Any alarming sound from your machinery may also be alarming for your bank account.
Unexpected breakdowns not only increase maintenance costs and machine downtime but may also lead to gaps in service. Maintenance is crucial to handling any machinery and ensuring continued operations. Proactively addressing issues before they cause losses should top your to-do list.
With technological advancement, we now have access to tools that work as a magic 8-ball to give you insights into machine health and the need for repair. One such tool is predictive maintenance software. Manufacturers are increasingly opting for this asset maintenance platform to avoid breakdowns, both machinery and mental.
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a proactive asset maintenance strategy. The practice uses sensor data and machine learning (ML) to identify maintenance needs and prevent equipment failure.
Predictive maintenance solutions aim to reduce downtime and maintenance costs to prolong the serviceable life of the equipment.
Read on to learn more about predictive maintenance and how it may be a boon for you in the manufacturing industry.
Importance of predictive maintenance in manufacturing
Predictive maintenance technology saves the manufacturer's time, resources, and cost, minimizes work hazards, and ensures a better return on investment (ROI). The upfront cost may seem high until increased production, reduced downtime, and cost savings quickly recover the initial investment.
Let’s take a closer look at how a predictive maintenance strategy provides a positive ROI for manufacturers.
Predictive maintenance and ROI
Below is a representation of ROI experienced by manufacturers since implementing PdM techniques, as recorded by the Manufacturers Alliance Foundation and Advanced Technologies Services, Inc., surveying 170 leaders in the manufacturing domain.
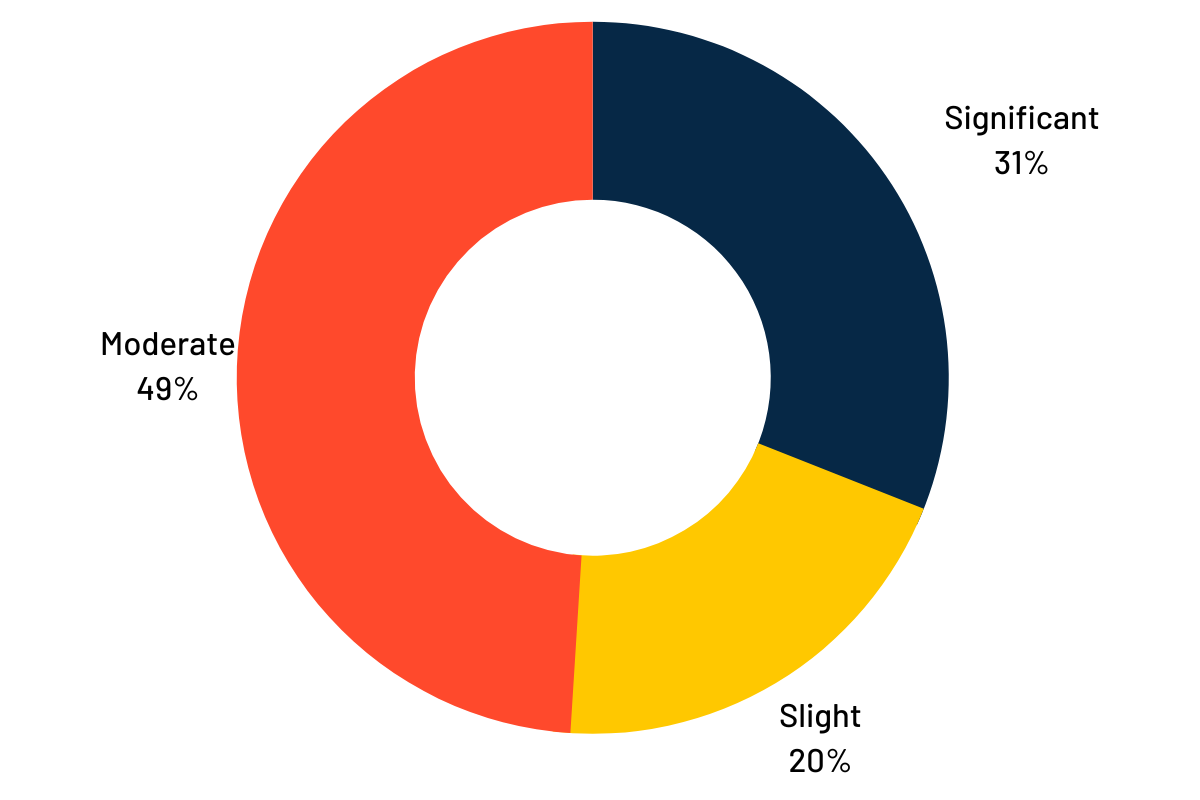
ROI post-PdM implementation
Source: Manufacturers Alliance
Industries with heavy reliability on equipment for operations can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs using predictive maintenance technology, which further converts to positive ROI. Not only that, but the Senseye Predictive Maintenance report estimates that by adopting PdM practices, The Fortune Global 500 industrial organizations could:
- Save 1.6 million hours of downtime annually.
