Qu'est-ce que l'analyse des journaux ?
L'analyse des journaux offre une visibilité sur la performance de l'infrastructure informatique et des piles d'applications. Elle examine et interprète les journaux produits par les serveurs, les réseaux, les systèmes d'exploitation et les applications.
Les journaux sont des documents horodatés d'un système informatique particulier. Ils incluent fréquemment des données chronologiques diffusées en temps réel en utilisant des collecteurs ou des archives pour une analyse ultérieure. L'analyse des journaux informe les utilisateurs sur la performance du système et peut signaler des problèmes potentiels tels que des failles de sécurité ou des pannes matérielles imminentes.
De nombreuses entreprises utilisent des logiciels d'analyse des journaux pour documenter efficacement les fichiers journaux des applications pour une meilleure analyse.
Comment effectuer une analyse des journaux
L'analyse des journaux examine les données des journaux produites par les systèmes informatiques, les applications et les dispositifs réseau pour résoudre les problèmes de sécurité, de conformité et de performance du système.
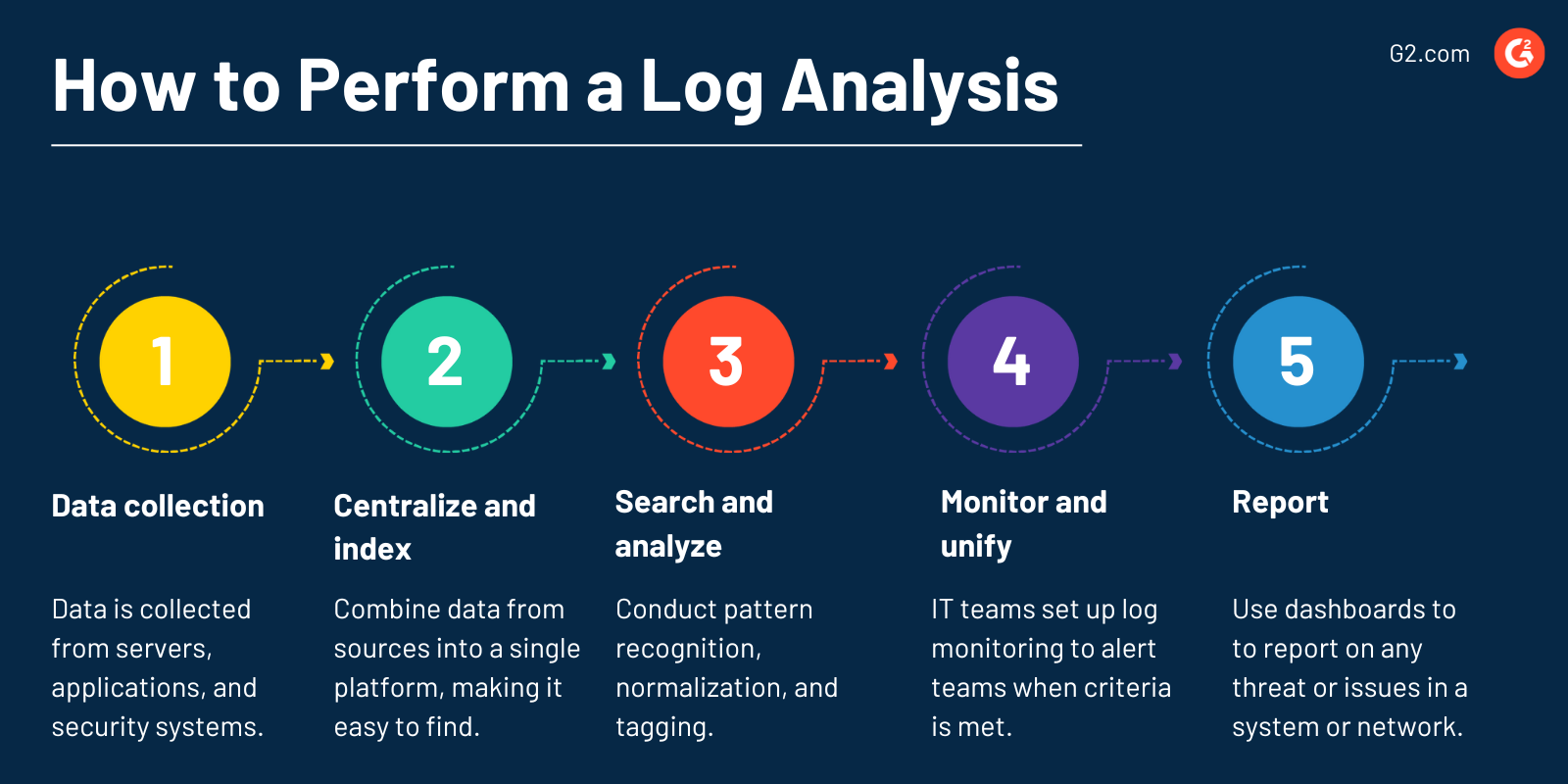
Elle suit ces étapes :
- Collecte de données. Les équipes informatiques installent un collecteur pour rassembler les données provenant de sources telles que les serveurs, les applications et les systèmes de sécurité. À travers un réseau actif, les fichiers journaux sont diffusés à un collecteur de journaux ou conservés dans des fichiers pour une analyse ultérieure.
- Centraliser et indexer. Pour rendre le processus de recherche et d'analyse plus efficace, les professionnels combinent les données de toutes les sources de journaux sur une seule plateforme. Les journaux deviennent accessibles après indexation afin que le personnel de sécurité et informatique puisse facilement trouver les données requises.
