The line between the physical and digital worlds is gradually fading. A few decades ago, ideas that were a dream are now a part of our lives. It’s fascinating how computing has evolved—from just computers to internet availability to connecting almost every device. Cities are now creating their digital twins for infrastructure planning, and brands are using hologram 3D models for walking the fashion runway.
Technology is constantly pushing us to do better, making it exciting to see how the future of the web unfolds.
How a tweet started the web 3.0 conversation
In December 2021, there was a lot of hullabaloo over web 3.0. Former Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey started the conversation with a tweet that read: “You don’t own “web3.” The VCs and their LPs do. It will never escape their incentives. It’s ultimately a centralized entity with a different label. Know what you’re getting into…”
The tweet started a frenzy over the internet and there was a lot said by many. To decode the school of thought behind the tweet, let us begin with understanding what web 3.0 really is.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 doesn’t have its universally accepted definition yet. It is an upcoming third generation of the internet that uses blockchain, decentralization, and artificial intelligence (AI) as its building blocks. The aim of web 3.0 lies in enhancing real-world human communication.It is anticipated that web 3.0 will combine features of web 1.0 and web 2.0, eliminating their shortcomings. But what happened to web 1.0 and web 2.0 that we've now reached this stage of technology?
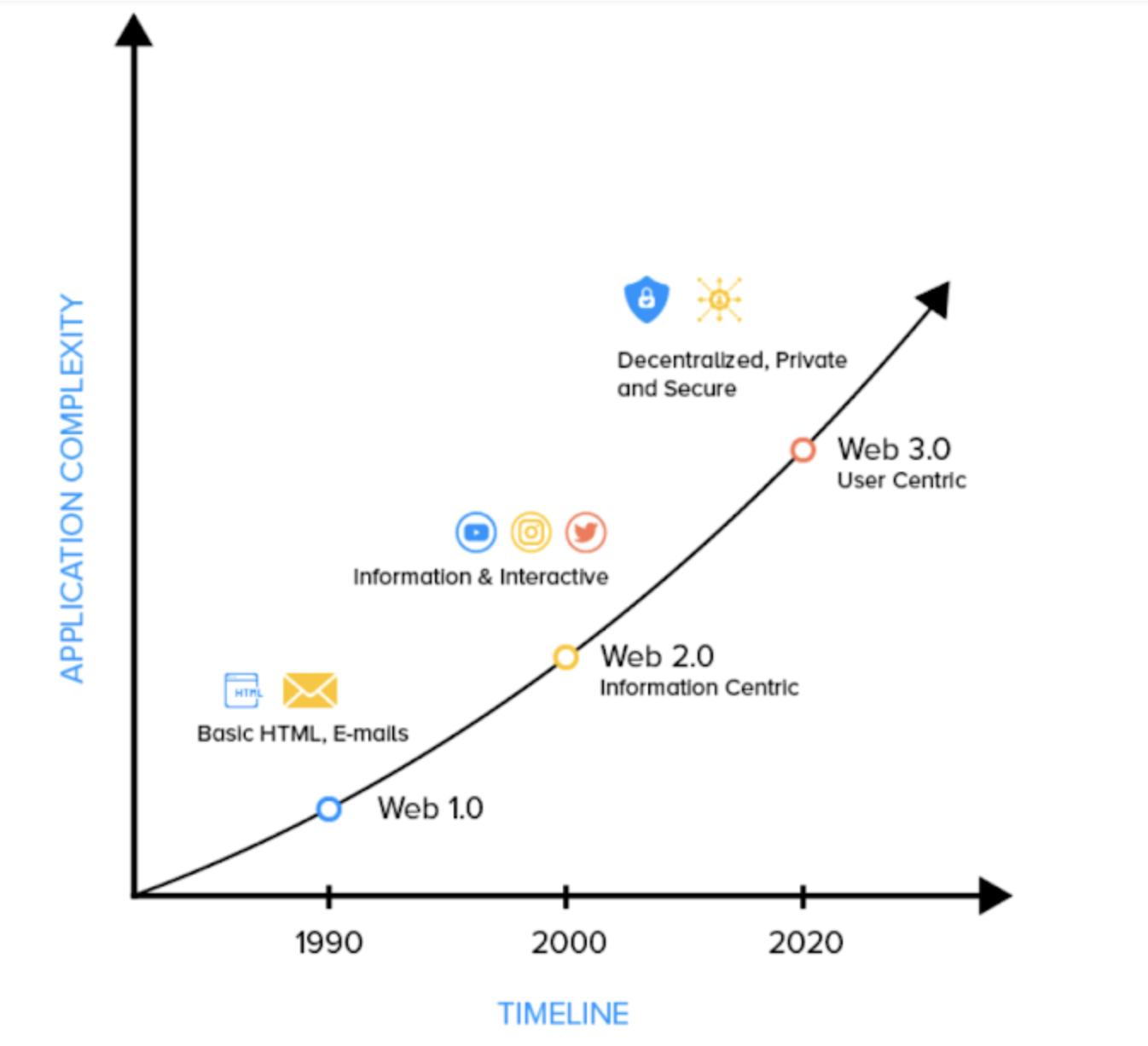
The evolution of the internet
Web 1.0, or the first generation of the internet, was launched in the 1990s. It was built with the aim to make scholarly and research articles available to users—in “read-only” form, with static websites (users could not interact with the content over websites). This shortcoming was taken care of in the next generation of the internet, web 2.0.
