What is building information modeling?
Building information modeling (BIM) is an all-inclusive process of generating and handling information for a constructed asset. BIM uses an intelligent model on a cloud platform to seamlessly incorporate well-organized, multi-disciplinary data and create a digital representation of the asset throughout its entire lifecycle.
BIM software comprises a centralized database containing all relevant building information and data, such as construction sequencing, cost, and lifecycle management details. It allows businesses to manage documents while ensuring smooth collaboration and simulation at every project’s stage.
Implementing BIM into the systems, processes, and business significantly improves business practices and enhances productivity and profitability.
Types of building information modeling
Building information modeling applications extract various views from a building model, serving drawing production purposes. BIM's scope extends beyond the planning and design phase by encompassing the entire building lifecycle. Below are the various types of BIM organizations use to support the lifecycle.
- Geographic building information modeling is crucial for project planning. Integration with geographic information systems (GIS) provides an illustrative view of design and construction within geographic conditions. BIM offers insights into flood-prone areas, influencing location, orientation, and materials. It allows precise object-level design and project management through accurate data collection.
- Structural building information modeling empowers civil engineers as they create comprehensive structural analyses. With support for numerous steel, concrete, timber, and aluminum codes, BIM also has a range of features like analytical modeling, building planners, auto drafter, and advanced concrete.
- Concrete building information modeling allows for precise and detailed parametric modeling for component-oriented concrete design. It facilitates foundation drawings with assigned layouts, general details, and title blocks.
- Precast concrete BIM simplifies precast construction through rapid planning and a better understanding of requirements. It designs complex precast parts through shop drawing technology while maintaining efficiency.
- Construction management BIM enables project constructability, exploration, and evaluation before construction begins.
- Architectural building information modeling (ABIM) enhances collaboration, input, and operation processes. It produces superior outcomes, offering new assessment options.
- Mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) BIM helps executives in the electrical, mechanical, and plumbing fields design building systems efficiently.
- Infrastructure BIM delivers coordinated model views to help stakeholders investigate multiple scenarios, guaranteeing data-driven assurance for on-time and budget-friendly project delivery.
BIM benefits
The advantages of employing BIM tools and processes are truly remarkable. They empower construction companies to carry out projects with minimal errors, and the benefits extend far beyond. Among other benefits, building information modeling:
- Makes planning easier. BIM extracts essential material information, aiding in accurate cost estimation and providing valuable data from the 3D model.
- Detects collisions. BIM identifies potential issues between various building elements to certify a more accurate and efficient construction process that aligns with real-world site conditions.
- Visualizes projects. Businesses can create 3D models so clients and stakeholders can see design concepts and make informed decisions.
- Promotes higher-quality work. Real-time collaboration between construction workers and developers leads to a well-coordinated and reliable model, resulting in successful project execution.
- Simplifies access to information. Cloud storage capabilities make it easier to access building information, which means authorized personnel can retrieve data from anywhere.
- Reduces errors and project delays. Digitized information transfer eliminates manual processes and improves accuracy and reliability.
BIM process
BIM enables preconstruction planning and project visualization through 3D drawing and space-use simulations. It allows all stakeholders to experience the space beforehand breaking ground.