- Rechercher et analyser. La reconnaissance de motifs, la normalisation, le marquage et l'analyse de corrélation aident à rechercher et analyser les journaux.
- Surveiller et notifier. En utilisant l'apprentissage automatique et l'analyse, les organisations informatiques mettent en place une surveillance automatique et en temps réel des journaux pour alerter leurs équipes lorsqu'elles répondent à des critères spécifiques. Avec l'aide de l'automatisation, de nombreux journaux à travers les systèmes et les applications peuvent être surveillés en continu.
- Rapporter. Les équipes informatiques utilisent des tableaux de bord personnalisés réutilisables pour rendre compte de toute menace ou problème de performance dans un système ou un réseau. Seuls les membres du personnel qui ont besoin de savoir peuvent accéder aux journaux de sécurité privés et aux analyses.
Avantages de l'analyse des journaux
L'analyse des journaux est un outil crucial pour des systèmes informatiques bien entretenus et sécurisés. Les organisations peuvent protéger leurs systèmes et garantir la conformité avec les lois de l'industrie en utilisant les informations découvertes grâce à l'analyse des journaux. Voici d'autres façons dont l'analyse des journaux profite aux entreprises.
- Amélioration du dépannage. Les entreprises qui surveillent et analysent régulièrement les journaux détectent rapidement les problèmes. Elles identifient les problèmes avec des outils d'analyse des journaux sophistiqués, réduisant considérablement le temps et le coût de la solution.
- Amélioration de la cybersécurité. Les organisations peuvent trouver des anomalies, contenir les menaces et prioriser les solutions plus rapidement en examinant et en analysant régulièrement les journaux.
- Amélioration de la satisfaction client. Les entreprises peuvent s'assurer que tous les outils et programmes destinés aux clients sont entièrement fonctionnels et sûrs en utilisant l'analyse des journaux. Les entreprises peuvent immédiatement identifier les perturbations ou prévenir les problèmes avec une analyse cohérente et proactive des événements de journaux.
- Meilleure performance du système. Les entreprises peuvent trouver des goulots d'étranglement, des limitations de ressources et d'autres problèmes de performance du système. Elles peuvent ensuite optimiser leurs systèmes et améliorer la performance en résolvant ces problèmes.
- Conformité. Plusieurs lois de l'industrie exigent que les entreprises surveillent et examinent leur infrastructure informatique. En fournissant un enregistrement de l'activité du système, l'analyse des journaux aide les organisations à répondre à ces exigences.
- Économies de coûts. L'analyse des journaux aide les organisations à réduire les temps d'arrêt, à diminuer les coûts de support et à maximiser l'utilisation des ressources, entraînant des économies de coûts.
Techniques d'analyse des journaux
Avec des volumes de données massifs, il est impraticable pour les experts informatiques de maintenir et d'analyser manuellement les journaux à travers un vaste environnement technologique. Un système de gestion des journaux automatise les phases clés de la collecte, du formatage et de l'analyse des données. Voici quelques techniques que les professionnels de l'informatique utilisent pour analyser les journaux.
- Normalisation assure que toutes les informations dans le journal des transactions sont formatées de manière cohérente, y compris les adresses IP et les horodatages.
- Identification des motifs distingue entre les événements de routine, les anomalies, et filtre les événements en fonction d'un livre de motifs.
- Étiquettes et classifications attribuent des mots-clés pour regrouper les événements afin d'examiner ensemble les occurrences liées ou similaires.
- Recherche corrélationnelle collecte les données des journaux de plusieurs sources et les analyse toutes à la fois en utilisant l'analyse des journaux.
- Ignorance artificielle omet les entrées qui sont sans rapport avec la fonctionnalité ou la santé du système.
Applications de l'analyse des journaux
Les applications d'analyse des journaux se répartissent généralement en trois grands groupes, détaillés ici :
- Surveillance. Les journaux aident les professionnels de l'informatique à suivre comment un produit ou un service est utilisé, principalement pour des raisons de sécurité. Les équipes peuvent repérer des schémas d'utilisation nuisibles en examinant les journaux.
- Audit. Les journaux facilitent les audits, notamment dans le secteur financier. Par exemple, dans le cas d'une bourse supervisée qui permet aux utilisateurs d'échanger entre différentes devises, les régulateurs peuvent demander l'accès aux journaux de la bourse pour examiner l'historique des transactions.
- Débogage. Les programmeurs utilisent les journaux pertinents pour détecter toute menace ou défaut dans un produit ou un service et prendre les mesures nécessaires pour les corriger.
Analyse des journaux vs. gestion de la performance des applications (APM)
L'analyse des journaux et la gestion de la performance des applications optimisent la performance des applications. Cependant, leurs objectifs sont différents.
L'analyse des journaux se concentre sur la gestion des données des journaux. Elle sert de préalable à une gestion plus large de la performance des applications.
La gestion de la performance des applications (APM) vise à améliorer la performance globale d'une application. L'analyse des journaux soutient l'APM avec des données de journaux, permettant aux équipes informatiques de résoudre tout problème de performance. Cela ne signifie pas que le seul but de l'analyse des journaux est de soutenir l'APM. L'analyse des journaux permet aux organisations de sécuriser les données sensibles, de prouver la conformité et de reconnaître les tendances à long terme, ce qui n'est pas faisable en utilisant l'outil APM comme technologie autonome.
En savoir plus sur les meilleurs outils de gestion de la performance des applications pour suivre et surveiller la performance des applications.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.