Information technology is at the forefront of modern businesses.
It’s the core element that enables day-to-day operations in organizations. ITSM, or IT service management, takes care of this core element and optimizes it for better outcomes while driving business value.
It wraps around the IT infrastructure and streamlines processes in the service lifecycle, enabling teams to operate strategically. Furthermore, ITSM software available on the market facilitates it by enabling more efficient, standardized, and effective service delivery.
Let’s dive deeper into understanding ITSM and discover how it can help you optimize your IT infrastructure.
What is IT service management (ITSM)?
IT service management (ITSM) is a process that ensures maximum business value with efficient use of information technology, people, and processes involved in the lifecycle of IT services.
These services go beyond resolving day-to-day IT issues and IT support to include designing, creating, delivering, and managing activities with information technology at its forefront. It includes core information technology services like AWS and Azure in addition to IT-enabled services, e.g. access to resources, service actions, and so on.
The main objective of ITSM is to provide business value to stakeholders and end-users while improving services continuously. It considers risks and challenges that may arise and sets up proper measures to tackle them and obtain desired results. ITSM draws inspiration from the popular principles and practices in management, such as Agile, Lean-IT, DevOps, and so on.
Who are the stakeholders of ITSM?
Simply put, stakeholders are people or organizations who have a stake in the services and their outcomes and want to draw value either through provision or service consumption.
They are the primary customers who pay the bills for these services, sponsors who authorize budgets, individuals or organizations providing financial support, or an end-user. Suppliers, who are responsible for providing these services, are also regarded as stakeholders.
ITSM stakeholders can be divided into two categories:
Internal stakeholders: Professionals who work in the same organization. For internal IT service providers, these are also the customers.
External stakeholders: Parties that are not a part of the same organization. They can be vendors, suppliers, customers, and others.
Before adopting an ITSM framework, be clear on who the actual stakeholders of IT services are. This will help you define roles and responsibilities to supporting units as well as manage interfaces between different roles and business processes.
Vous voulez en savoir plus sur Outils de gestion des services informatiques ? Découvrez les produits Outils de gestion des services informatiques (ITSM).
What is the purpose of ITSM?
IT service management aims to reduce IT costs, improve service quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and nurture agility. Most importantly, it intends to deliver value, a perceived benefit or usefulness of a service to a stakeholder.
This value is a combination of both reality and perception of service in the minds of customers. So the outcome of these services must take care of both to prove beneficial. IT service management ensures that this value, encapsulated with good reality and perception, aligns with the business goals and objectives.
As technology evolves, your stakeholders' perception of service may change. ITSM ensures that your service delivery reflects the same. IT service management capabilities hold systems for providing both good reality and good perception over time in varying circumstances.
Altogether, the ITSM process helps you get outcomes enriched with the business value while keeping an untattered focus on costs and satisfaction rates.
How do you implement IT service management (ITSM)?
Implementation of IT service management requires a cultural change. Stakeholders have to see IT as a service provider rather than recognizing it as just another department in the organization.
Naturally, the implementation process of ITSM differs for organizations as their business values are unique. There are different frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), Cobit, ISO/IEC 20000, Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF), DevOps, and more that you can use for implementing ITSM in your organization.
There are a few things you ponder on while implementing IT service management.
Evaluate your need
In a company of 20 people, adopting ITSM may not deliver significant results, whereas it would be beneficial in an organization with a larger headcount. So before implementing ITSM, consider your team's size, ability to scale in the near future, possible introduction to new technology, and other similar factors.
It's possible you were doing ITSM informally when your company was small, but when you scale, adopting a formal method will be an advantage, as it would be replicable.
Define your problem statement
Without proper clarity on your IT service problems, chances are, you would be walking a bumpy road even after implementing ITSM. It's paramount that you define your critical issues first and then choose the ITSM framework.
Whether you want to reduce IT costs or improve service delivery quality, define your problems first and then list the desired outcomes that would be achieved by solving those problems. It will help you align your service toward obtaining results and driving the business value you seek.
Choose your ITSM framework
After defining your problem statement, the next step is to select the framework that you would use to implement ITSM in your organization. Every framework (ITIL, Cobit, ISO 20000, etc.) will help you streamline your service, reduce friction, and ensure proper IT management. Still, choose one that aligns with your desired business values better, as the IT processes involved in these frameworks are different.
What is the difference between ITSM and ITIL?
IT service management is an actual practice or a professional discipline for managing IT operations and processes, whereas ITIL is a guiding framework to implement ITSM. ITIL framework ensures standardization in managing IT services, provides common terminology, and facilitates effective communication between organizations and vendors.

