What is threat remediation?
Threat remediation is a planned approach organizations take to identify and prevent threats against IT assets. It helps organizations fix security vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them.
Threat remediation confirms the organization can respond to attacks, limit the damages, and eliminate threats. It involves monitoring the network for anomalies. When a vulnerable asset is found, the vulnerability is fixed, and after installing a relevant patch, the threat is eliminated altogether.
Many organizations use network detection and response (NDR) software to find any suspicious activity in their network and automate the remediation process.
Types of threat remediation
Organizations use various remediation strategies to maintain a robust security posture. Below are two types of threat remediation an organization can employ.
- Automated remediation automatically starts the remediation process or notifies end-users if they want to trigger remediation steps. This is an event-triggered process.
- Manual remediation is a user-triggered process. Teams need proper training in vulnerability and patch management to eliminate the threat.
Threat remediation benefits
Threat remediation considers weaknesses that could expose an organization’s assets to threat actors. It fixes the weak spots before they cause any harm. There are several other benefits of threat remediation, including:
- Addressing cybersecurity threats in real time. Remediation efforts are practical as they’re carried out in real time. It helps fight emerging threats.
- Achieving customer trust. An effective remediation process proves to customers that their data is safe.
- Preparing for future risks. Both the positive and negative results of a threat remediation effort offer insight. They highlight what went wrong and which tactics succeeded, clarifying what needs to improve for the future.
- Preventing financial losses. A cybersecurity risk can mean loss of money, revenue, customer trust, and legal consequences. Remediating a threat saves time, money, and resources.
Threat remediation steps
Implementing the right threat remediation strategy is important for staying protected against vulnerabilities. Weak points spread if not attended to. Some of the typical steps involved in a threat remediation approach are below..
- Regulate a standard risk assessment. The risk assessment process identifies potential threats that might affect the organization. It first evaluates the current IT infrastructure to detect any underlying vulnerabilities. It then thoroughly assesses various factors such as security systems, processes, policies, and structures.
- Prioritize threats. When an organization faces substantial security issues, it must prioritize threats based on severity. Security teams rank threats that pose a more significant risk.
- Manage and fix vulnerabilities. Find vulnerabilities and estimate the time to fix them. Deploy a vulnerability management program to enforce standard IT configurations.
- Implement monitoring processes. Let monitoring systems continuously look for vulnerabilities. These tools can segregate data for remediation.
- Patch up vulnerabilities. After fixing the vulnerabilities, update and install patches to completely eliminate threats.
- Train employees. Create awareness among staff about the harmful threats that the organization may face. Ask them to stay alert and cautious. It’s best to create a regular awareness program during which security teams can educate employees about common vulnerabilities and cybersecurity best practices.
Threat remediation best practices
Follow these best practices to ensure a robust cybersecurity posture and eliminate threats.
- Install updates and patches. Organizations have to ensure business continuity and update and patch systems without disrupting operations.
- Identify and categorize assets. Discover and track IT workloads, systems, and information assets. Create a database that updates in real time and monitors system and configuration changes.
- Evaluate business value and risk. Understand the location of IT assets and how they behave. Isolate critical assets based on their business value and the risks associated with it.
- Monitor and scan. Pinpoint potential threats and vulnerabilities in the IT network. Monitoring and scanning is a continuous process that keeps track of network traffic behavior and data logs.
- Improve continuously. A single threat remediation strategy won’t guarantee the best results for an extended period of time. Keep an eye on systems and never stop looking for threats.
- Automate process. Automating processes ensures a systematic threat remediation framework without delays and human errors. It fosters a data-driven approach.
Threat remediation vs. threat mitigation
Some may confuse threat remediation with threat mitigation, but the two have key differences.
