What is a centralized database?
A centralized database is a system where data used by an organization is stored and managed in a single platform. This data is accessible by either the local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN).
Many industries use centralized databases to effectively manage the information they need. Tools like sales or construction CRM software can track clients and vendors, project timelines, leads and prospects all in one centralized system.
The main reason that businesses use centralized databases is because information stored within the platform needs to be accessible to many users at any moment. Multiple users can work simultaneously without interrupting others on the team.
As most centralized databases are hosted on more than one server, there’s also less disruption if downtime occurs.
Basic elements of centralized databases
There are five separate elements that make up a centralized database. These are:
- Software. This is the internal mechanism of the database, which consists of programs that manage and control the information stored in the database. Software in a centralized database generally includes database software, network software, and the operating system.
- Hardware. While the database itself may not use hardware, physical devices are still needed to connect the information in the database to the end user. Computers, hard drives, or any other electronic devices that the database interfaces with are part of the hardware.
- Data. The actual information stored in the database is the data. This could be anything a company wants to keep in the database, from contact details to budget information.
- Procedures and rules. Any instructions set in the database are considered procedures or rules. These can be any automated instructions for the database to run independently, such as generating reports each day or week, backing up the data, or setting up any new sections of the database.
- Database access language. The database access language writes commands to manage the information within the database. Accessing, updating, and deleting data all require commands from the user, which are then run through the access language for the database to complete the request.
Benefits of centralized databases
There are many benefits that come with managing data within a centralized database. These include:
- The integrity of data is protected. When data is stored in a single location, it can be more easily managed by users. This makes communication and coordination across the team more efficient, and data isn’t duplicated or irrelevant.
- Data is more secure. Centralized data can have all security efforts focused in one place. Although distributed systems can be safe due to their fragmentation, this also makes it easy for a database security update to be missed. With a centralized system, security updates can all be made to a single database.
- Information can be easily moved and shared. When new hardware needs to access the database, this is much easier to configure as data is pulled from a central location. Users can also be added or removed from this one system.
- It’s usually cheaper. With only one database to maintain and manage, operation costs are typically less compared to several distributed databases.
Best practices for centralized databases
When implementing a new centralized database, businesses should follow several best practices, such as:
- Reviewing the data strategy against business goals. All data in the database should be assessed with overall business targets in mind. Key stakeholders should be considered when deciding on the management and use of data, and how the database fits into existing or planned projects or processes should be reviewed.
- Continually check data. It’s easy for databases to become very large in a short amount of time, particularly in a centralized system where multiple users are inputting information. Data should be reviewed frequently to ensure it’s still necessary and not taking up memory in the database that could be used for other important information.
- Implementing role-based user security. Not every user of the database needs the same level of information access. Security of a centralized database is critical, so roles should be assigned to each user with only the level of access they need for their job function.
Centralized databases vs. distributed databases
It’s common to confuse a centralized database with a distributed database, but the two have key differences.
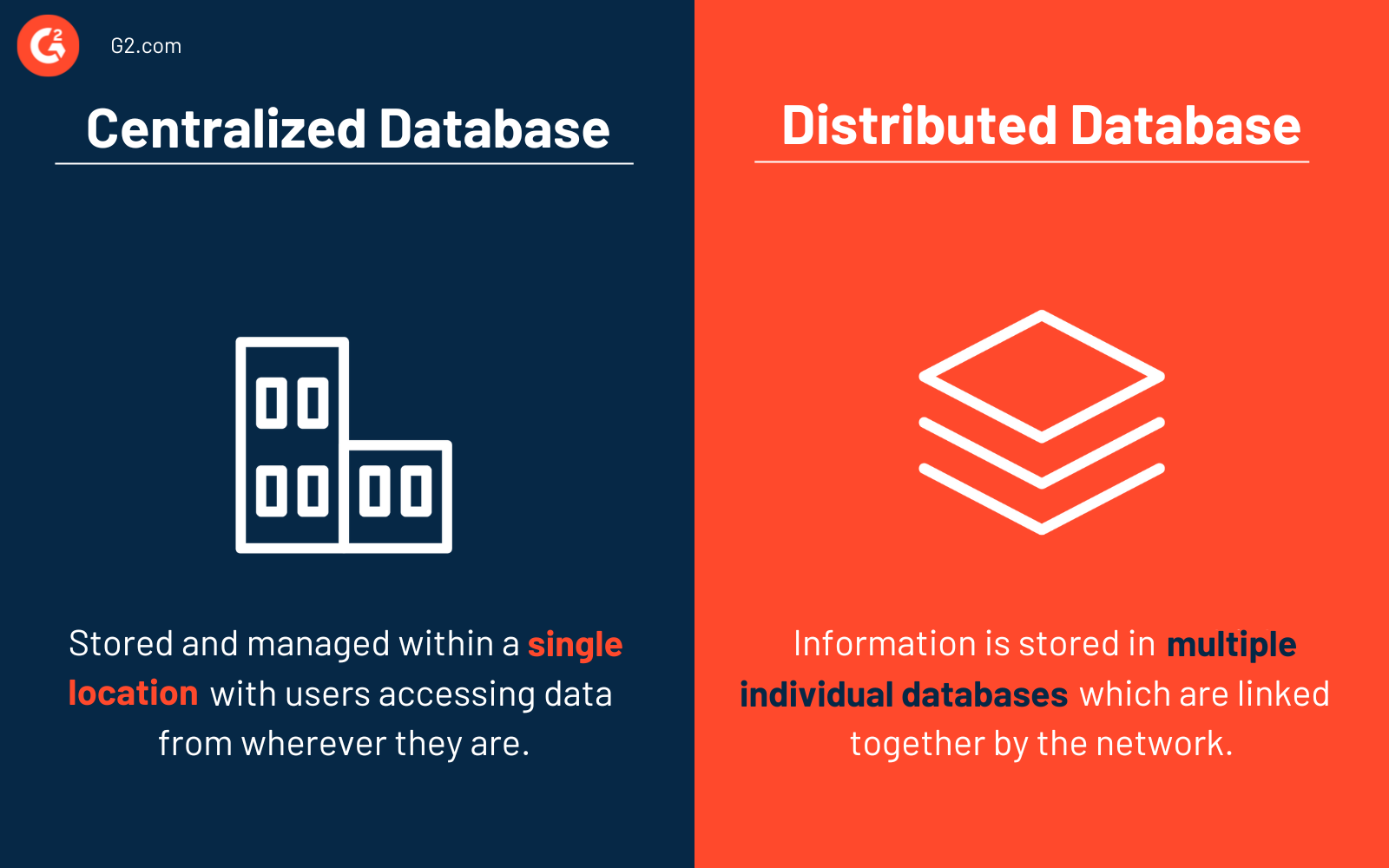
A centralized database is stored and managed within a single location, with users accessing this data from wherever they are. No copies of the data need to be made for users to find what they’re looking for, as everything is stored in one place.
With distributed databases, information is stored in multiple individual databases linked together by the network. These databases can all be stored in different physical locations and accessed from multiple networks. While this can keep information more secure, it’s easy for data to be replicated and to create data redundancies.
Keep your business’s most important information safe using data privacy management software.

Holly Landis
Holly Landis is a freelance writer for G2. She also specializes in being a digital marketing consultant, focusing in on-page SEO, copy, and content writing. She works with SMEs and creative businesses that want to be more intentional with their digital strategies and grow organically on channels they own. As a Brit now living in the USA, you'll usually find her drinking copious amounts of tea in her cherished Anne Boleyn mug while watching endless reruns of Parks and Rec.