People often misinterpret ITIL as a prescriptive framework, whereas it follows a descriptive model. ITIL lays down concepts and principles to implement ITSM with examples of what people do that works now. Remember, these examples are not prescriptions; they may or may not work for you.
If you see an example that looks like it works for you, it may make sense to leverage it, but ITIL's intentional focus is on getting the outcomes, the ends right and clear, and not on prescribing 100% effective forever practices. ITIL's guidance disperses the essence of what people do now that works, which clearly means it's commonly accepted and implemented and not a leading-edge practice.
How does ITIL fit in with other ITSM frameworks?
ITIL is a framework for practitioners written by practitioners. But also, there are various other complementary frameworks and practices developed by different stakeholders for different reasons.
You can find whitepapers that map ITIL to almost any other framework or practice. ISO/IEC - 20000, the first international standard for service management, fits ITIL perfectly well for a purpose – in this case – providing the standard for organizational level certification and audits around IT service management. However, there are emerging practices like Agile, Lean-IT, and DevOps in particular that ITIL4 has embraced substantially.
ITSM in ITIL v3 vs ITIL v4
ITIL v3 was introduced in 2007 back when most IT was on-premise and Cloud was just starting out. This means the practices listed in ITIL v3 resonates well with what you see as the traditional IT infrastructure.
Now, we work with a hybrid of on-premise IT and the cloud. In moving ahead from ITIL v3 to v4, you see that more or less the service outcomes remain the same, but the process of reaching the outcomes changes.
In ITIL v3, it's through a service lifecycle of 26 processes and four functions. In contrast, in ITIL v4, it's through 18 practices, which include processes and functions like DevOps, Agile, and Lean practices in a service value chain.
The basic concept of ITIL v3 is implementation of 4 Ps of ITSM. These 4 Ps refers to people, processes, products, and partners. You can think of them as a proper scope of consideration for project management, any change, or any risk in IT. It helps you add value to every interaction you make in IT while evaluating the surface risks people might face.
On the other hand, ITIL v4 introduces four dimensions of service management. These are organizations and people, information and technology, partners and suppliers, and lastly, value streams and processes. These are roughly similar to the four Ps in ITIL v3, but the key difference is combining information with technology and value stream with processes.
What are the five stages of ITIL?
In ITIL v3, ITSM is achieved through five stages in the service lifecycle. These stages and the processes are mentioned as under:
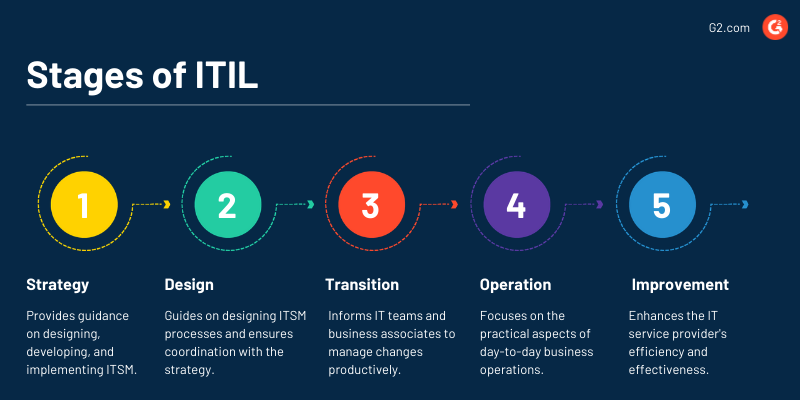
1. Strategy
The service strategy stage provides guidance on designing, developing, and implementing ITSM. It involves evaluating costs and risks associated with the IT service portfolios while using this information in making operational decisions. There are five ITIL processes involved in the strategy stage as follows:- Strategy management is about ensuring you have a strategy defined that guides and aligns your services toward the customers and the market you serve. It differentiates your value proposition for the overall service and informs management about your current and future services, capabilities, and resources.
- Service portfolio management targets delivering maximum returns of IT services at an acceptable risk. It includes rolling out suitable improvements to the service portfolio as conditions change.
- Financial management ensures legitimate bookkeeping of IT costs, and the data is mapped to different categories of IT services. It allows you to make strategic investment and budgeting decisions.
- Demand management is about understanding and influencing the demand for services and providing capacity to meet the demand. It enables you to avoid insufficient capacity that hinders service quality and excess capacity, impacting IT costs negatively.
- Business relationship management ensures that customers' needs are met adequately with a proper catalog of services. It empowers you to build positive relationships with your customers.
