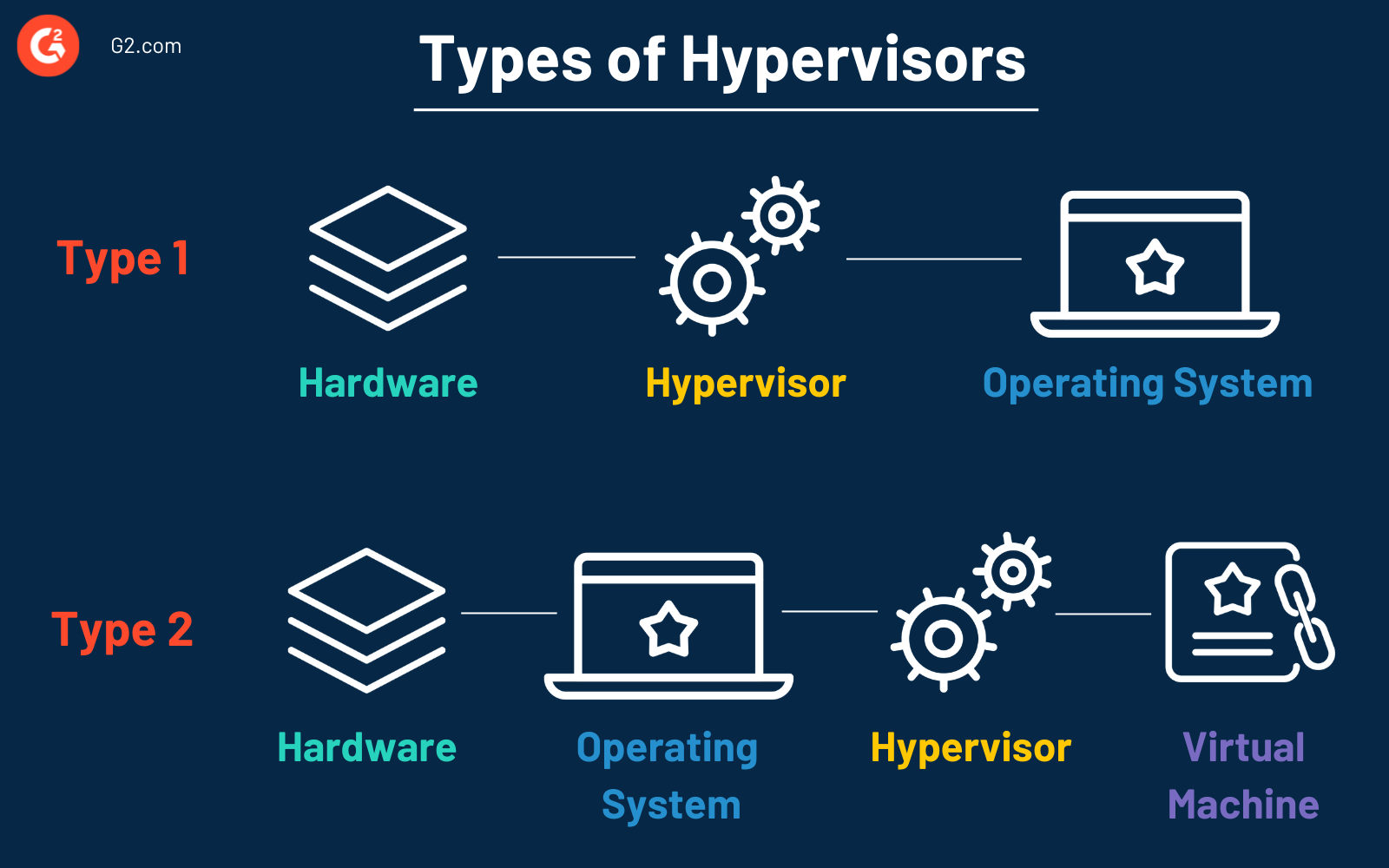
- Type 1 or “bare-metal”: A Type 1 hypervisor runs on the host computer’s hardware. This means that users install virtualization software onto the hardware directly, which makes them efficient. Then, the software creates virtual machines. . These types of hypervisors are also very secure since there’s a degree of isolation for each VM.
- Type 2 or “hosted”: A Type 2 hypervisor, or a hosted hypervisor, runs on the host machine's operating system (OS). Type 2 hypervisors have an additional layer between the host and the virtual machine compared to Type 1. They run similarly to a traditional computer program and are best suited for desktop and development environments with less resource-intensive workloads.
Benefits of hypervisors
Organizations that use hypervisors experience many benefits.
- Resource optimization: Since multiple virtual machines run concurrently on one single physical server with hypervisors, organizations optimize their hardware. Due to more efficient usage, teams often cut costs since they don’t require as many physical machines.
- Scalability and flexibility: Hypervisors provide dynamic allocation and reallocation of resources, making it easy for organizations to scale. Using hypervisors is an excellent option for businesses with changing demands and workloads since they can allocate more VMs (or fewer) based on their organization’s needs.
- Improved security: Hypervisors are independent and isolated from one another despite running on the same host computer. The isolation of virtual machines prevents malware, crashes, and other cyber attacks on one VM from hurting the others, thus improving overall security.
- Portability: Since the virtual machines are independent of the host machine, they’re portable. IT teams can allocate resources across servers as needed. Hypervisors make it easy to shift resources like memory, storage, and processing power.
Challenges with hypervisors
While hypervisors enable scalability and improve security, teams can experience some potential challenges. These might include:
- Potential for virtualization sprawl (VM sprawl). Hypervisors simplify the creation of new virtual machines, but uncontrolled growth can lead to management issues and resource distribution challenges. IT administrators must document and keep track of the number of virtual machines within the organization to prevent VM sprawl.
- Issues with resource distribution. Although hypervisors help monitor and allocate resources, the distribution won’t always be perfect. Some VMs may function well, while others may not have access to enough resources for optimal functioning.
- Periods of network congestion due to server overload: Rapidly adding VMs onto a server can lead to network issues as VMs compete for available bandwidth. A congested network may cause some VMs to report network errors or potential crashes.
Hypervisors vs. containers
Hypervisors and containers are both used in virtualization but serve different purposes.
Hypervisors are software tools that enable the creation of virtual machines. They allocate resources like CPU, storage, and memory to each VM, allowing multiple VMs to run simultaneously on the same hardware.
Containers are lightweight and portable units that package an application and its dependencies. Containers allow applications to run across multiple environments.
Read more about the best virtual machine software in 2024 and choose the best suited for your business.

Alyssa Towns
Alyssa Towns works in communications and change management and is a freelance writer for G2. She mainly writes SaaS, productivity, and career-adjacent content. In her spare time, Alyssa is either enjoying a new restaurant with her husband, playing with her Bengal cats Yeti and Yowie, adventuring outdoors, or reading a book from her TBR list.