What is threat hunting?
Threat hunting is a proactive cybersecurity technique that regularly monitors networks and devices for potential cyber threats.
After bypassing a network’s first levels of security, criminals can easily go undetected, lurking for weeks, possibly months, before attacking or being discovered. Unlike threat detection, which is a more reactive approach, threat hunting anticipates where within the system these cyber criminals could be.
Through active monitoring using security information and event management (SIEM) software, IT and security teams identify suspicious activity and take action before a cyberattack takes place.
Types of threat hunting
Any threat hunting exercise assumes that cybercriminals are already within the network or device’s system. Investigations into these possible intruders fall into one of three categories.
- Hypothesis-driven is usually triggered by a new threat identified in a wider market. This could be industry-specific or based on the technologies a company is currently using. IT teams will gather information, usually through crowdsourcing, then investigate their own systems to see if anything suspicious has occurred.
- Known indicators of compromise or attack go a step beyond hypothesis-driven investigations and use threat intelligence data to understand the motives or goals behind a possible attack. Indicators of compromise (IOCs) or indicators of attack (IOAs) are mapped and used as triggers for future malicious activity.
- Machine learning uses data analysis techniques to review large amounts of information as a way of training artificial intelligence (AI) programs to detect inconsistencies and irregularities in data that could possibly suggest malicious activity.
Steps for a threat hunting investigation
Regardless of the threat hunting methodology used, companies have to complete five critical steps to ensure a successful investigation.
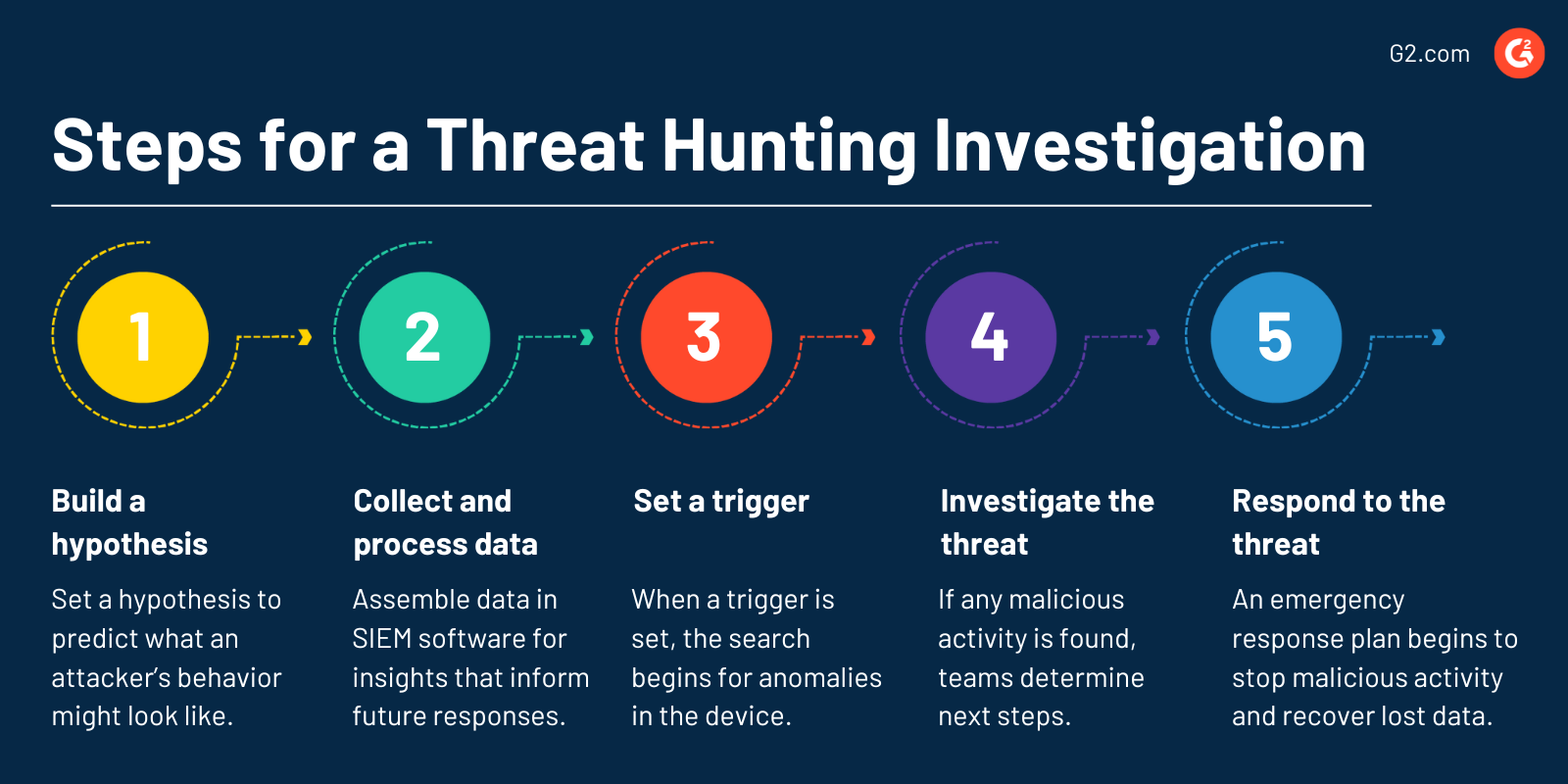
- Building a hypothesis. Like any scientific experiment, threat hunting requires a hypothesis to predict an attacker’s behavior. Ideas should be discussed across the team as they gather information about potential threats or types of activity to watch for.
- Collecting and processing data. Assembling and centralizing data in SIEM software gives teams with a history of threats valuable insights that can inform future responses.
- Setting a trigger. This is one of the most important parts of a threat hunt. Once a trigger is established, tracking searches for anomalies in the device or network. Any unusual behavior that’s triggered prompts teams to take further action.
- Investigating the threat. If any malicious activity is found, teams look further into the trouble and determine their next steps.