2. Design
The service design stage guides designing and developing ITSM processes while ensuring proper coordination with the developed strategies. The service design stage consists of eight different processes as follows:- Design coordination ensures uniform and rational design of new and tailored IT services by orchestrating ITSM systems, architectures, technology, processes, information, metrics, and resources.
- Service level management is about maintaining your customer satisfaction with your IT services. It involves focusing on the services you provide, their outcomes, service levels, and costs.
- Service catalog management enables you to maintain a unifying source of information for all services that can be accessed whenever needed.
- Availability management assures that the services are available during normal conditions. In the case of service outages, it takes care of bringing that service up and running at the earliest.
- Capacity management helps you ensure that your IT capacities, storage, bandwidth, etc. matches business needs at all times. It helps you understand the current business needs, IT capacity, and allows you to forecast them for the foreseeable future. Altogether, it enables you to deliver the right resources at the right time.
- IT service continuity management, which you may know as disaster recovery or contingency planning, is about ensuring that, in an abnormal operating circumstance, or a business interruption, predetermined or agreed IT service can be restored.
- Information security management deals with aligning IT security with business security. It ensures that information security is effectively managed for all IT services and IT service management activities while protecting confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and technology assets.
- Supplier management ensures that all contracts with suppliers support business needs and their services meet contractual responsibilities for quality and cost so that you consistently obtain value for money.
3. Transition
The service transition stage of ITIL informs IT teams and business associates to manage changes productively. It helps you avoid disruptions in other services or processes and allow you to adopt and adapt the new or altered services effectively. The service transition stage encompasses the following processes:- Transition planning and support ensure the requirements stated in service strategy, facilitated in service design, are actualized in service operation. It involves planning and coordinating resources to bring in the new or changed service in production.
- Change management helps you minimize the operational hurdles that may emerge in introducing a new service. It empowers you to answer what changed and get customers what they need quickly with quality and continuous improvement.
- Service asset and configuration management ensure a logical model of the IT infrastructure that correlates IT services, assets, and IT components. It is controlled and maintained for fact-based Management of IT services in a configuration management database (CMDB) and to comply with corporate governance requirements.
- Release and deployment management takes care of releasing productions successfully while enabling their effective use and delivering customer value. It involves defining and agreeing on releasing deployment plans with customers and other stakeholders.
- Service validation and testing help to identify if the service offering is fit for use and drives business value for the customers.
- Change evaluation guarantees that risks have been managed by carefully evaluating and assessing new or changed IT services. It also helps you determine whether to validate a change or not.
- Knowledge management facilitates making informed decisions by ensuring that the right information on service usage, consumption, and delivery constraints are conveyed and delivered to the right place or competent person at an appropriate time.
4. Operation
The service operation stage focuses on the practical aspects of day-to-day business operations. It enables your IT department to realize frictionless operations while ensuring reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. It concentrates on providing value to both customers and the service provider with the processes and functions as follows:
- Event management deals with the changes in an event's state and its effective management throughout the service management life cycle. It includes detection, diagnosis, taking appropriate actions, determining control actions, implementing routines driven with events, and so on.
- Incident management talks about minimizing disruption in business caused due to unplanned interruptions in IT services or impact on service quality. It helps you expedite on restoring services at the earliest when incidents occur.
- Request fulfillment ensures that users can get the information on the availability of standard services and request them as needed. It includes providing support with information, complaints, or comments, with automation in routine requests.
- Problem management is about problem resolution. It involves understanding and communicating the top end problems, how to solve them, and the steps further.
- Access management guides granting access permission to authorized users of service while restricting access for those who do not have clearance.
- Service desk comprises professional well-equipped for dealing with IT service activities requested through call, web interface, or an automatic reporting infrastructure. It can be fully or partially automated.
- Technical management is built of IT teams and departments that provide technical expertise and oversees the management of IT infrastructure while driving various strategies. It aims at providing upper-tier IT support for products and technologies in your IT infrastructure.
- Operations management includes departments and teams that manage day-to-day operations in an IT organization. It covers facilities like restores, managing amenities like power, airconditioning and the likes.
- Application management is a department or a team that deals with managing the application's lifecycle. Ongoing support, maintenance, and improvement of applications in a part of this function. Like technical management does for infrastructure, application management typically drives the strategies and choices for application platforms, products, and technologies, and provides upper-tier support for them as well.
5. Continual improvement
The continual service improvement stage consists of just one process. It's the seven step improvement process. The strategy aims to enhance the IT service provider's efficiency and effectiveness by monitoring and improving performance. It defines and manages the steps needed to identify, gathers, process, analyze, present, and implement a process, service, or improvement.
