¿Qué es una copia de seguridad en línea?
Una copia de seguridad en línea, a veces llamada copia de seguridad en la nube, es un servicio en el que los datos se copian a una ubicación fuera del sitio o en la nube. El servicio almacena copias de datos en la nube para que estén disponibles en caso de una falla del sistema, desastre natural u otro evento que cause pérdida de datos. Las copias de seguridad en línea son una parte integral de un plan de recuperación ante desastres.
Algunas empresas utilizan software de almacenamiento de objetos para alojar información y archivos de objetos. Estos sistemas de software funcionan bien para datos no estructurados y diferentes tipos de archivos como correos electrónicos, archivos multimedia o páginas web.
¿Cómo funcionan las copias de seguridad en línea?
Una copia de seguridad en línea utiliza una conexión de red para enviar datos a un servidor basado en la nube. Los archivos de datos se cifran antes de llegar al servidor de copia de seguridad en línea. Este proceso ocurre automáticamente, y las empresas pueden elegir con qué frecuencia desean que se realicen las copias de seguridad automáticas. Una vez que todos los datos y archivos están almacenados en la nube, se pueden acceder desde cualquier lugar con una conexión a internet.
Beneficios de las copias de seguridad en línea
Una gran ventaja de las copias de seguridad en línea es que no se ven afectadas por desastres que dañan o arruinan la infraestructura de TI, como inundaciones o incendios. Otros beneficios clave de las copias de seguridad en línea incluyen los siguientes:
- Accesibilidad de datos. Siempre que tengan una conexión de red, una solución de copia de seguridad en línea da a los equipos acceso a sus datos en cualquier lugar, en cualquier momento. Las copias de seguridad en línea también ayudan a prevenir interrupciones en las operaciones y servicios.
- Seguridad mejorada. Muchas copias de seguridad en línea tienen funcionalidades de seguridad mejoradas que protegen los datos de posibles amenazas cibernéticas y físicas. Los servicios de copia de seguridad en línea pueden ser más seguros que los protocolos de la empresa, especialmente si se utiliza almacenamiento de datos físico como discos duros que pueden perderse o dañarse.
- Conveniencia para el equipo. La conveniencia de las copias de seguridad en línea permite a los equipos centrarse en su producto o servicio mientras un proveedor dedicado gestiona el proceso de copia de seguridad. Transferir la responsabilidad de gestionar y mantener las copias de seguridad puede liberar tiempo para que los miembros del equipo se concentren en otras necesidades y tareas sin la carga mental de preocuparse por las amenazas a los datos.
- Menos hardware. Las copias de seguridad en línea no requieren hardware, por lo que las empresas pueden ahorrar dinero y espacio en equipos adicionales. A menos que lo deseen, las empresas ya no necesitan otros servidores locales, discos duros o unidades flash para propósitos de copia de seguridad.
Desventajas de las copias de seguridad en línea
Como con todas las formas de tecnología, las copias de seguridad en línea tienen algunas desventajas potenciales que vale la pena entender. Las organizaciones deben ser conscientes de lo siguiente antes de proceder con las copias de seguridad en línea como parte de su plan de recuperación ante desastres:
- Requisitos de conexión a internet: Los sistemas y servicios de copia de seguridad en línea requieren una conexión a internet. Cuando los servicios de internet están caídos, los equipos pueden no poder acceder a sus archivos e información. Los problemas de internet pueden llevar a tiempos de inactividad costosos y tener un impacto negativo significativo en el negocio.
- Problemas potenciales de ancho de banda: Hacer copias de seguridad de grandes cantidades de datos requiere mucho ancho de banda. Una conexión a internet lenta dificulta la transferencia de datos debido a problemas de ancho de banda.
- Recuperación de datos que consume tiempo: Restaurar datos de una copia de seguridad en línea requiere tiempo, especialmente para grandes cantidades. Las empresas pueden experimentar una brecha en el acceso mientras se restauran los datos.
- Menos control: Los datos se mueven bajo la supervisión de un proveedor externo con copias de seguridad en línea. Antes de seleccionar un proveedor de copias de seguridad en línea, las organizaciones deben aprender tanto como sea posible sobre ellos y sus procesos de seguridad, protección de datos, equipos y acceso de control.
Mejores prácticas para copias de seguridad en línea
Los servicios de copia de seguridad en línea son una excelente opción para una estrategia de almacenamiento de copias de seguridad. En general, los equipos deben implementar estas mejores prácticas al usar este método:
- Programar copias de seguridad automáticas. Hacer copias de seguridad de datos de manera regular y frecuente asegura que los datos críticos no se pierdan. Las organizaciones deben identificar el mejor horario de copia de seguridad para sus necesidades y ejecutar copias de seguridad automáticas para proteger los datos.
- Cifrar datos. Las empresas deben entender sus opciones de cifrado y cómo su proveedor de servicios protege sus datos. Aunque el cifrado de datos generalmente está incluido en estos servicios, las organizaciones pueden ir un paso más allá utilizando métodos de cifrado en dispositivos como computadoras y teléfonos móviles.
