Qu'est-ce que la planification des tâches ?
La planification des tâches, également connue sous le nom de planification par lots, est un processus qui alloue les ressources du système pour contrôler l'exécution des programmes en arrière-plan non surveillés. Le planificateur décide quelles tâches exécuter, à quel moment, et les ressources de l'unité centrale de traitement (CPU) nécessaires pour accomplir la tâche. Il s'assure que toutes les tâches sont terminées selon les priorités définies.
Les logiciels de planification des tâches peuvent effectuer la planification et surveiller les tâches ou les lots en temps réel. Les planificateurs modernes ont une interface graphique (GUI) avec un système de contrôle à point unique. De nombreuses entreprises utilisent des logiciels d'automatisation de la charge de travail pour automatiser les tâches sujettes aux erreurs liées à la planification des tâches, au traitement et à l'entreposage.
Les logiciels d'automatisation de la charge de travail aident les entreprises à réduire l'interaction manuelle, permettant au département informatique de se concentrer sur des tâches de plus haute priorité. Les professionnels de l'informatique peuvent rapidement résoudre les problèmes de journalisation centrale et de reporting et utiliser d'autres capacités telles que l'auto-remédiation, les alertes et les notifications.
Les planificateurs de tâches utilisent certains paramètres standard pour décider quelle tâche exécuter. Ces paramètres sont les suivants :
- Priorité de la tâche
- Dépendance de la tâche
- Disponibilité des ressources informatiques
- Dépendance des fichiers
- Dépendance de l'invite de l'opérateur
- Temps d'exécution estimé
- Temps d'exécution écoulé
- Temps d'exécution alloué à un utilisateur
- Tâches simultanées autorisées pour un utilisateur
- Disponibilité des périphériques
- Occurrence d'événements prescrits
- Disponibilité de la clé de licence lorsqu'une tâche utilise un logiciel sous licence
Types de planification des tâches
Les entreprises planifient des tâches ou des lots à travers plusieurs types de processus de planification. Voici trois types courants de planification des tâches que les équipes informatiques utilisent pour optimiser leur environnement.
- Planification à long terme : Une longue liste d'éléments est prête à être traitée lorsque de nouveaux processus sont créés. Cela nécessite une puissance de traitement substantielle et ajoute à la surcharge du système d'exploitation. Le système d'exploitation maintient une longue liste, et il y a une augmentation du changement de contexte et de l'envoi. Ce type s'occupe de la gestion d'une telle longue liste de processus. Un planificateur à long terme décide des tâches qui vont dans la file d'attente de traitement des planificateurs à court ou moyen terme. Il limite les processus qui entrent dans la file d'attente en fonction de différents algorithmes de traitement.
- Planification à moyen terme : Pour certains systèmes d'exploitation, un nouveau processus commence dans un état échangé. Un échange se produit lorsqu'un processus est retiré de la mémoire vive (RAM) et est ajouté au disque dur. Ce type fait partie de la fonction d'échange. Lorsqu'il y a de l'espace libre dans la mémoire principale, le planificateur décide quel processus peut être échangé. Cela dépend de la mémoire, de la priorité et d'autres ressources requises. Un planificateur à moyen terme effectue souvent la fonction d'échange pour les processus échangés.
- Planification à court terme : Un planificateur à court terme, également appelé répartiteur, commence lorsqu'un nouvel événement se produit. Cela se produit plus fréquemment et peut interrompre un processus en cours. Les planificateurs à court terme sont rapides et sélectionnent de nouveaux processus prêts à être exécutés, allouant le CPU à l'un d'eux, ce qui se produit très fréquemment.
Algorithmes de planification des tâches
La planification à court terme utilise principalement des algorithmes de planification des tâches pour allouer des processus et optimiser le comportement du système. Voici quelques algorithmes ou politiques de planification courants qui influencent quels processus devraient être attribués au CPU.
Algorithme de planification FCFS
L'algorithme de planification des tâches premier arrivé, premier servi (FCFS) suit la méthode premier entré, premier sorti. Au fur et à mesure que les processus rejoignent la file d'attente prête, le planificateur choisit la tâche la plus ancienne dans la file d'attente et l'envoie pour traitement. Le temps de traitement moyen pour ces tâches est relativement long.
Voici les avantages et les inconvénients des algorithmes FCFS.
- Avantage : FCFS ajoute un minimum de surcharge sur le processeur et est meilleur pour les processus longs.
- Inconvénient : Des effets de convoi se produisent lorsqu'une petite tâche attend longtemps pour passer en traitement, ce qui entraîne une utilisation plus faible du CPU.
