What is a blockchain network?
A blockchain network is an advanced database mechanism that stores information securely and transparently. This network comprises a chain of blocks, each with a list of transactions.
Every time a block reaches its capacity for storing transactions, a new block is created with the address of the previous one. This “lead” to the last block makes it hard to alter previous transactions, thus securing the network better.
The blockchain network is based on the concept of decentralizing control. Decentralization makes the system more robust and dynamic, which helps the rest of the network to remain unaffected in case one system/node fails. Many companies use blockchain platforms to create this network for tracking and documenting transactions.
Types of blockchain networks
With blockchain technology taking over in all industries, different blockchains are made to meet the requirements of various sectors.
- Public blockchain networks are open to all. Anyone can join, participate, and access these networks. Just like any other blockchain network, it’s transparent and decentralized.
- Private blockchain networks, as the name suggests, are private. Only a limited number of people can access it. However, they may not have edit control.
- Consortium blockchain networks are controlled by multiple organizations. To join a blockchain consortium, members need an invitation. Businesses that require high levels of security and find interest in collaboration create these networks.
- Sidechains are blockchains connected to another blockchain, also known as the main chain. Sidechains may or may not resemble the features of the main chain.
Benefits of blockchain technology
Blockchain technology brings many benefits to assist transaction management. Below are a few notable ones.
- Remarkable safety and security. Blockchain relies on cryptography, distribution of data, and group agreement to make its software difficult to crack. It has no detectable spot of failure, and a single user cannot tamper with the data.
- Agility and simplicity. Business transactions often face delays and complications, especially when legalities and stakeholders come on board. Blockchain offers clarity, along with smart contracts, to speed up business deals.
- Faster audits. Companies need a secure and efficient way to record, share, keep, and review digital transactions. In a blockchain, all entries are fixed and chronological. It expedites the audit procedure.
Features of a blockchain network
Traditional databases and blockchain networks store and manage data, but they differ in several key aspects. Here are some features that make a blockchain network unique.
- Decentralization. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain refers to the distribution of control across many nodes or computers.
- Transparency. Every transaction is visible to everyone on the network to prevent fraud.
- Security. Blockchain uses cryptography. Cryptography guarantees that transactions are encrypted and difficult to alter.
- Immutability. No data can be changed, modified, or deleted once data is added to the blockchain.
- Anonymity. Users can choose to stay anonymous while viewing all the transactions.
- Scalability. The network grows more powerful and dynamic because adding new nodes or systems is easy.
- Consensus mechanisms. Every node follows rules to make certain all the transactions are fair and valid.
- Peer-to-peer. Blockchain allows direct transactions between users.
- Distributed ledger. This feature offers a shared database in the blockchain network that records the transactions. They have strict rules about who can edit, as well as how to do so.
Blockchain network use cases
Major industries like financial services, supply chain management systems, health care, and voting systems rely highly on blockchain network systems. Here are some common uses.
- Cryptocurrency. Digital currencies like Bitcoin rely on blockchain to record transactions. It makes them secure and harder to counterfeit.
- Smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts. The terms are written directly into lines of code. They assist with tasks like property sales and insurance.
- Tracking goods. Businesses use blockchain to keep tabs on production, shipment, and receipt in a supply chain. Companies can verify the authenticity of the products by looking at a decentralized record, ensuring that products are real.
- Patient records. Blockchain can securely store health records accessed only by authorized individuals. It improves the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
- Drug traceability. Blockchains can also trace the production and distribution of pharmaceuticals, making sure that medicines are genuine and safe.
Blockchain network vs. blockchain protocol
Blockchain networks and blockchain protocols are very different from each other.