Benefits of ITSM
ITSM or IT service management offers many benefits to organizations that implement it. The most prominent benefits of ITSM practice are as follows:
Increases efficiency and reduces operational costs
ITSM helps organizations to gain maximum output from their current IT infrastructure. Asset management, being one of the components here, promotes a better usage of IT products and technology, and facilitates cost-effective procurement and disposition of IT assets.
Altogether, ITSM practice empowers your organization to scale IT operations more effectively, without intensive hiring, as it brings automation to clear out the redundant workload.
Minimizes risks
ITSM ensures that new or changed services are gradually rolled out with the change management process while reducing the interruption of business operations. It helps you understand policies and roles that aid the process and enables you to adapt to the change progressively.
ITSM practice helps your business adhere to IT compliance by maintaining standard IT services and ensuring accountability. It mandates a service desk and IT helpdesk to exercise a formal procedure for delivering different types of IT services.
As a manager, the practice enhances your ability to track how incidents or service requests are addressed. It helps you achieve high-level visibility on how organizations are delivering IT services.
Measures performance effectively
Adopting ITSM structures and processes helps you benefit from the formalized system that drives improvement over time. As an IT manager, you can identify and track defined key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluate your team's performance.
When you have a structured incident response process, your average response time, and mean time to resolution can decrease. In contrast, a focus on crisis management will help you reduce your mean time to recover (MTTR) whenever a service interruption occurs.
ITSM offers a management framework to improve IT service delivery through a process of continual service improvement.
Improved service and customer experience
At an enterprise level, the customers are users within the business who depend on IT services to carry out their job. With the service strategy process, enterprises align the services with the need of the business, which means the enterprise is working on services that the business actually wants. It leads to better customer experience.
On the other hand, ITSM involves maintaining a formalized ticketing and incident response system. It improves the service quality as the IT department responds to every incident report or service request submitted.
Challenges of ITSM
While implementing ITSM in your organization you may face certain challenges. Take a look at the challenges mentioned below and create your strategy to address them as they emerge.
Knowledge transfer
For successful incident resolution, technicians need to share their knowledge regarding how the issue was fixed. Placing comments like resolved or fixed would not help other technicians who are handling similar types of incidents.
It's important that before closing an incident, you should document your methods and steps involved in its resolution. It will help others to gain substantial inputs for future reference when a similar incident makes a mark.
Auto-generated alerts
As an IT admin who manages hundreds of applications on multiple servers, you receive tons of auto-generated monitoring alerts every day.
If one of these alerts slips past your focus, you may unintentionally welcome an unprecedented disaster. To avoid it, it's essential to categorize these alerts properly, prioritize them, and escalate them to application owners at the earliest. This precautionary action acts as a core component in the emergency management process.
Mixing incident and service requests
Service requests can be as simple as "providing access to a software" or "unlocking a laptop." You can manage these with a self-service portal or by providing technical assistance. Whereas, incidents requests are those that may take more effort and time to resolve.
You should distinguish between the two, as it would take different resolution steps, and the service level agreements (SLAs) would vary. If you mix it up, it can increase the workload on your IT professional as well as the IT costs.
Adoption of new technology
Many organizations are reluctant to adopt new methods or technologies. Some might feel uncomfortable to change if they have absorbed a predefined process into their muscle memory. But it's highly advisable if a certain process or tech helps you clear the redundancies in your routine, you must adopt it.
It helps you improve efficiency and gain productivity by leveraging automation for repetitive tasks. Also, place a standard operating procedure (SOP) and define workflows before implementing the change, so that your teams can be on the same page.
Transparency
Sometimes, the technician may need assistance from the admin or application owner to resolve the issue for incident requests. Reaching them separately just adds up a delay in the resolution of the request.
Instead, if an incident request arrives where you need help from other teams, you can loop them as well as the customer in the incident. It will help you gain transparency over all conversations and actions taken to resolve the request, enhancing your customer's satisfaction.
Top 5 ITSM tools
IT service management (ITSM) tool allows organizations to provide more efficient, standardized, effective and optimized IT services.To qualify for inclusion in the top 5 ITSM software list, a product must:
- Formalize IT processes and practices according to an ITSM framework
- Offer an internal service request and incident ticketing system
- Track internal service requests and incidents at micro and macro levels
- Organize and manage IT assets
- Centralize a business’ IT service knowledge
* Below are the five leading ITSM software from G2's Fall 2020 Grid® Report. Some reviews may be edited for clarity.