- Save $734 billion with a 6% productivity improvement.
- Save $236 billion through a 40% reduction in maintenance costs.
Did you know? In certain sectors, unplanned downtime can cost up to $2 million an hour.
In addition to all the benefits mentioned above, the PdM strategy also saves on maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) inventory. Since machine parts only require replacement when critical, keeping stock is unnecessary, reducing overhead.
Although the exact ROI depends on the complexity of machines, the scale of operations, and current spending on maintenance, PdM generally shows significant investment returns over time.
¿Quieres aprender más sobre Software de Mantenimiento Predictivo? Explora los productos de Mantenimiento Predictivo.
How does predictive maintenance work?
Predictive maintenance tools use data analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and oddities indicating equipment failure. The three basic steps followed through the process are data collection, mining, and calculation.
- Data collection: In the first step, sensor installation takes place. The goal is to collect a large set of quality data, including real-time analysis, historical data, and other relevant data points, to compare any deviations in real-time machine performance. Data collection uses various techniques to measure different aspects of the machine, like temperature, vibrations, and emissions.
- Data mining: The next step is making sense of the collected data. Here's where the Internet of Things (IoT) comes in handy. It allows the sensors to send all the information to a central system so you can interpret the data to see what's happening. To make this work, the ML models identify trends and set ideal parameters for typical equipment performance. Upon determining any deviation from the specified parameters in real-time data, the system automatically alerts the supervising personnel to perform maintenance before failure occurs.
- Calculation: The calculation part predetermines each asset's failure period through automated data analysis. This step builds and applies algorithms that offer a prognosis for different assets. Using the analysis to schedule maintenance makes the whole process more time and cost-effective.
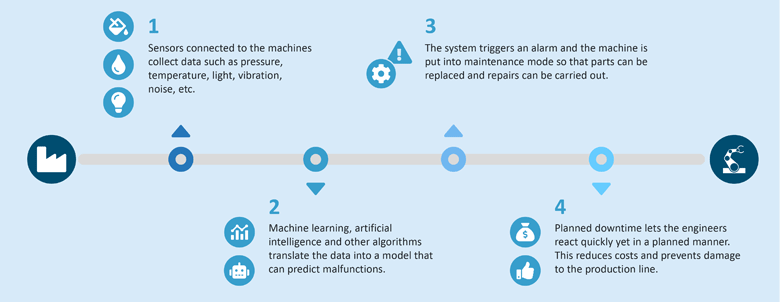
Source: Seeburger blog
History of predictive maintenance
The maintenance history takes us back to the first industrial revolution. Back then, maintenance procedures were purely reactive. You might have also heard this method described as corrective or emergency maintenance. Whatever the name, it means no one fixed anything until it was broken, which was inefficient and costly, and consumers often had to wait a long time to receive the products because of machine failure.
