What is third-party software?
Third-party software is an application created by a company that doesn’t manufacture the device or operating system (OS) in use. A vendor provides software for your use and manages it for you.
Most modern vendors store third-party software on the cloud and provide customers access based on user credentials. Companies choose to onboard third-party software to help them handle certain processes, security, compliance, and use cases they don’t specialize in.
Third-party software saves companies from the hassle of building software in-house, but it comes with security risks. Many organizations use third-party and supplier risk management software to prevent data breaches or noncompliance while using these software applications.
Types of third-party software
Third-party software comes in different formats, catering to the needs of developers and businesses in different ways. Common types of third-party software include:
- Libraries: They help write and deliver mobile applications through the source code for a component. They can be either open-source or closed-source. Open-source applications are available to everyone for free, while closed-source applications require purchase.
- Platforms: These are pre-built and ready-made solutions that companies employ to execute a specific function, such as user logging, maps, or chats. Often, they’re offered as a software as a service (SaaS) product.
- Tools: They help to create a higher-quality product, making users’ lives easier.
Third-party software benefits
Although security and reliability are tricky to deal with, third-party software offers several benefits for its users, such as:
- Cost savings: Clients using a third-party solution can pay a monthly fee rather than the initial upfront cost for developing the feature from scratch. Some platforms are free until a certain threshold, after which they may be charged monthly for the utilized resources.
- Faster time to market: Third-party software helps accelerate the overall product development process, getting the product to market faster.
- Verification of value: One can quickly verify if the concept solves the problems of the target customers and fulfills their requirements.
- Easy integration for developers: Modern third-party software integrates with other business tools and systems, giving users holistic solutions.
- Less maintenance effort: Vendors are responsible for managing and maintaining the software. It helps the user’s IT department to focus on more critical things.
- Potentially greater capabilities: Third-party software can deliver more value and extra benefits to the user.
Best practices to deal with security risks of third-party software
Below are a few best practices that can help you ensure security while onboarding or integrating third-party software with your application:
- Conduct thorough vetting: Review the app's security policies and compliance certifications and understand its data handling and storage practices.
- Update regularly and patch: Outdated software can be a significant vulnerability, so keep these applications updated to their latest versions.
- Monitor and audit access permissions: Implement strict access controls and review them frequently to ensure only authorized personnel have access.
- Use robust authentication methods: Implement multi-factor authentication, which adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Develop an incident response plan: Create a response plan with steps to quickly identify and contain a breach, assess the damage, and notify all relevant stakeholders.
- Encrypt sensitive data: If the third-party application handles sensitive data, ensure the data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Conduct periodic security audits: Review logs, test for vulnerabilities, and assess compliance with security policies periodically to ensure security.
Third-party software vs. first-party software
Confusing third-party software with first-party software is common, but the two have key differences.
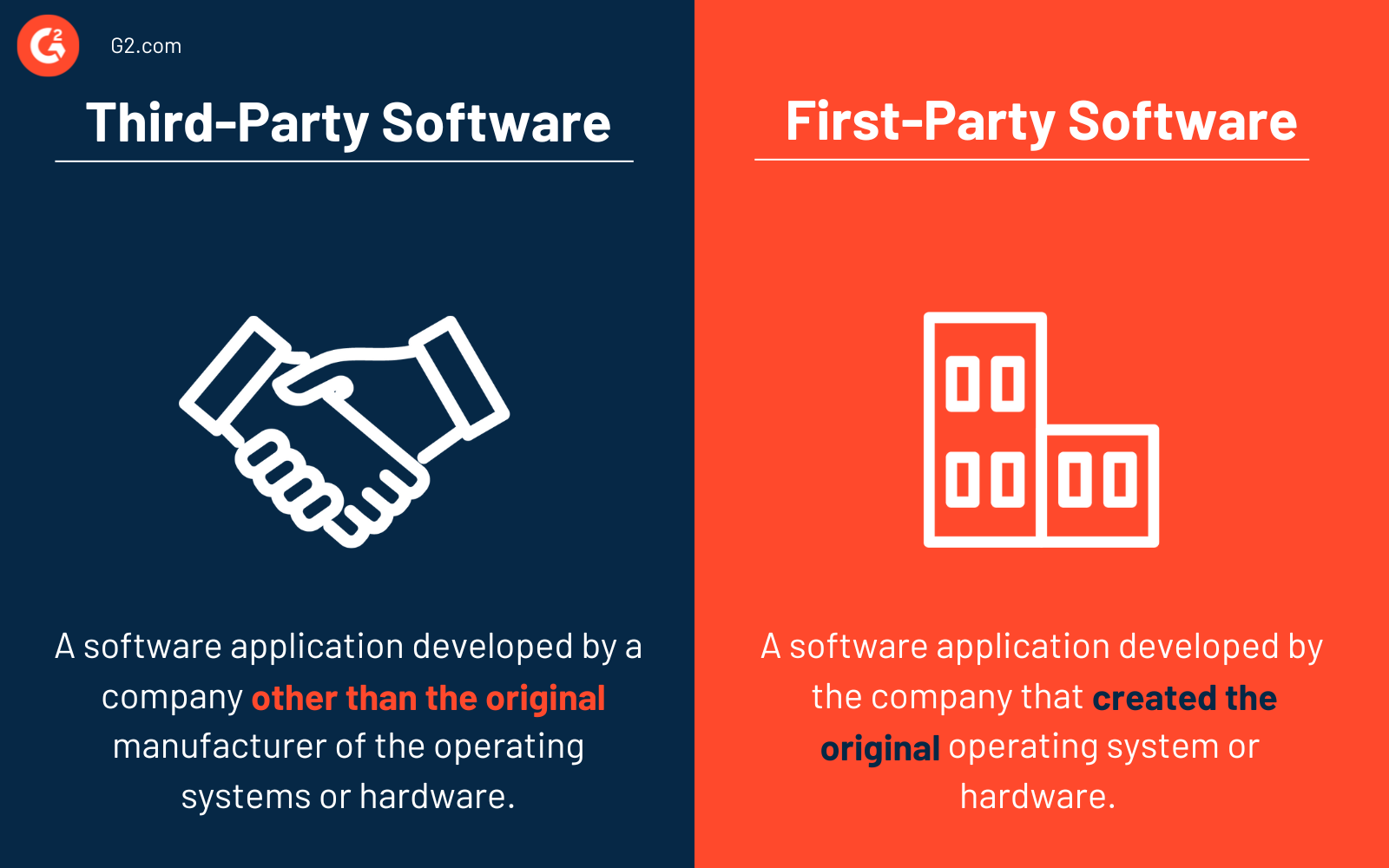
Third-party software is software applications developed by a company other than the original manufacturer or vendor of operating systems or hardware. They can be obtained and installed separately from vendors’ websites. The development resources differ based on the size and focus of the third-party developer.
Third-party software involves separate licensing and costs with different pricing models. They often provide services tailored to users’ specific needs.
First-party software is software developed by the company that created the operating system or hardware, for instance, Microsoft Office, macOS, and iOS. Substantial resources have been allocated for development as it is the company's core product. This type of software provides functionalities and features integral to the operating system or device.
First-party software comes bundled with the OS and often provides limited features. The OS or device manufacturer manages updates and provides support for the software.
Learn more about security compliance software to check whether third-party software complies with set security standards.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.