1. Zendesk Support Suite
Zendesk Support Suite enables your organization to have natural conversations with your customers. The suite is well-equipped to meet complex needs of the business and simple enough to understand and get up and running immediately.
What users like:
“I think that Zendesk has made creating general support functionality very simple. It's easy to create triggers (for routing, automatic replies, etc.) and doesn't take a ton of work to implement other than testing the flow by creating tickets. Additionally, macros help create easy answers and replies for your tickets and for your support teams to use.
You can also use a macro to assign ticket values when replying, making it a one touch reply for your more common issues and known solutions. All in all, agent management is a breeze, and assigning groups is relatively straight forward.”
- Zendesk Support Suite Review, Brandon E.
What users dislike:
“Unfortunately, the rating system can be a bit difficult to navigate. If a customer were to give a bad rating to a ticket and eventually change their rating to a good one, the metrics and the agent's statistics would not properly show this change.”
- Zendesk Support Suite Review, Aicha B.
2. Freshservice
Freshservice helps you modernize your service delivery using ITIL best practice while ensuring customer satisfaction. It’s a cloud-based service desk and ITSM solution that serves more than 40000 SMB, mid-market, and enterprise customers worldwide.
What users like:
“It quickly adjusts to your needs, and the product is improving continually. Their support is fantastic. Even if you have a simple question via live chat, the guys are on it so fast. We have an end-user support base of approx 250 and increasing; Freshservice meets all of our requirements easily.”
- Freshservice Review, Ewan C.
What users dislike:
“The only downside I've found so far is that you are allowed only one SLA chart in your dashboard. The way we have groups set up doesn't allow for us to see all the SLA information, by group, that we would like to see.”
- Freshservice Review, Zachary D.
3. SolarWinds Service Desk
SolarWinds Service Desk is a fully integrated cloud-based service desk and IT asset management solution. It’s based on ITSM best practices and uses automation, AI, and machine learning to optimize and streamline IT support services.
What users like:
“I really like how easy it is to install, upgrade and manage. We are now taking advantage of the ability to track our assets, along with expiration dates, followed up with notification emails. This really is a phenomenal product, and it costs pennies to purchase and maintain.”
- SolarWinds Service Desk Review, Jennifer A.
What users dislike:
“There are some limitations like how much you can customize when notifications are sent or not sent. Also some areas don't get any notifications which is annoying. The reporting is confusing and not straight forward. After a year of use and vendor training, we still don't quite understand how it works and just export our tickets into a CSV to do manually reporting.”
- SolarWinds Service Desk Review, Caleb K.
4. SysAid
SysAid is a service management solution that drives value across organizations by enhancing end-user experience and increasing agents’ productivity. It resolves business complex challenges with a built-in asset management, automation, and orchestration capabilities.
What users like:
“Incident management is the strongest feature of SysAid. It’s really easy to set up and use for experts and novices. Allow customize reports in no time, show lists, views and more, enabling you analyze your data. It has strong BI tools. SysAid's Team is continually working to update those features. You can design your lists for status, and KPIs and put on your dashboard. It’s highly customizable.
The BI section, perhaps, is new and powerful too. You can make almost every kind of stuff in there. Another cool feature is the flow management, you can decide how it works.”
- SysAid Review, Alejandro D.
What users dislike:
“The out of the box reporting does not always suit my organization's needs. However, I have spoken to SySaid about this and they have taken many steps to improve reporting. They are currently working on new features to make the out of the box reports much more useful. It is nice that they take their customer's suggestions under consideration.”
- SysAid Review, Jaclyn S.
5. Jira Service Desk
Jira Service Desk delivers a seamless service experience while catering to your unique needs. It promises a competitive set up time and pricing, making it suited for modern IT teams.
What users like:
“Jira Service Desk is very user friendly and I can design my own dashboard for better visibility and monitoring our team. It can also generate reports to better interpret the number of tickets we handle everyday.”
- Jira Service Desk Review, Jefferson C.
What users dislike:
“The least helpful thing about Jira Service Desk is the difficulty in creating queues for individual employees based on labels. This is a minor inconvenience and does not detract too much from the overall user experience for Jira Service Desk platform.”
- Jira Service Desk Review, Taylor B.
Optimize IT services with ITSM
ITSM allows you to manage your IT infrastructure in the most efficient way possible, enabling coordinated planning, designing, and delivering IT services. It helps your organization adopt and adapt to new changes and processes more easily and profitably than before.
Now that you have an in-depth understanding of ITSM, learn more about how ITIL, DevOps, and SRE work together to deliver maximum efficiency in managing your IT infrastructure.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.

