What is user role and access management?
User role and access management—sometimes also referred to as user permissioning--is a way for administrators to define what kind of access to resources such as files, applications, and systems a user has. Companies grant access to users by group or role type instead of on an individual basis to save administrative time in user provisioning and deprovisioning; to define and monitor access to company assets at scale; to limit user access to company assets to the minimum amount required to complete their job; and to meet regulatory security and privacy compliance requirements.
The types of role descriptions vary by company need and policy. Users are often granted role types based on their job functions. Many companies assign roles based on groups, such as company departments, job titles, duties, locations, and employee management levels. The role types, not individual users, are then granted specific permissions to access and take actions within company resources. For example, a departmental leader role may be granted permission to make global changes in a software application, while a manager role would be granted permission to make changes only to specific files. Similarly, an entry-level employee role user may be granted view-only access to the files within that system, if any access at all.
Types of access control management
Methods for access control management have grown over the years from role-based to attribute based to policy based. Depending on a company’s need for granularity and flexibility with access control will determine which user role and access management philosophy they will adopt.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): With RBAC, users are assigned role types based on static factors such as job title, company department, office location, and job function, and then the role type is granted access to company assets.
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC): Similar to RBAC, ABAC permissions users to access or take action in company resources based on user attributes, such as clearance level if accessing sensitive information, resource type, such as specific file types, and other factors like time and location-based access.
- Policy-based access control (PBAC): PBAC facilitates more flexible access control than static RBAC in that it provides flexibility for temporary, geographic, or time-based access based on company policies.
Benefits of using access management
The benefits of employing a user role and access management policy include:
- Easier and faster user provisioning and deprovisioning, saving administrator time
- Increased security by limiting access to the lowest level needed to complete the task
- Reducing employees misusing assets, known as insider threats
- Complying with data security and data privacy regulatory requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), and more
Impacts of access control management
The impact of user role and access management policies on the company and end users is generally positive.
- Speed: User role and access management allow administrators to grant users access quickly based on a user’s groups and role types.
- Accuracy: Administrators are more accurate in providing the least amount of privileges to a user when using predefined roles.
- Monitoring: Developing policies for role-based access requires a company to understand who has access to important company resources. Tools like user provisioning and governance tools can help company administrators monitor that these policies are being enforced properly.
- Compliance: Many companies are required to meet strict data security and data privacy regulations, including user role and access management policies.
Basic elements of role-based access control (RBAC)
The types of user role and access management can vary. For RBAC specifically, it may include the following types, based on the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) model:
- Flat RBAC: This is the most straightforward type of user role and access management based on employee role.
- Hierarchical RBAC: Hierarchical RBAC grants higher-level employees the permissions of their subordinates.
- Constrained RBAC: This type allows for the separation of duties often required by regulations.
- Symmetrical RBAC: Symmetrical RBAC adds permission reviews to constrained access.
Access management best practices
In order to make user role and access management work well, companies must follow these best practices:
- Determine if RBAC, ABAC, or PBAC is best for the organization
- Understand that users may have multiple role types apply to them
- Ensure that role administrators create policies for role assignment, role authorization, and permissions authorization
- Utilize software solutions, such as user provisioning and governance tools to manage company access policies
Access management vs. identity management
It's common to confuse access management with identity management, but the two have some key differences.