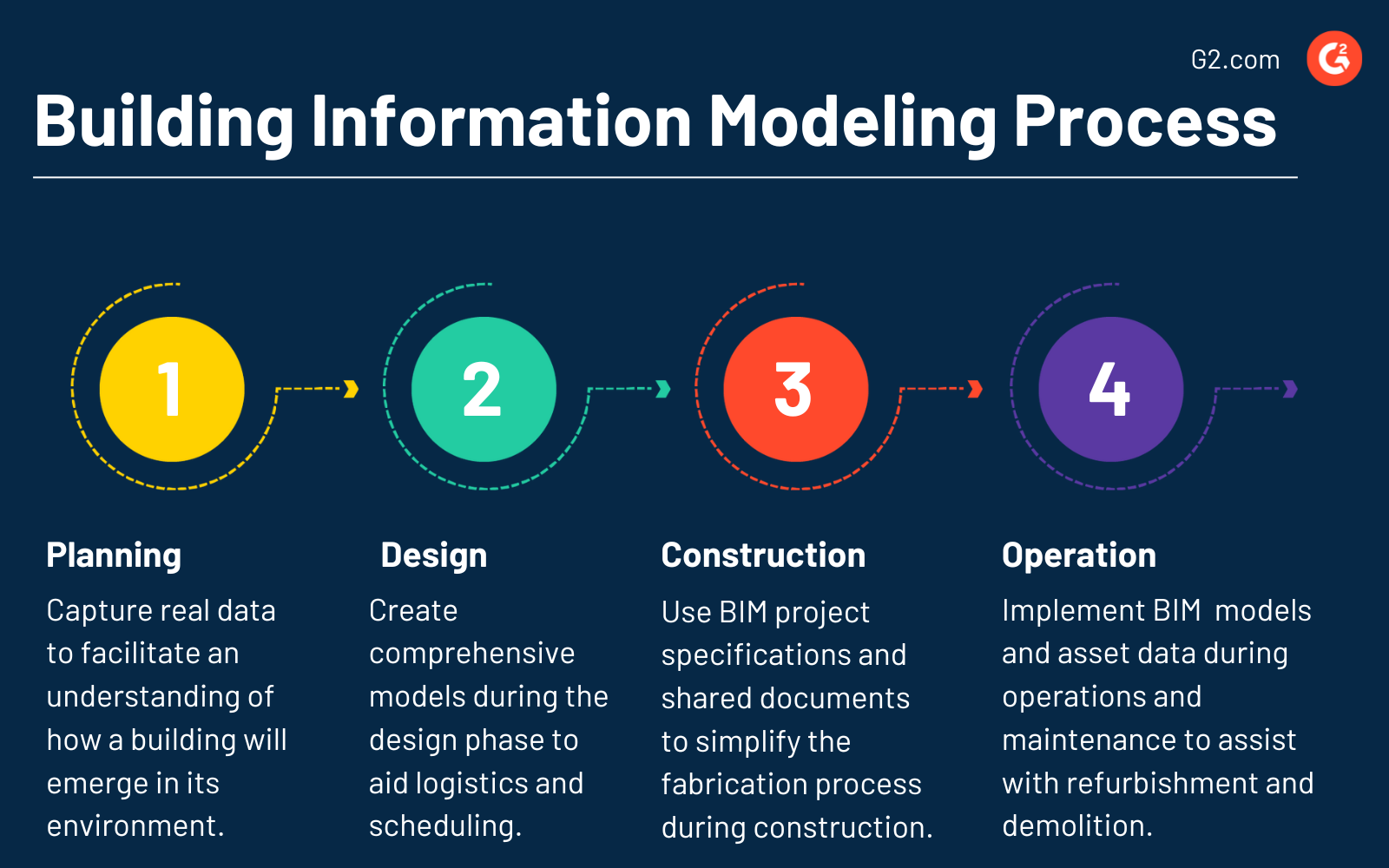
Below is the standard process companies use to run BIM.
- Planning. Try to capture reality and real-world data, facilitating a deeper understanding of how a building will emerge in its environment.
- Design. Create comprehensive models during the complex design phase, supporting conceptual design, analysis, and detailed documentation. It aids in logistics and scheduling.
- Construction. Use BIM project specifications and shared documents to simplify the fabrication process during construction.
- Operation. Implement BIM’s information-rich models and asset data to remain valuable during operations and maintenance, assisting with refurbishment, extensions, and demolition as needed.
Building information modeling best practices
BIM facilitates collaboration among teams and stakeholders, easing the design and construction phases using these best practices:
- Formulate a clear BIM strategy. Define project goals, scope, level of detail, and team member responsibilities.
- Adopt standardized naming conventions. Ensure consistent and effective communication using uniform naming conventions for objects and elements.
- Utilize a common data environment (CDE). Centralize project data, including the BIM model, in a shared repository to encourage collaboration and reduce errors.
- Develop a BIM execution plan (BEP). Outline BIM usage, roles, tools, and processes in a comprehensive document.
- Employ 3D modeling software. Utilize 3D modeling software for creating and managing BIM models, providing necessary training to team members.
- Engage all stakeholders. Involve architects, engineers, contractors, and owners in project planning and execution to encourage collaboration.
- Regularly monitor and update the BIM model. Keep the model accurate and current by conducting regular reviews, correcting errors, and incorporating design and construction changes.
Building information modeling vs. computer-aided design
BIM is a specialized approach for designing and documenting building information. BIM models integrate data for analyzing the real-world performance of each design to enable efficient project management.
Computer-aided design (CAD) involves utilizing computer-based software to assist design processes. It’s a standard tool engineers and designers use to create 3D drawings and 2D models. CAD is a versatile design tool applicable in diverse fields, including building designs, machinery, and furnishing.
Learn more about product design and what it takes for a product to go from idea to creation.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.