Classical computing has come a long way, from solving simple mathematical problems to using additional resources to solve highly complex tasks. However, the limitations of classical computing prevent it from solving the much more complex challenges the world faces today, and that's where quantum computing steps in.
Although not commercially available (on a large scale) currently, quantum computing is expected to change the world as we know it by bringing in the next generation of transformation to finance, medicine, encryption, artificial intelligence (AI), and numerous other fields.
From bit to qubit—the transition from classical to quantum computing
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is an area of computing that harnesses the use of quantum mechanics to solve highly complex problems much quicker than a classical computer.
In classical computing, which includes phones, laptops, and almost all other devices, information is stored in a binary format. This information exists as a bit, which is either 0 or 1.
In quantum computing, the information does not only stay in 0s and 1s but can also exist in between both bits simultaneously. Here, the basic unit of memory is not a bit but a quantum bit (qubit). A qubit is created by using a physical system (electrons or photons). Since these qubits essentially exist in an “in-between state”, they can be a part of several different arrangements all at once, which is known as quantum superposition. When different qubits are linked together, the process is known as quantum entanglement. Quantum superposition and entanglement together allow numerous qubits to represent different things at the same time.
Quantum computing was created to solve large and unstructured problems. It promises to solve complex tasks in a matter of a few minutes or hours, which would have taken a classical computer thousands of years. For example, in 2019, Google announced that it achieved “quantum supremacy” for the first time. Their 54-qubit Sycamore processor was able to perform a mathematical calculation in 200 seconds, which would have taken 10,000 years to complete on the world’s fastest supercomputer.
When talking about the science behind quantum computing, it's important to note that the state that a qubit exists in is extremely sensitive, and any interference could cause the qubit to lose its state. For example, quantum computers are extremely sensitive to heat. Air molecule collisions could cause a qubit to lose its quantum properties and settle back as 1 or 0. This is known as quantum decoherence.
Quantum decoherence could cause the entire system to crash.
Preventing crash due to quantum decoherence
To ensure systems don't crash, most quantum computers are kept in cold weather, almost near absolute zero (0 Kelvin) to ensure they stay in the quantum state. To put this in perspective, 0 Kelvin is -459.67°F, and the coldest temperature ever recorded on Earth was -135.8°F in Antarctica; this means even the world itself is not cold enough to support quantum computers!
How will quantum computing impact businesses?
As companies inch closer toward commercializing quantum computing products, it becomes increasingly important to identify the various applications that will benefit from it. Quantum computing can be used for numerous applications to solve complex problems that cannot be done efficiently on a classical computer. These problems could be across any number of areas, such as supply chain and logistics, AI and machine learning, finance, cryptography, healthcare, cybersecurity, traffic optimization, weather forecasting, energy utilization, and so on.
The limits of quantum computing are boundless once both hardware and software challenges toward implementation are solved. The key challenge is to ensure that qubits maintain their state of superposition unaffected by external influences such as heat or vibrations.
Although there are many industries, there are a couple of recurrent themes that pop up when we discuss quantum computing—optimization and research. Here is a list of applications that quantum computing could improve drastically or solve:
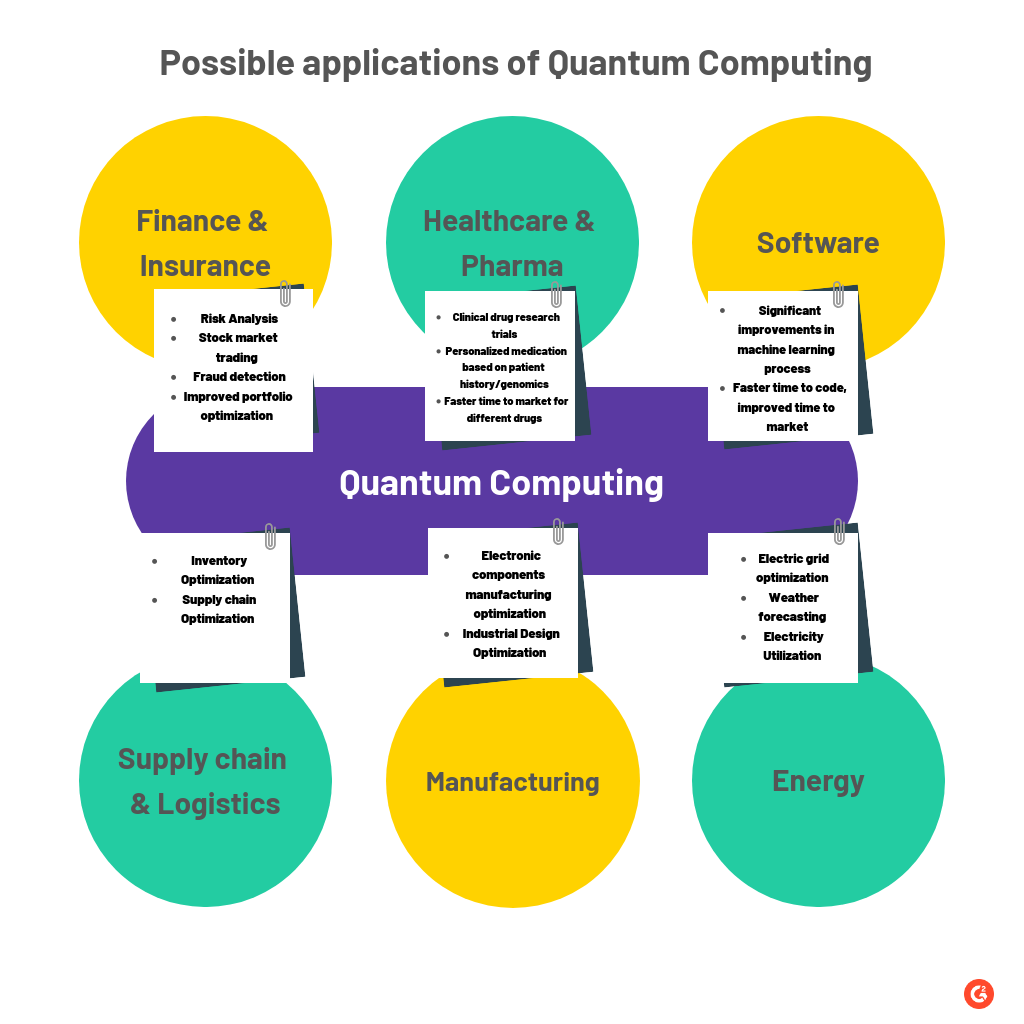
Let's talk about a couple of key areas in detail:
Drug discovery and research: Healthcare has been at the forefront as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Companies are now spending billions of dollars on drug discovery and research and development in the medical field, running vaccination trials, conducting new drug research, studying molecular biology, and other healthcare fields.