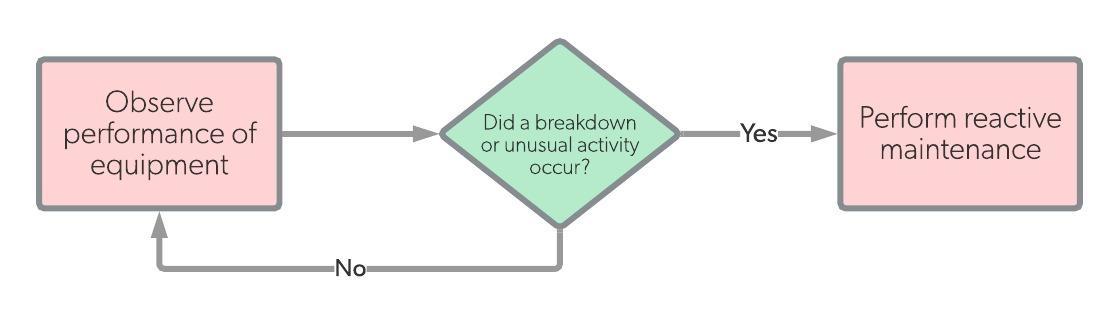
Source: UpKeep
The preventive maintenance (PM) or planned maintenance strategy came with the second industrial revolution and increased production. Maintenance of machines grew more prominent, and inspections became regular regardless of the machine's condition.
The third industrial revolution and the conclusion of World War II brought productive maintenance, an approach that combined corrective and preventive. It used a data-driven approach to identify and address the cause of breakdowns, such as misalignment or contamination. The third industrial revolution also gave rise to two other concepts: reliability centered maintenance (RCM) and total productive maintenance (TPM).
Predictive maintenance was born with the start of the fourth industrial revolution and technological advancement. Equipment is now monitored in real-time using sensors and sophisticated technologies like IoT. Data comes from multiple sources to make it easier to predict issues. This approach is more cost and time-efficient than the previous maintenance strategies.
Predictive maintenance technologies
Predictive maintenance relies on various technologies to collect and analyze data. Maintenance teams use the following condition-monitoring techniques to detect any irregularities in a device's performance.
1. Vibration analysis
This technology detects abnormal vibrations or frequencies of machinery that could point to possible issues with lubrication, loose components, or misalignment. The data is fed into a collector and analyzed as a time wave (amplitude vs. time), fast fourier transform (amplitude vs. frequency), or both.
Although a hand-held accelerometer can also do the job, sensors are preferred for measuring vibrations. A mounted sensor registers a higher measurable frequency and is better calibrated, offering more accurate long-term monitoring results.
2. Infrared thermology
The infrared analysis detects energy released from the equipment, converts it to temperature, and compares temperature readings over time. As an asset becomes worn out, the machine releases more energy than usual, resulting in higher temperature readings. The infrared images obtained show higher temperatures as "hotspots."
3. Oil analysis
As the name suggests, oil analysis compares machine oil with baseline or new equipment oil to look for differences. It examines impurities (water, metal bits, other liquid particles, and contaminants), debris components, and oil composition. Any impurity in the oil could mean the equipment is tattering or even leaking.
4. Acoustic monitoring
Acoustic monitoring utilizes sensors to detect any abnormality in the sound produced by components of a machine rubbing together. The sensors detect these high pitch sounds and transform them into visual elements. However, this technique requires a noise-free background to work optimally.
5. Emission monitoring
Emission monitoring looks for an abnormally high percentage of pollutants (carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides) emitting from the equipment's exhaust. Excess pollutants could indicate defects like faulty fuel and ignition system defects.
Predictive maintenance vs. preventive maintenance vs. condition-based maintenance
We learned a bit about the different maintenance techniques used in the past. Let’s dive deeper into the differences between predictive maintenance and other technologies.
Predictive maintenance vs. preventive maintenance
Unlike reactive maintenance, preventive maintenance is also a proactive maintenance strategy independent of machine failure. Predictive and preventive maintenance are similar in correcting abnormalities before a machine breaks down. However, PdM uses sensors and ML to predict failures just before the device could break down. In contrast, PM is scheduled in set intervals regardless of any signs of machine failure.