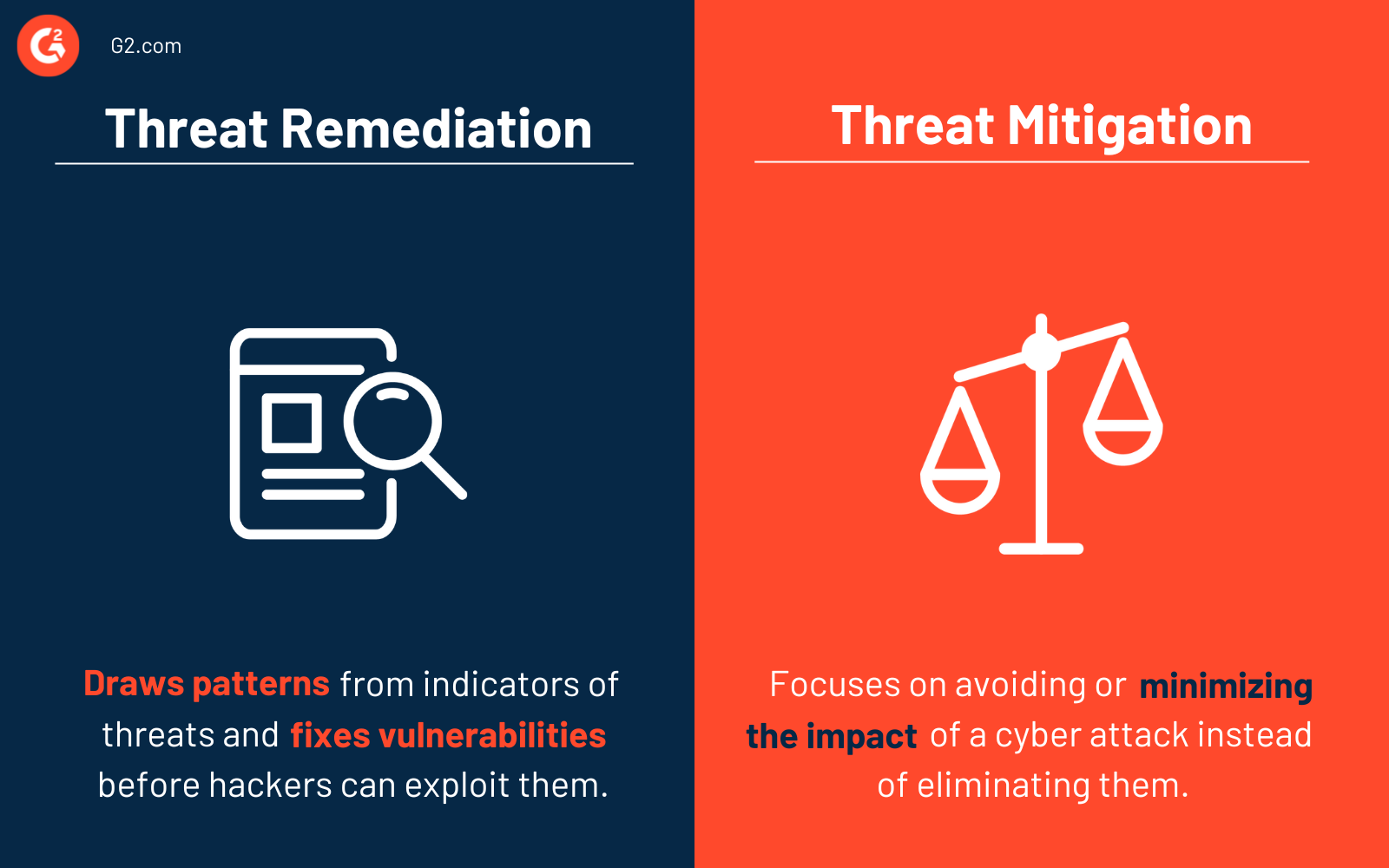
Threat remediation refers to identifying and eliminating risks. It draws patterns from indicators of threats and fixes vulnerabilities before malicious hackers exploit them.
Threat mitigation focuses more on avoiding or minimizing the impact of a cyber attack. It doesn’t eliminate threats as that can sometimes cause operation disruption.
Learn more about cyber attacks and discover various forms they can take.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.