- Responding to the threat. At this point, the business’s emergency response plan should be rolled out to shut down any malicious activity, recover lost data, and patch security breaches.
Benefits of threat hunting
Taking a proactive stance toward cybersecurity is an organization’s best defense against criminals and the possibility of data loss. Threat hunting is also useful when it comes to:
- Improving threat response times. As teams actively monitor for threats around the clock, they can quickly catch and deal with any shady activity.
- Reducing risk to the business. All digitally-run companies take risks with their information, but threat hunting can curb many of these by continually looking for and acting on problems before they escalate. Instead of a business losing all its data, threat hunters can prevent attacks or shut them down before too much information is lost.
- Staying updated on the latest cyber threats. Proactive IT teams are more aware of current threats when they engage in threat hunting. Information and research is widely shared in cybersecurity communities, meaning teams stay updated on the most menacing activities.
Best practices for threat hunting
Organizations' threats are ever-changing, but establishing routines and best practices around threat hunting makes combating any cybersecurity issues much easier. Businesses should consider implementing best practices such as:
- Establishing what’s normal for the company. Determining a baseline is essential when setting up new investigative systems. This means teams see when activity outside the norm takes place, which triggers further action.
- Following a standard procedure. Many cybersecurity teams follow an effective workflow: observe, orient, decide, act (OODA). This naturally allows discussion and action to move swiftly when malicious activity arises.
- Providing sufficient staff and resources. Effective cybersecurity protections can only happen when IT teams feel adequately supported. Having the necessary staff on the team to manage threats and act when problems happen significantly improves response times. Resources are also important, so training and software must also be considered.
Protect your business from malicious activity and cyber criminals with risk-based vulnerability management software.

Holly Landis
Holly Landis is a freelance writer for G2. She also specializes in being a digital marketing consultant, focusing in on-page SEO, copy, and content writing. She works with SMEs and creative businesses that want to be more intentional with their digital strategies and grow organically on channels they own. As a Brit now living in the USA, you'll usually find her drinking copious amounts of tea in her cherished Anne Boleyn mug while watching endless reruns of Parks and Rec.