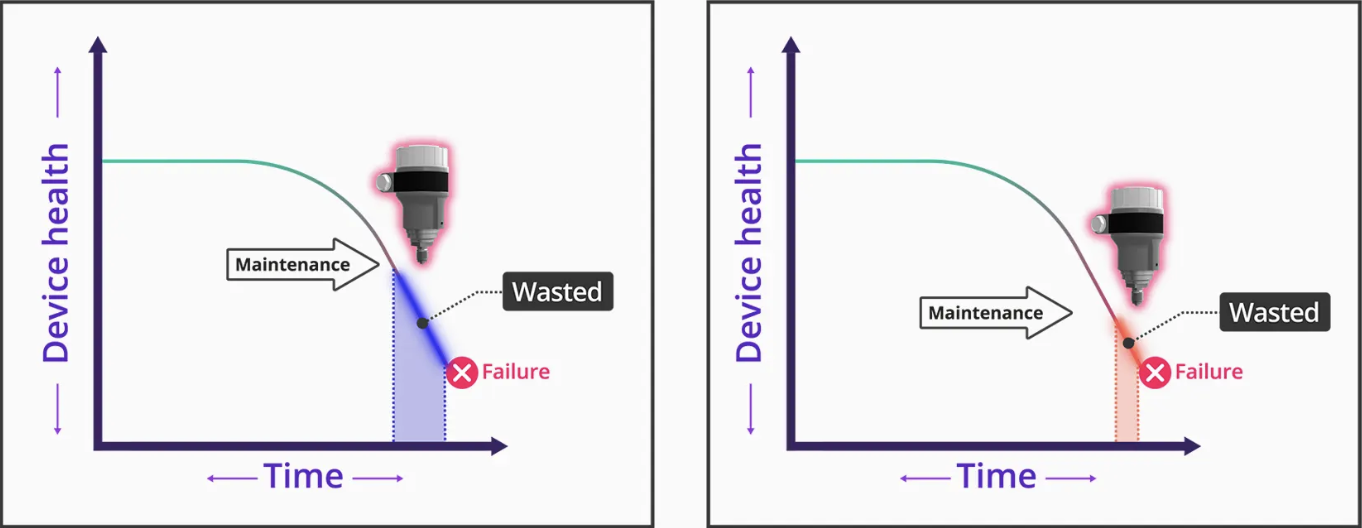
Preventive maintenance Predictive maintenance
Source: RealPars
Although preventive maintenance has a much lower upfront payment, unnecessary maintenance schedules could put money down the drain in the long term.
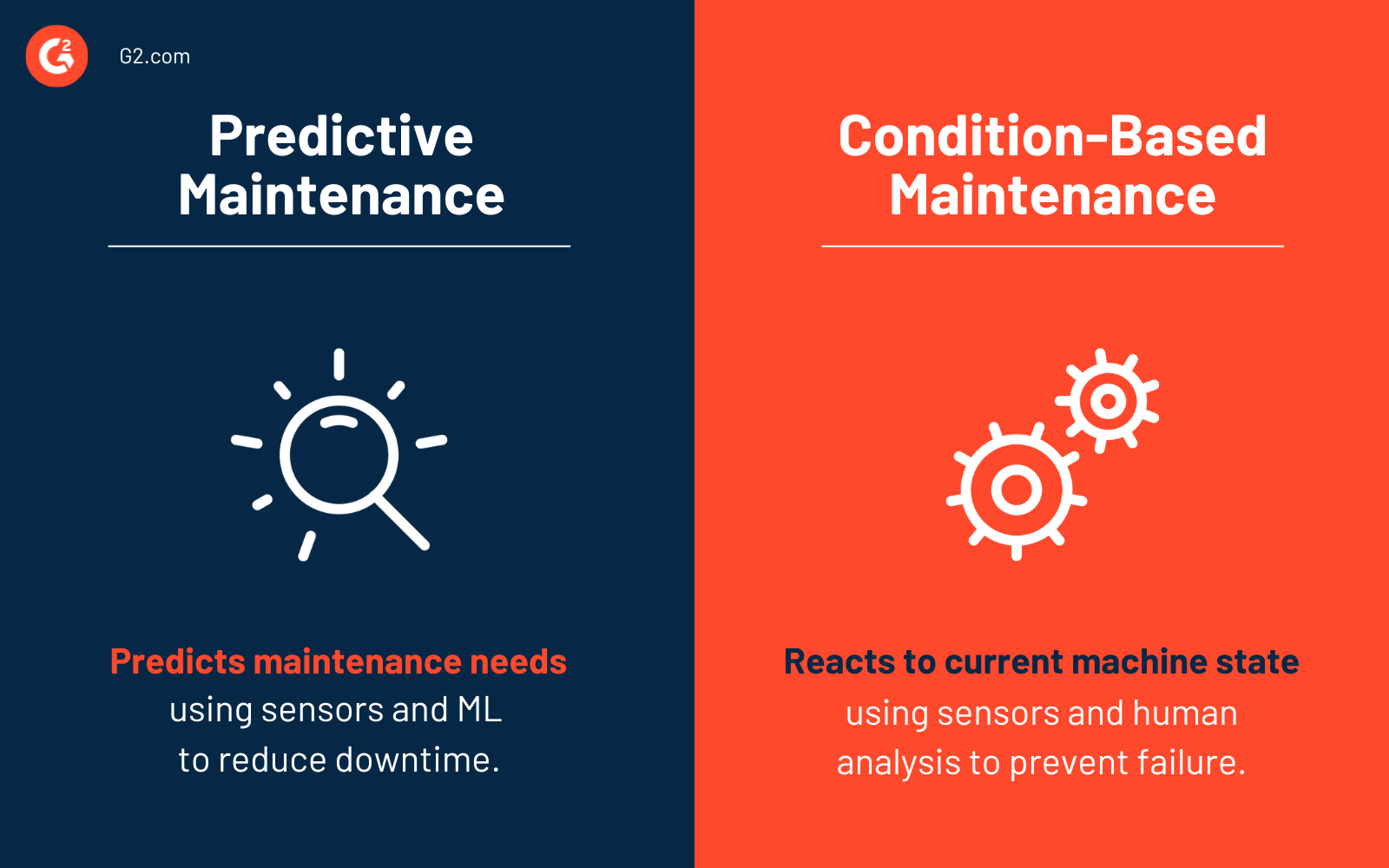
Predictive maintenance vs. condition-based maintenance
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) uses sensors to detect tangents in the machine’s optimal performance and health, but the analysis part is wildly different in the two scenarios.
CBM employs a human workforce to analyze the information sensors collect and perform corrections accordingly. The maintenance team uses upper and lower limits to look for deviations in asset performance. Condition-based maintenance doesn’t predict future failures but points out current problems in the machine.
Since human resources conduct the data analysis part, the only upfront cost here is the sensors, which makes it cheaper than predicate maintenance. However, the manual method of analysis is also susceptible to error.
How to implement predictive maintenance
Implementing a PdM strategy is a substantial investment. To begin with, you need to identify critical assets that are vital to your operations. Highlight equipment with the highest repair cost using breakdown and root cause analysis (RCA) reports. This step gives you a clear understanding of your ROI post-PdM implementation.
The next step is a critical one: train your staff. A well-informed crew ensures the protocol stays effective. Educate your team about the new tools to quickly identify maintenance alerts and efficiently maintain and repair IoT tools.
Once you're through these two basic actions, establish baselines. These baselines are set based on optimal machine performance, and the PdM system compares equipment readings to these acceptable limits. Any deviation from the baseline is a trigger to schedule maintenance.
Next, identify suitable condition monitoring devices and sensors according to your requirements and install IoT devices. For example, connecting a temperature sensor to the boiler.
Once installed, connect your IoT devices to asset management software, like predictive maintenance software or a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS). This step provides a remote dashboard for maintenance engineers to monitor and analyze data regularly.
Lastly, schedule maintenance. Inspection processes are automatically triggered by predictive maintenance software when a machine crosses the predetermined conditions or the maintenance team schedules a manual inspection.
Predictive maintenance in the field
Suppose you own a ready-to-drink powder mix company and you implement a predictive maintenance strategy. The PdM approach helps you prevent waste, assure good quality products, and avoid unplanned downtime or late deliveries.