Planification SJF
La planification du plus court travail d'abord (SJF), également connue sous le nom de plus court travail suivant (SJN), sélectionne une tâche qui nécessiterait le temps de traitement le plus court et l'attribue au CPU. Cet algorithme associe chaque processus à la durée de la prochaine rafale de CPU. Une rafale de CPU se produit lorsque les processus utilisent le CPU avant qu'il ne soit plus prêt.
Supposons que deux tâches aient la même rafale de CPU. Le planificateur utiliserait alors l'algorithme FCFS pour résoudre l'égalité et déplacer l'une d'elles vers l'exécution.
Voici les avantages et les inconvénients de la planification du plus court travail d'abord.
- Avantage : Le débit est élevé car les tâches les plus courtes sont préférées à un processus de longue durée.
- Inconvénient : Enregistre le temps écoulé qui ajoute une surcharge supplémentaire sur le CPU. De plus, cela peut entraîner une famine car les processus longs resteront longtemps dans la file d'attente.
Planification par priorité
La planification par priorité associe une priorité (un entier) à chaque processus. Celui avec la priorité la plus élevée est exécuté en premier. Habituellement, le plus petit entier est attribué à une tâche avec la priorité la plus élevée. S'il y a deux tâches avec une priorité similaire, l'algorithme utilise FCFS pour déterminer laquelle passerait en traitement.
Voici un avantage et un inconvénient de la planification par priorité.
- Avantage : Les tâches prioritaires ont un bon temps de réponse.
- Inconvénient : Les tâches plus longues peuvent subir une famine.
Planification en tourniquet
La planification en tourniquet est conçue pour les systèmes de partage de temps. C'est un planificateur préemptif basé sur l'horloge et est souvent appelé planificateur de découpage temporel. Chaque fois qu'un intervalle d'horloge périodique se produit, le planificateur déplace une tâche en cours de traitement vers la file d'attente prête. Il prend la prochaine tâche dans la file d'attente pour traitement sur une base premier arrivé, premier servi.
Décider d'un quantum de temps ou d'une tranche de temps est délicat dans cet algorithme de planification. Si la tranche de temps est courte, les petites tâches sont traitées plus rapidement.
Voici quelques avantages et inconvénients de la planification en tourniquet.
- Avantages : Fournit un traitement équitable à tous les processus, et la surcharge du processeur est faible.
- Inconvénients : Le débit peut être faible si la tranche de temps est très courte.
Comment fonctionne le logiciel de planification des tâches ?
Le logiciel de planification des tâches d'entreprise se compose d'une interface de planification des tâches et d'un agent d'exécution. Ces éléments jouent un rôle vital dans le fonctionnement global d'un système de planification des tâches.
Voici quelques responsabilités principales d'un planificateur de tâches ou de lots :
- Définir les tâches à exécuter à l'aide de la fonction de glisser-déposer
- Créer une file d'attente et planifier les tâches pour prioriser l'exécution des tâches
- Attribuer des tâches au bon agent en fonction de plusieurs facteurs tels que la priorité, la fréquence, et plus encore
D'autre part, un agent d'exécution s'occupe des processus suivants :
- Soumettre des tâches à l'exécution
- Surveiller les tâches pendant l'exécution
Un agent d'exécution se réfère à des informations techniques telles que la disponibilité du CPU, le temps d'exécution projeté, et les dépendances pendant l'exécution.
Les entreprises peuvent automatiser diverses tâches avec des logiciels de planification de la charge de travail.
Voici quelques-unes des tâches courantes que les planificateurs de tâches automatisent.
- Déclenchement d'événements : Les planificateurs de tâches peuvent détecter des événements déclencheurs tels que des e-mails, des modifications de fichiers, des mises à jour système, des transferts de fichiers, et des événements définis par l'utilisateur. Ils peuvent être connectés à différentes API pour détecter ces déclencheurs.
- Traitement des fichiers : Les outils de planification des tâches surveillent les mouvements de fichiers. Dès qu'un fichier déclencheur entre dans le système, il informe l'agent d'exécution de traiter la tâche prédéfinie.
- Transfert de fichiers : Les programmes de planification des tâches peuvent déclencher un protocole de transfert de fichiers (FTP) pour initier un transfert sécurisé du serveur vers Internet ou extraire des données d'Internet vers le serveur.
- Journalisation des événements : Les systèmes de planification des tâches génèrent et enregistrent des journaux d'événements pour la conformité réglementaire.
Planification des tâches vs. planification du CPU vs. automatisation de la charge de travail
Comprendre ces trois termes est essentiel lors de l'apprentissage de la planification des tâches.