Quantum computing could help shorten clinical trials that take months or years significantly since all the data would be processed and simulated at a much faster pace. This could mean shorter time for drugs to reach the market, shorter drug approval times, and shorter simulations. In recognition of this new quantum future, healthcare companies are investing in quantum computing. For example, in January 2021, Boehringer Ingelheim, a major healthcare company, announced that the firm has entered into a collaborative agreement with Google Quantum AI to focus and develop on researching quantum computing in pharmaceutical research.
Financial sector: One of the biggest areas where quantum computing is expected to make great strides is in the financial sector, specifically within customer targeting, prediction analysis, risk profiling, and trading in financial instruments or markets. Quantum computing is expected to drastically improve the Monte Carlo simulation methods. Monte Carlo simulation is a mathematical technique where researchers or experimenters can consider risk factors when making decisions. It provides a range of possible factors or outcomes based on the variables given.
Quantum computing can make these simulations significantly faster, helping companies come to much faster decisions and analyze complex data. Financial heavyweights such as Barclays and JPMorgan were some of the first firms in the world to tap into quantum computing for the financial sector by collaborating with IBM on its IBM Q network back in 2017.
AI and machine learning: AI and machine learning have made great strides across all industries. The technology is at the forefront of numerous areas right now such as manufacturing, robotics, and app development, and will change the course of life as we know it. Tasks such as image recognition, voice and video recognition, making predictions, fraud detection, and others are all being handled by AI and machine learning in the background.
As the number of applications increases, so does the amount of data. Having a ton of data is a good thing, but not knowing how to use this data presents a significant challenge. It is very hard for traditional computers to keep up with the operational and processing needs of this data, which needs to be highly accurate as well as work at high speeds.
This is where quantum computing could come in. Complex AI and machine learning problems could be solved in hours instead of years! Investments in the space have begun picking up pace too. In June 2021, computer scientists led by ETH Zurich began conducting an early exploration for reliable quantum computing-driven machine learning.
Latest innovations in the quantum computing space
The quantum computing space (both hardware and software) has seen several investments in the last couple of years. Companies such as Google, IBM, D-Wave Systems have released their own versions of quantum computers both as hardware or on the cloud, but these are still under scrutinous reviews to determine whether or not they can be called a true “quantum computer”.
Firms across the globe have recognized the amazing potential of quantum computing and that recognition has manifested as a significant spike in investments.
Some of the key investments in the last year have been listed below:
.png)
| September 2020 |
|
| October 2020 |
|
| December 2020 |
|
| January 2021 |
|
| May 2021 |
|
| June 2021 |
|
| July 2021 |
|
The growth of quantum cloud service
The hardware for developing quantum computers is a challenge, delaying its commercialization on a large scale. The massive energy requirements along with design and developmental issues to ensure quantum computers are kept stable at sub-zero temperatures are complex and expensive.
To overcome this, quantum computing vendors are looking at the cloud to bring quantum computing to a bigger audience. One of the key trends we observe in the quantum computing space is the interest surrounding quantum cloud service.
In quantum cloud service, as the name suggests, app developers and scientists can build hybrid quantum applications and observe practical impacts. The software enables the person to access quantum services over a cloud computing platform. D-Wave Systems, a key vendor in the quantum computing space announced the release of Leap 2, which is a quantum cloud service. The software allows users to solve problems that have up to 10,000 variables. Since quantum cloud services are primarily focused on developers at present, it supports a prebuilt, ready-to-code integrated development environment (IDE) in the cloud.
| Read more: What is an IDE (Integrated Development Environment)? → |
The era of quantum computing nears
As more companies realize the possible benefits of quantum computing once it is commercialized at scale, the investments continue to grow. Crossing the physical barriers is the first and biggest challenge that lies ahead for quantum computer researchers. Several firms such as IBM, Google, Microsoft, and numerous medium-sized firms are making huge inroads into the field of quantum computing to ensure that quantum computing is more a reality than a myth in the next decade.
Edited by Sinchana Mistry
Want to learn more about Integrated Development Environments (IDE)? Explore Integrated Development Environments (IDE) products.

Preethica Furtado
Preethica is a Market Research Manager and Senior Market Research Analyst at G2 focused on the data and cloud management space. Prior to joining G2, Preethica spent three years in market research for enterprise systems, cloud forecasting, and workstations. She has written research reports for both the semiconductor and telecommunication industries. Her interest in technology led her to combine that with building a challenging career. She enjoys reading, writing blogs and poems, and traveling in her free time.