You start by setting baselines and using sensors in critical machines like mixers, where vibration analysis is a viable option. In case of any problems like misaligned blades, automated examination and analysis will trigger an inspection for the repair crew.
So by early detection and timely repairing, you avoid production losses and high maintenance costs.
Predictive maintenance case study: Frito-Lay
When they wanted to implement predictive maintenance in four of their manufacturing plants, Frito-Lay, a subsidiary of PepsiCo, collaborated with Augury, a tech startup focused on machine health solutions and condition analytics. The results definitely speak in favor of the PdM program.
According to Anna Farberov, general manager of PepsiCo Labs, the technology helped Frito-Lay add about 4,000 hours of manufacturing capacity annually and save over one million pounds of food due to unexpected downtime. She added that the program had reduced unexpected breakdowns and lessened incremental costs for replacement.
As a result, PepsiCo intends to implement the technology in most US Frito-Lay plants and other facilities.
Predictive maintenance use cases
Predictive maintenance is an excellent tool for manufacturers, but it also helps businesses across several different verticals and domains better manage and maintain their assets. Some common use cases excluding manufacturing include:
- Supply chain management. Using predictive maintenance tools to define the offline time for machines or potential disruptions in operations helps supply chain operators plan things accordingly.
- Healthcare. Ensuring that all vital medical instruments perform at their best is paramount. Predictive maintenance alerts the hospital staff whenever any deviation occurs in X-ray systems, MRI machines, or ventilators. By continuously analyzing this data, critical and fatal failures can be avoided.
- Government agencies. The military is another department that needs all its equipment performing at its peak. Using predictive maintenance techniques, officials can maintain the assets at their best and foresee any demand for military equipment like aircraft or weapon systems.
- Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs): OEMs can offer predictive maintenance as a service by collecting data from equipment and providing customized insights and maintenance schedules to individual customers.
Benefits of predictive maintenance
Over time, the manufacturing industry has undergone a transformational journey. The processes have become more sophisticated and efficient, leading to growth in production, lower product pricing, higher product quality, and waste reduction.
To match the consumer demand, manufacturers need to step up their game. Keeping up with the trends and embracing technology is the only way to stay competitive in the fast-paced world. Implementing predictive maintenance minimizes downtime, cuts operational costs, boosts productivity, and ensures the safety of people working with the machinery. A PdM strategy keeps the machines and manufacturers one step ahead of potential setbacks.
- Reduced downtime. By detecting potential problems beforehand, manufacturers proactively address any maintenance issues. It minimizes the time equipment is out of service, increasing production and productivity.
- Increased efficiency. Manufacturers effectively maximize output by taking corrective actions for any possible problems and ensuring the smooth running of equipment.
- Improved safety. A malfunctioning due to irregular maintenance of machines poses a danger to workers. Manufacturers significantly reduce the risk of accidents or injuries by guaranteeing the proper functioning of machinery.
- Lower maintenance cost. Manufacturers reduce the risk of expensive emergency repairs and replacements by making sure equipment is serviced at the right time.
- Longer equipment life. Proper maintenance extends the equipment's life span, which ultimately helps manufacturers get more value for their money and equipment.
Challenges of predictive maintenance
Although PdM is a killer strategy with many benefits, manufacturers must address certain implementation challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for the success of a predictive maintenance program.
- High costs. Implementing a PdM program requires significant investment in technology, data science expertise, and data collection. Manufacturers should consider the cost-benefit tradeoff to ensure the benefits outweigh the cost.
- Data quality. Manufacturers rely on the accuracy and quality of data. However, data corruption from disconnected or dead sensors and out-of-date databases leads to incorrect predictions and unreliable maintenance schedules.
- Implementation time. A successful PdM program depends on multiple aspects, such as sensor and other resources availability, the complexity of equipment, the training period, and the amount of data required for analysis. Coordinating and implementing these steps while minimizing disruption to ongoing operations is complex and time-consuming.
- Analytical expertise. The business requires an in-house data science team, advanced analytics, and machine learning experts to extract actionable insights from the data. The right team can accurately decipher the results and implement predictive models based on the readings. Organizations may face challenges finding the right talent or training the team.