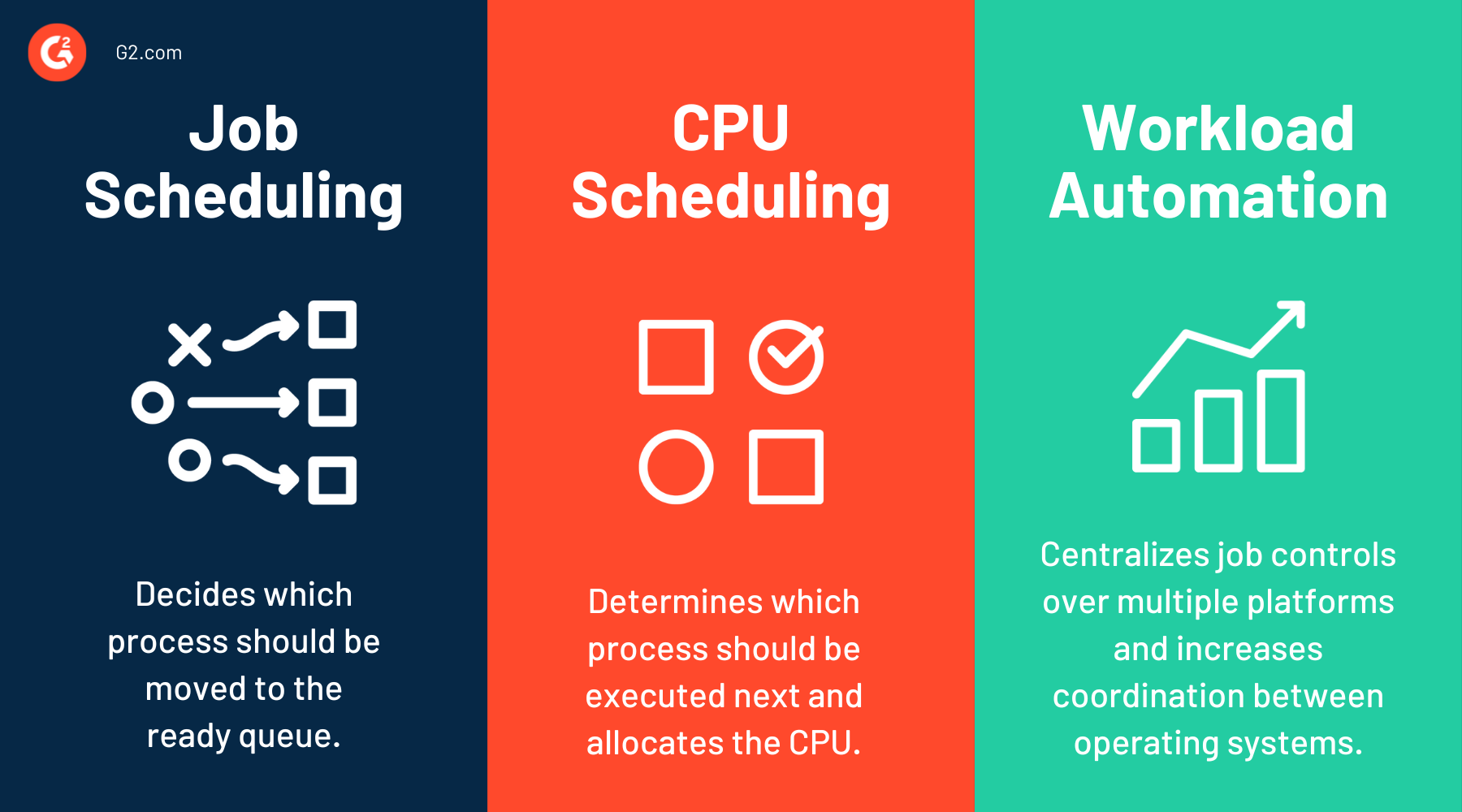
La planification des tâches et la planification du CPU sont toutes deux associées à l'exécution des processus. La planification des tâches est le mécanisme qui décide quel processus doit être déplacé vers la file d'attente prête. Habituellement, les planificateurs à long terme effectuent la planification des tâches.
D'autre part, la planification du CPU est un mécanisme qui détermine quel processus doit être exécuté ensuite et alloue le CPU en conséquence. Les planificateurs à court terme effectuent généralement la planification du CPU.
Les outils traditionnels de planification des tâches automatisent les tâches pour des plateformes ou des applications spécifiques. À l'inverse, les logiciels d'automatisation de la charge de travail centralisent les contrôles des tâches sur plusieurs plateformes, augmentant la coordination entre les systèmes d'exploitation et réduisant les conflits.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.