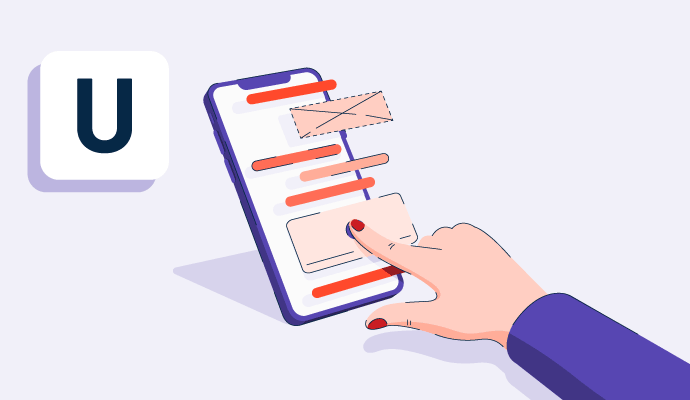
¿Qué es una interfaz de usuario (UI)?
Una interfaz de usuario es un punto de conexión entre humanos y tecnología, o la forma en que una persona puede interactuar con un sitio web, aplicación o dispositivo. Esto incluye cualquier elemento visual o interactivo que compone el software o sitio, como botones o gráficos.
El objetivo de la UI es hacer que la experiencia del usuario sea lo más intuitiva posible. Las empresas pueden usar herramientas como constructores de páginas de destino para armar un diseño para una interfaz de usuario. Aunque la mayoría del diseño de UI se centra en elementos visuales, las interfaces de usuario multimedia tienen características como entradas basadas en sonido.
Los equipos de UI y experiencia de usuario (UX) trabajan estrechamente para asegurar que el producto final maximice la eficiencia y accesibilidad.
Tipos de interfaces de usuario
Las interfaces de usuario están compuestas por diferentes elementos, pero la mayoría de las interfaces se pueden categorizar de la siguiente manera:
- Interfaz gráfica de usuario. Esta interfaz es estándar para la mayoría de las computadoras, utilizando una entrada táctica como un teclado y emparejándola con una salida visual a través de un monitor.
- Interfaz de usuario táctil. Dispositivos como teléfonos inteligentes y tabletas usan UI táctil para permitir la interacción con una entrada háptica.
- Interfaz de usuario por voz. Muchos dispositivos ahora ofrecen UI por voz que permite a las personas hablar con sus dispositivos. Asistentes virtuales y el dictado por voz son ejemplos de esto.
- Interfaz basada en menús. Las interfaces de usuario que ofrecen opciones dentro de la propia UI suelen estar basadas en menús. Por ejemplo, un cajero automático permite a los usuarios decidir entre varias opciones para el siguiente paso.
Elementos básicos de una interfaz de usuario
Cada interfaz de usuario se crea utilizando capas de elementos interactivos que atraen a los humanos. También emplean entradas y salidas para que los usuarios interactúen con el software, aplicación o sitio web en el que están, tales como:
- Controles de entrada. Estos elementos interactivos permiten a las personas agregar su propia información al sistema. Los campos de texto, botones de opción múltiple y menús desplegables son las entradas más comunes para las interfaces de usuario.
- Componentes informativos. Estos elementos comparten información con los usuarios al interactuar con el sitio o software. Notificaciones, cuadros de chat, ventanas emergentes y barras de progreso se pueden usar en sitios web y aplicaciones para proporcionar detalles importantes.
- Componentes de navegación. Moverse por un sitio web debería ser fácil. Las barras de menú y las pestañas facilitan esta navegación.
- Contenedores de elementos. Cualquier contenido relacionado puede mantenerse junto en un contenedor. Por ejemplo, acordeones o menús desplegables pueden usarse en un sitio o aplicación para ocultar información. Estas son secciones de contenido apiladas verticalmente donde se puede revelar más información cuando el usuario hace clic en los encabezados individuales del menú.
Beneficios de una buena interfaz de usuario
Tener un diseño de interfaz de usuario accesible y bien planificado tiene numerosos beneficios, independientemente de si la interfaz se usa internamente o está orientada al cliente.
- Aumento del compromiso del cliente y las ventas. Para las interfaces que usan los clientes, las empresas suelen ver mejoras en las tasas de compromiso del cliente y, a menudo, más ventas. Una buena interfaz de usuario da a los clientes la oportunidad de completar investigaciones o transacciones con mínima frustración, dejándolos más propensos a permanecer leales a esa empresa.
- Mejora de la productividad y eficiencia para los usuarios. Cuando una interfaz de usuario presenta información claramente y asegura una fácil navegación entre diferentes partes de una aplicación móvil o software, los usuarios pasan menos tiempo tratando de alcanzar un objetivo final.
- Reducción de los costos de soporte al cliente. Cuando las interfaces de usuario son intuitivas y fáciles de usar, los clientes pueden resolver sus propios problemas sin ayuda adicional. Esto significa que se necesitan menos recursos para proporcionar soporte al cliente, dejando a los empleados libres para trabajar en otras áreas dentro de una empresa.
Mejores prácticas para el diseño de una interfaz de usuario
Todas las interfaces de usuario deben diseñarse teniendo en cuenta la UX, por lo que es esencial que ambos equipos trabajen juntos. Un diseño de interfaz de usuario exitoso debe:
- Minimizar la sobrecarga de información. Si hay demasiados detalles, un usuario final puede tener dificultades para entender qué acciones deben tomar a continuación. Las interfaces de usuario deben diseñarse para resaltar los detalles más importantes y evitar cualquier cosa irrelevante para las acciones siguientes del usuario.
- Ser responsivo en todos los dispositivos. Las interfaces de usuario de sitios web y software deben diseñarse teniendo en cuenta diferentes dispositivos y redimensionarse en consecuencia. Esto es especialmente importante si los usuarios cambian de un dispositivo a otro mientras acceden a la interfaz.
- Centrarse en la usabilidad. Todo sobre una interfaz de usuario debe ser intuitivo y fácil de interactuar. La usabilidad debe ser la prioridad antes de que se considere el valor estético.
- Ser consistente con otras partes del software o sitio. Una vez que se ha elegido un diseño para una parte de un sitio o aplicación, la interfaz de usuario debe reflejar esto lo más fielmente posible. Esto mitiga cualquier confusión o frustración.
- Mantener el atractivo visual e interés. Cualquier contenido dentro de una interfaz de usuario debe ser estéticamente agradable. Los diseños minimalistas suelen funcionar mejor que las interfaces de usuario llenas de muchos elementos interactivos como gráficos o videos que pueden distraer al usuario de detalles importantes.
Diseña y maqueta diseños de interfaz de usuario que ayuden a tus clientes y empleados a interactuar con tu negocio de manera más efectiva con software de diseño gráfico.

Holly Landis
Holly Landis is a freelance writer for G2. She also specializes in being a digital marketing consultant, focusing in on-page SEO, copy, and content writing. She works with SMEs and creative businesses that want to be more intentional with their digital strategies and grow organically on channels they own. As a Brit now living in the USA, you'll usually find her drinking copious amounts of tea in her cherished Anne Boleyn mug while watching endless reruns of Parks and Rec.