- Data management. Predictive maintenance protocols require large amounts of data from various sources, including sensors, equipment logs, and maintenance records. Handling this large quantity of data is difficult. To avoid loss or mismanagement of data, manufacturers need a robust data management system that helps store mixed data and provides fast and reliable access to it.
Predictive maintenance best practices
Implementing a PdM strategy requires careful planning and execution. Following certain best practices ensures you get value for your money and set up the program for success. Adhering to these best practices improves equipment reliability and increases overall operational efficiency.
- Start small. PdM implementation is an extensive project. Start small by selecting one or two critical pieces of equipment before going full-fledged with the program. This strategy gives you insight into the performance and effectiveness of PdM so you can make changes as required.
- Specify the required resources. Determine all the resources you need to successfully implement predictive maintenance, from sensors to technicians to data analytics experts.
- Collect data. Collect lots of data from previous maintenance logs, repair histories, and IoT sensor readings to get a solid foundation for the entire PdM program.
- Monitor results. To get more accurate results and better predictions, frequently review and update your approach and optimize factors such as baselines. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify areas of improvement and the effectiveness of your program.
- Improve as you go. As with anything else, analyze the data to improve your process. With the accumulation of more high-quality data and the development of better algorithms, it’ll be easier to set up a program that produces better results in terms of saving time and money.
Some manufacturing KPIs to track:
- Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
- Downtime
- Uptime
- Labor cost
- Lead time to customers
Future in manufacturing
The future of predictive maintenance in manufacturing is very promising. According to a report by Statista, the global predictive maintenance market is expected to reach about 64.3 billion U.S. dollars by 2030. As the technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence continue to evolve, you can only imagine how efficient maintenance will become.
An impact we’re likely to see is greater interconnectivity between different systems for enhanced asset management. Modern CMMS and PdM software integrate with various business management software like enterprise resource planning (ERP). It allows for a holistic view of overall operations from production to maintenance.
Prescriptive maintenance, or RxM, is another by-product of technological advancement that takes predictive maintenance one step further. Prescriptive maintenance uses advanced machine learning algorithms to suggest the best course of action for a possible issue, enabling manufacturers to significantly reduce operational risks significantly.
Also, increased use of technologies like digital twin that generate a virtual replica of the physical equipment, along with immersive experiences like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and extended reality (XR) will let manufacturers efficiently monitor the actual working condition of the machine and accelerate diagnostics.
Best predictive maintenance software
Preventing is better than cure, and prediction is a step toward taking the proper preventive measures.
Promoting asset maintenance from reactive to predictive eliminates the risk of being caught in an ugly situation. With data-driven insights and a glimpse into the future provided by predictive maintenance tools, you can make informed decisions about asset maintenance and keep your machinery working at its full potential. Cost savings, profit, and productivity are a plus.
To be included in the predictive maintenance category, a product must:
- Offer real-time condition monitoring data
- Identify and predict issues before they disrupt asset performance
- Set condition-based maintenance plans
- Detect possible failures using big data and IoT sensors
- Provide directions for the optimization of asset performance
* Below are the top 5 leading predictive maintenance software from G2’s Spring 2023 Grid® Report. Some reviews may be edited for clarity.
1. Limble CMMS
Manage your maintenance operations better with Limble CMMS. The software makes it easy for you to install sensors and inexpensively test if the maintenance approach works for you. Some features include automated maintenance scheduling, interactive standard operating procedure checklist, depreciation schedules, plug-and-play setup, and instant alerts.
What users like best:
“I love Limble because it allows me to bring a whole new level of organization to my company. Even though I have never used this kind of software before, the videos provided made it super easy to learn and optimize how I use it daily. I can manage my time and organize our workload.”
- Limble CMMS Review, David S.
What users dislike:
“The reports are far from perfect. All the information is there and easily found. The part that needs updating is how the information prints out. I need a report that I can submit to the stakeholders without exporting and manipulating in MS Excel.”
- Limble CMMS Review, David C.