Web 2.0 is the current generation of the internet. It provides more liberty in terms of content creation and monetization, making it more interactive. However, web 2.0 is flawed with regard to data handling as it is largely centralized.
In an effort to eliminate such issues with web 2.0, developers are keen on taking the internet to the next level. Welcome, web 3.0!
Source: appinventiv
The IT architecture behind making web 3.0 a reality
Today’s technology space is already in the late phase of web 2.0 and early stages of web 3.0. To know how web 3.0 is different on a technological level, it is essential to understand the IT architecture. The IT architecture is comprised of three main layers:
- Interaction: The content, software, or hardware that we interact with
- Computation: The background work that enables interaction
- Information: The data that helps functions to be completed properly
The illustration below shows the transition of the web with respect to components of IT architecture.
Source: Deloitte Insights
On the interaction front of the technology, we have wearable tech such as smartwatches, health trackers, and safety wearables. Whereas, the base of these products is the distributed ledger technology, which is at the heart of decentralization. It helps users access the records across the network in a few seconds. Web 3.0 has a lot more to offer.
Transition to web 3.0
Today’s internet ecosystem deals with a plethora of issues such as data security, making organizations look for robust data governance software. Data governance software helps keep the security of data in check by creating policies and looking after who can access the data and up to what depth. With the introduction of web 3.0, we can expect some of these issues to be tackled, and also promise internet users with more:
- Decentralization
- Permissionless access
- Ubiquitous data
- Advanced AI
Decentralization
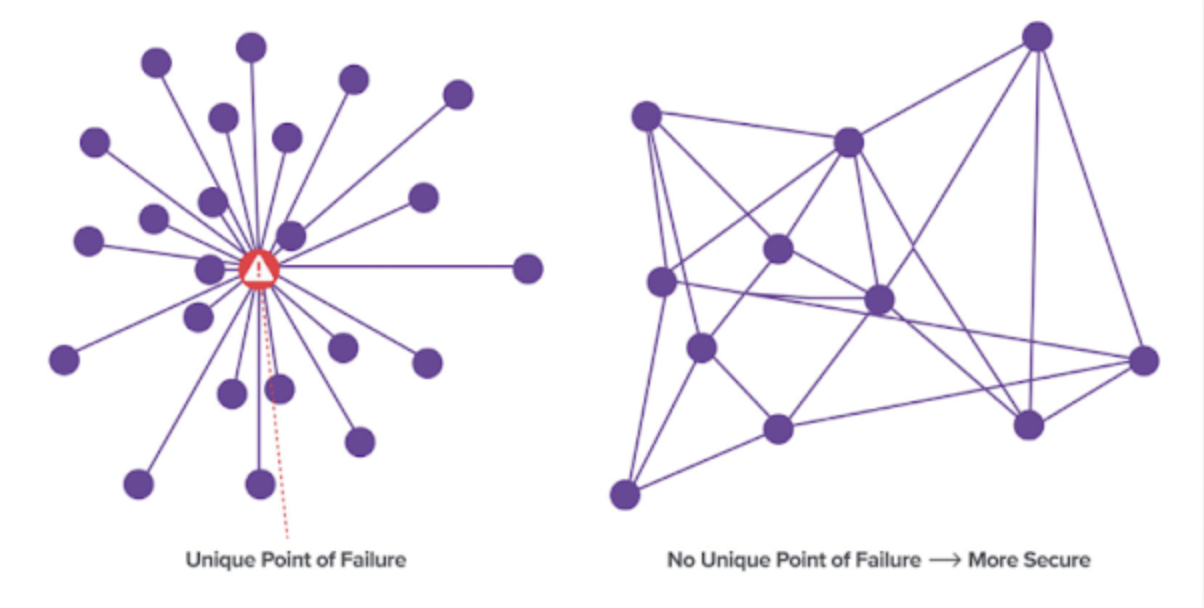
Since data in web 2.0 is stored in central repositories, owned by limited companies, it gave birth to behemoths such as Facebook and Google who have control over the data of billions of internet users. Centralized data repositories are an easy target for hackers because of a unique point of failure, i.e., servers of these companies.