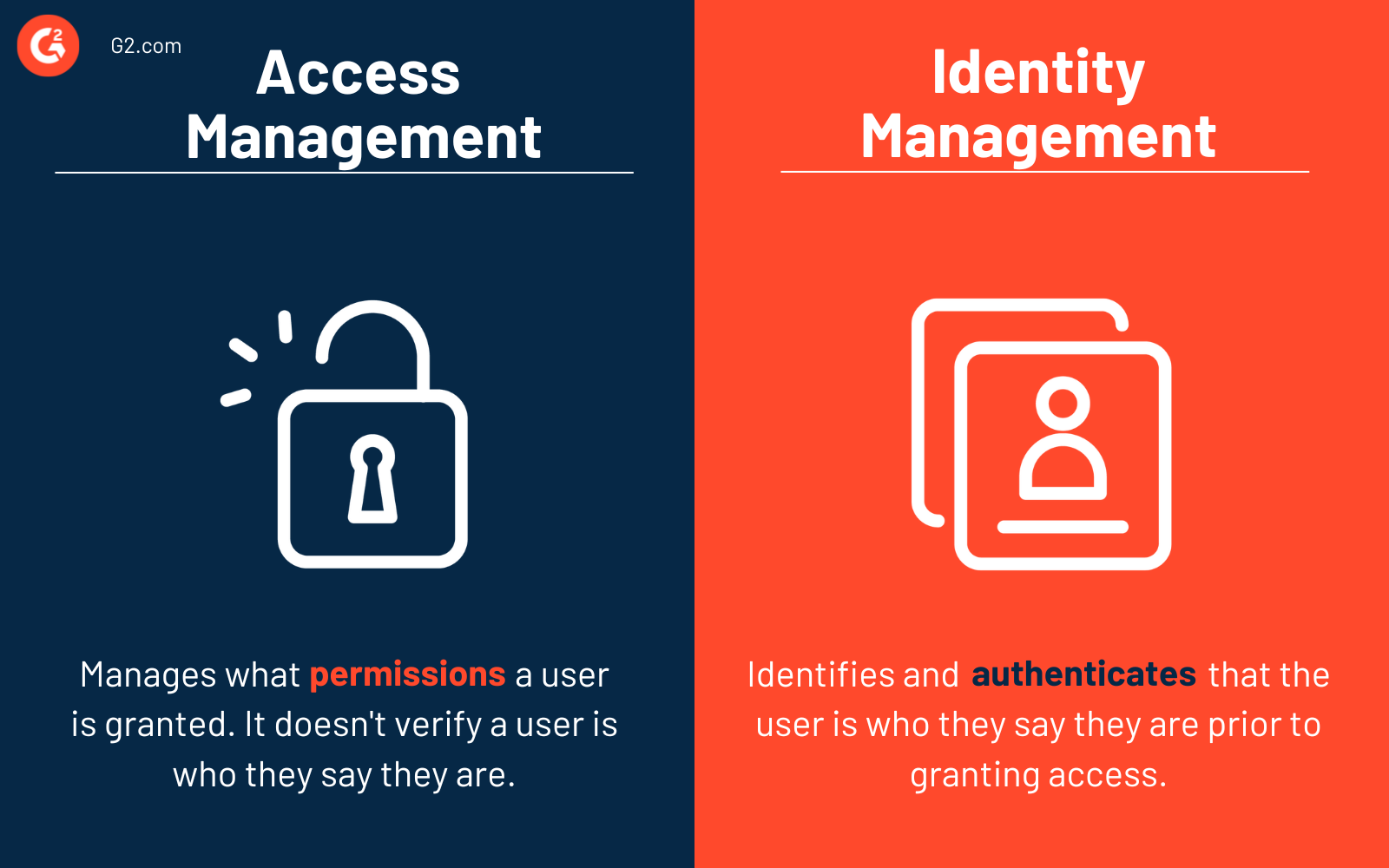
Access management manages what permissions a user is granted; it does not verify that the user is who they say they are prior to granting access to permissioned resources.
Identity management identifies and authenticates that the user is who they say they are prior to granting access. Identity and access management (IAM) software solutions often consist of identity tools such as single sign-on (SSO) software, password manager software, multi-factor authentication software, user provisioning and governance tools, and more.

Merry Marwig, CIPP/US
Merry Marwig is a senior research analyst at G2 focused on the privacy and data security software markets. Using G2’s dynamic research based on unbiased user reviews, Merry helps companies best understand what privacy and security products and services are available to protect their core businesses, their data, their people, and ultimately their customers, brand, and reputation. Merry's coverage areas include: data privacy platforms, data subject access requests (DSAR), identity verification, identity and access management, multi-factor authentication, risk-based authentication, confidentiality software, data security, email security, and more.