2. Fracttal One
Fracttal One is a mobile-first platform available on Google Play or App Store. It’s a cloud-based, versatile software that caters to organizations of different sizes across industries. Use it to collect, track and analyze critical data related to the conditions of your assets. It works on a monthly subscription basis, charged according to the chosen plan.
What the users like best:
“Fracttal One is a dynamic, flexible, intuitive, and user-friendly software. It allows you to keep records and control all activities and can also be integrated with external applications to improve its potential. It has a fairly broad and flexible categorization for all assets, making the search easier.”
- Fracttal One Review, Jean Pierre Joel C.
What users dislike:
“My main issue is that you need to invest more time setting up your assets, lists, materials, suppliers, and locations. I suggest having some pre-configured templates on good practices so you can start using the app sooner by making some adjustments or customizations.”
- Fracttal One Review, Ian P.
3. Fiix
Fiix is a CMMS with several valuable tools for asset management, work order management, analytics, and reporting. A stand-out feature is mobile maintenance, which allows users to look into machine health, from anywhere, at any time, without an internet connection. Fiix also provides users with training for setup.
What the users like best:
“The program is very easy to use. Utilizing the work orders is so simple my mechanics truly appreciate this. I also love how Fiix continues to evolve and add new product features!”
- Fiix Review, Jeff P.
What users dislike:
“One of my biggest pet peeves with Fiix is making purchase orders. You cannot make a change without canceling and reinstating the order, even if it is not approved.”
- Fiix Review, Sheldon T.
4. eMaint CMMS
eMaint CMMS has features like work order management, asset management, inventory management, and preventive management to help businesses better control their assets. eMaint is also scalable and you can customize it per your organization's needs.
What the users like best:
“eMaint has something for everyone's business, whether it's keeping track of inventory, labor hours, or parts for your assets. Interactive maps make it easy for all levels of computer users to utilize.”
- eMaint CMMS Review, Scott V.
What users dislike:
“I dislike the lack of mobility and communication within eMaint. You can set up workflows to notify people of updates, but then all communications get left out of the system. Lack of mobility inhibits floor personnel from using the system. Technicians end up waiting until breaks or other periods to update the system rather than having a great user interface that allows them to complete what they need in a flash. I also dislike the long development timelines. Major improvements or bug resolutions can sometimes take a few months.”
- eMaint CMMS Review, Logan E.
5. L2L Smart Manufacturing Platform
L2L Smart Manufacturing Platform is a solution designed to “empower frontline workers.” The cloud-based software offers real-time data collection and collaboration, quick access to manuals and spare history, escalation notification on delays, and project management. L2L also has multiple resources on its website, like case studies, eBooks, and training guides for smoother onboarding.
What the users like best:
“The documentation is extensive. The support team is quick and will help you figure things out or even pass it along to their developers if necessary. The power of APIs allows me to do more than just integrations; I can develop custom features and functions, expanding the baseline functionality and feature set.”
- L2L Smart Manufacturing Platform Review, Justin F.
What users dislike:
“The overall flow of some of the screens could be a little more streamlined to make it a little easier to navigate.”
- L2L Smart Manufacturing Platform Review, James P.
A magic 8 ball for your machinery
Having a fully-functioning predictive maintenance program is like accessing your machine's fortune. It’s a revolutionary approach for manufacturers, transforming the maintenance discipline, one machine at a time.
By harnessing the power of PdM strategy, manufacturers can use advanced analytics and data-driven insights to look into the good and the bad. The good thing is that the bad outcomes are easily reversible by scheduling timely maintenance. If your goal is to maximize the equipment's lifetime and uptime and drastically reduce the maintenance cost, give predictive maintenance a chance.
Ready to take your manufacturing game to the next level? Learn how a manufacturing execution system (MES) helps you optimize production output for productivity and profits.

Harshita Tewari
Harshita is a Content Marketing Specialist at G2. She holds a Master’s degree in Biotechnology and has worked in the sales and marketing sector for food tech and travel startups. Currently, she specializes in writing content for the ERP persona, covering topics like energy management, IP management, process ERP, and vendor management. In her free time, she can be found snuggled up with her pets, writing poetry, or in the middle of a Netflix binge.