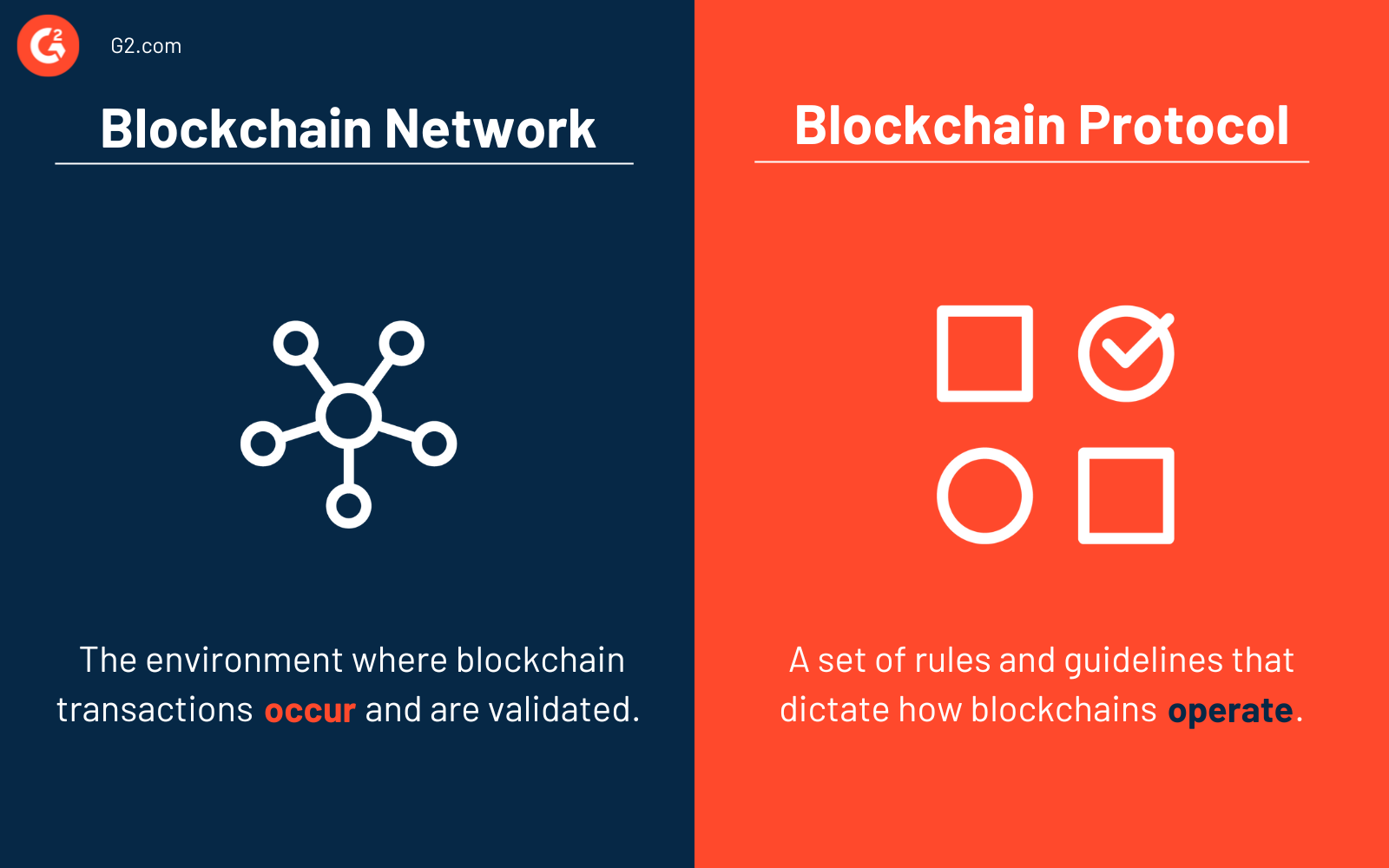
A blockchain network is the environment where blockchain transactions occur; they also get validated there. The network consists of nodes, which are essentially computers participating in the network. The network can be public, private, or consortium.
A blockchain protocol is a set of rules and guidelines that dictate how blockchains operate. They include rules for verification, adding new blocks, and ways to reach consensus among nodes. The protocol ensures all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the blockchain.
Learn more about blockchains and understand how they work.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.