- Combinar copias de seguridad en línea con copias de seguridad fuera de línea para una máxima efectividad. Aunque las copias de seguridad en línea son una excelente opción, no son perfectas. Una estrategia de copia de seguridad holística considera tanto las copias de seguridad en línea como fuera de línea para una protección óptima de los datos.
Copia de seguridad en línea vs. copia de seguridad fuera de línea
Las empresas utilizan copias de seguridad en línea y fuera de línea para maximizar la protección de datos.
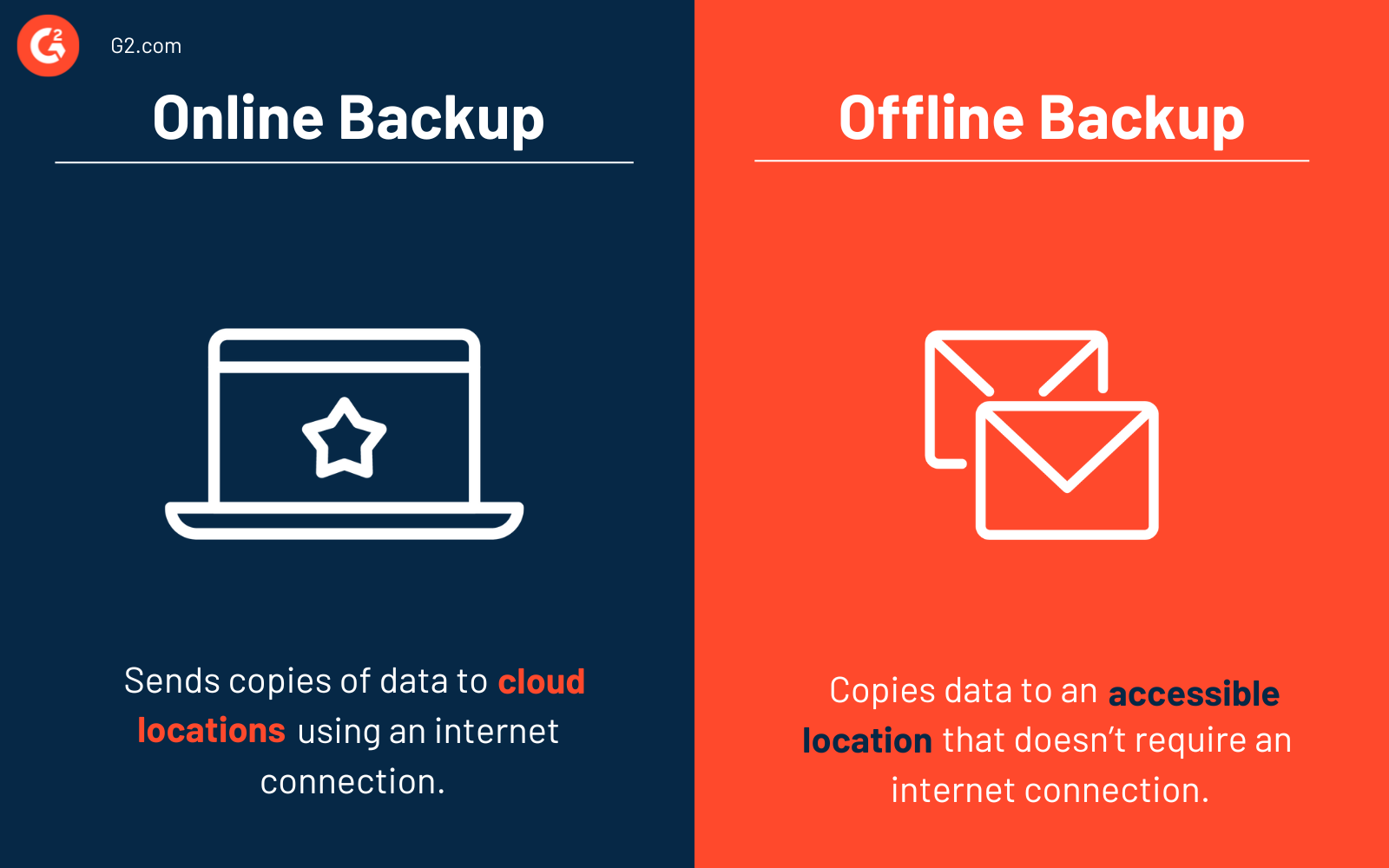
Una copia de seguridad en línea envía copias de datos a ubicaciones en la nube utilizando una conexión a internet. Las organizaciones pueden enviar archivos específicos o todo su sistema a la nube con servicios de copia de seguridad en línea. En la mayoría de los casos, los usuarios pagan una tarifa de suscripción para utilizarlos.
Una copia de seguridad fuera de línea copia datos a una ubicación accesible que no requiere una conexión a internet, como un hardware como un disco duro externo. Las copias de seguridad fuera de línea son transportables y necesitan un lugar de almacenamiento seguro.
Lee más sobre por qué las copias de seguridad son esenciales y qué buscar en una solución de copia de seguridad.

Alyssa Towns
Alyssa Towns works in communications and change management and is a freelance writer for G2. She mainly writes SaaS, productivity, and career-adjacent content. In her spare time, Alyssa is either enjoying a new restaurant with her husband, playing with her Bengal cats Yeti and Yowie, adventuring outdoors, or reading a book from her TBR list.