For example, in October 2021, Facebook, Instagram, and Whatsapp were down—it was later known that the outage was due to the failure of the DNS server.
Data in web 3.0 is stored in “blocks”. It is distributed across smaller servers which are referred to as “nodes”. Thus, it keeps data secure by maintaining no unique point of failure. The illustration below explains the difference between the two.
Source: a16z
Permissionless access
In web 2.0, many websites and apps demand access to users’ contacts, location, and other such sensitive information. After obtaining these permissions, the companies demanding the information have complete visibility of users’ data. This data contains a wealth of knowledge about (potential) consumer behavior which can help companies promote their products and services. Thus the impression created is that of “free services usage” when there is compromise done with users’ safety and the way we use the internet is actually decided by these big tech giants. On the contrary, web 3.0 promises access to the users without any conditions or permissions.
Ubiquitous data
Ubiquitous data means having data present everywhere, at the same time. Web 2.0 already has ubiquitous data, but web 3.0 makes it possible for any user to access the data from any device, beyond mobiles and computers—using IoT for smart wearable devices.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Advanced AI will help in understanding user intention behind any search and thus provide more intuitive and user-centric interactions compared to web 2.0.
The base of web 3.0 is blockchain, and it is open for all those interested to develop and grow the ecosystem. Many startups have taken the initiative to develop web 3.0—the graph by crypto venture capitalist (VC) firm Electric Capital cites the growing number of active web 3.0 developers since 2009. Web 3.0 developers have grown by 75% since January 2021.
Source: Electric Capital
|
Did you know? Web 3.0’s decentralized apps (dapps) will make the idea of interoperability possible. Dapps are apps that can run on any platform and are not restricted to a particular operating system. This will save businesses from developing various versions of the software for different operating systems. |
Impact of web 3.0 on businesses
- Time saving: Automation at almost every step will save a major chunk of time and allow both employers and employees to focus on tasks that demand their attention. Smart contracts are one such example. These are self-executing agreements, where the terms are written in lines of code. The agreements are executed automatically when the terms are met, thus saving time.
- Online customer acquisition: Web 3.0 is transforming the web into semantic web. It is an AI-powered web where “intelligent” algorithms understand the context and provide customized results to the query. This will help businesses reach out to their potential customers with the desired, curated content.
- Boost to creator economy: With new avenues of creating content, creators will be able to monetize their content. The direct connection with fans or communities reduces the power of middlemen.
Every entrepreneur is curious to develop and VCs are keen to invest in web 3.0. Jack Dorsey’s tweet implies that the power or the control over data will be concentrated in the hands of early adopters of this technology. According to him, decentralization in web 3.0 is a myth because the VCs that are investing in blockchain startups will replace current giants like Google and Facebook.
However, it is too early to predict if web 3.0 will follow this route. Blockchain-backed cryptocurrencies have steeply raised in value. The stocks of cryptocurrency startups have grown exponentially. Nevertheless, this growth is being compared to the dot-com boom of the 1990s by a few experts. According to them, there will be a bust after this sudden rise in the stocks, leading us to the bear market.
The rise of data governance
Decentralization of data will give users control over their data—an advantage in normal situations. However, with decentralization, it can be challenging to track the source when hateful or misleading information is being circulated.
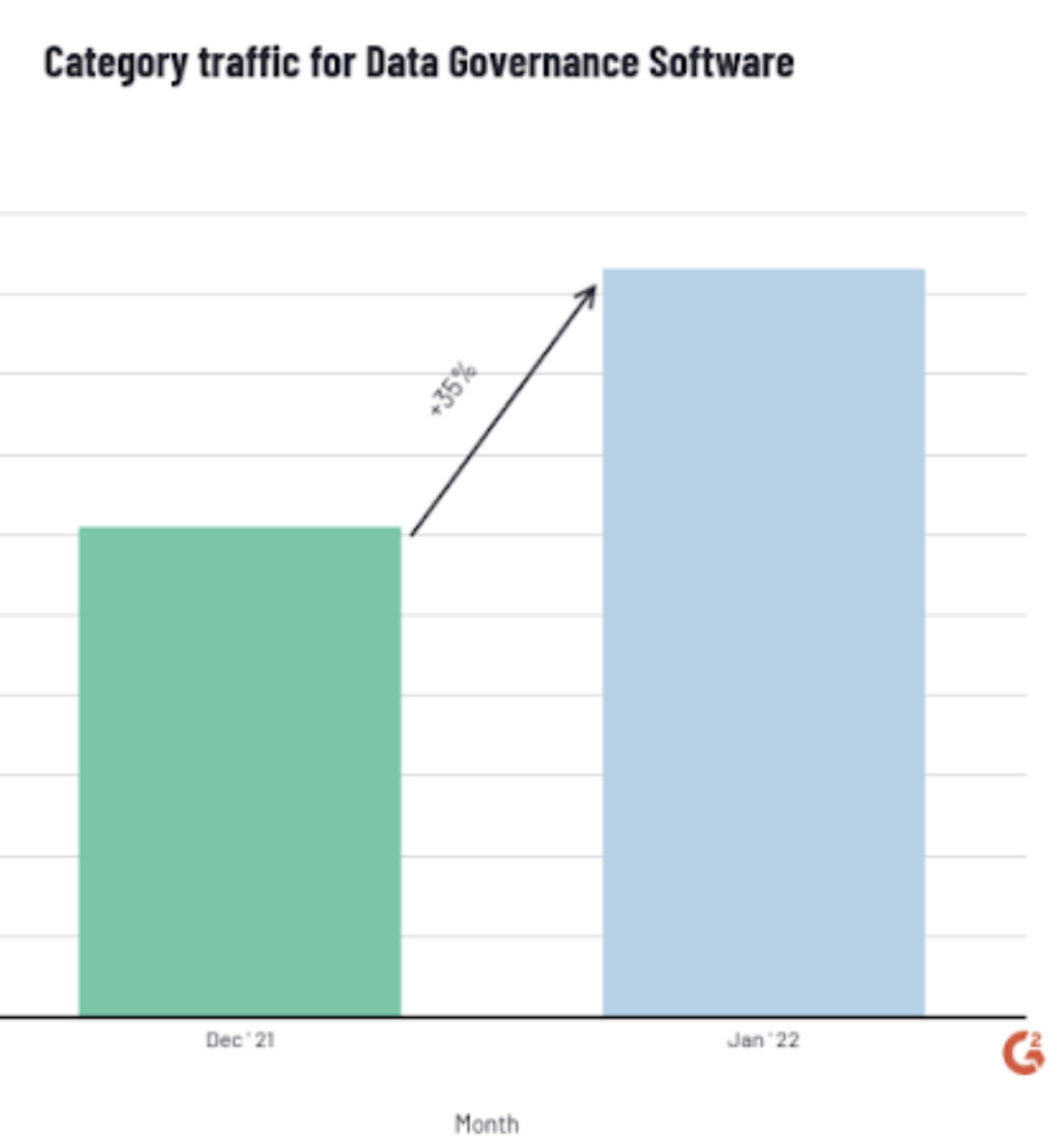
Data governance software is built around the bottom layer of blockchain. Its multidimensional verification mechanisms help prevent malicious attacks. Companies are investing in data management, which can be seen from the traffic trajectory of the Data Governance category of G2. The category traffic in January 2022 has grown 35% since December 2021.
The rise of data governance
With the growing popularity of blockchain technology, there is a loosely bound assortment of entities in the market that are busy developing the ecosystem in their own ways. Web 3.0 will change the way we interact digitally. Therefore, it is necessary that businesses equip themselves with technology to support their journey into web 3.0.
Quer aprender mais sobre Plataformas de Blockchain? Explore os produtos de Plataformas de Blockchain.

Shalaka Joshi
Shalaka is a Senior Research Analyst at G2, with a focus on data and design. Prior to joining G2, she has worked as a merchandiser in the apparel industry and also had a stint as a content writer. She loves reading and writing in her leisure.
