Die Legitimität von Transaktionen gewährleistet die Integrität eines Finanzsystems. Deshalb untersuchen Banken und andere Kreditinstitute betrügerische Aktivitäten sorgfältig. Aber was passiert, wenn Peer-to-Peer-Kryptowährungstransaktionen dasselbe durchlaufen? Niemand schützt Ihre Interessen, und es gibt keine Bank, die Gelder schützt.
Betreten Sie die Welt der Kryptowährung und des Bitcoin-Minings.

Bitcoin-Mining ist der Prozess der Erstellung und Hinzufügung neuer Bitcoins zum dezentralen Bitcoin-Blockchain-Ledger, nachdem Bitcoin-Transaktionen validiert und bestätigt wurden. Bitcoin-Miner verlassen sich auf ausgeklügelte Hardware, um komplexe kryptografische Hash-Gleichungen zu lösen und den nächsten Bitcoin-Block zu finden. Miner, die den Block zuerst finden, erhalten Bitcoin-Belohnungen, daher der Name Bitcoin-Mining.
Kryptowährungs-Mining-Software ermöglicht es Minern, Transaktionen zu einem verteilten Ledger hinzuzufügen, nachdem sie in einem Blockchain-Netzwerk validiert wurden. Eine Blockchain enthält zeitgestempelte Aufzeichnungen aller vorherigen und nachfolgenden Transaktionen. Miner verwenden Knoten oder Mining-Maschinen oder -Rigs, um diese Transaktionen zu validieren und Mining-Belohnungen für ihre Rechenleistung zu erhalten.
Was ist Krypto-Mining?
Kryptowährungs-Mining oder Krypto-Mining ist ein Transaktionsprozess, der neue Kryptowährungen erstellt. Es validiert und zeichnet auch Krypto-Transaktionsdaten auf einer Blockchain auf. Miner erhalten Mining-Belohnungen wie Transaktionsgebühren und neu erstellte Kryptowährungen aufgrund des Minings von Krypto mit intensiven Rechenressourcen und anderen kryptografischen Mitteln.
Der Prozess der Erstellung von Krypto-Münzen und der Validierung von Transaktionen ähnelt dem Prozess der Goldgewinnung und -zirkulation, daher der Name 'Mining'.
Stellen Sie sich Kryptowährungen als nur-anhängbare öffentliche Ledger vor. Menschen fügen Seiten oder Blöcke zu einem Ledger hinzu. Die Methode, den nächsten Block hinzuzufügen, ist das Mining.
Wie funktioniert Krypto-Mining?
Krypto-Mining dreht sich um Miner, die die Legitimität von Transaktionen überprüfen und Kryptowährung als Belohnung verdienen. Das Verständnis von wie Blockchain funktioniert ist entscheidend, um die Technologien und Prozesse hinter dem Kryptowährungs-Mining zu erlernen.
Kryptowährung und Blockchain
Nehmen Sie eine beliebige traditionelle Kryptowährung, und Sie werden sehen, dass sie ein dezentrales Ledger verwendet, auch bekannt als Blockchain. Die verketteten Datenblöcke in einer Blockchain enthalten Schlüsseldaten und kryptografische Hashes. Diese Blöcke repräsentieren Datentransaktionen, die Miner am Ende eines Ledgers hinzufügen.
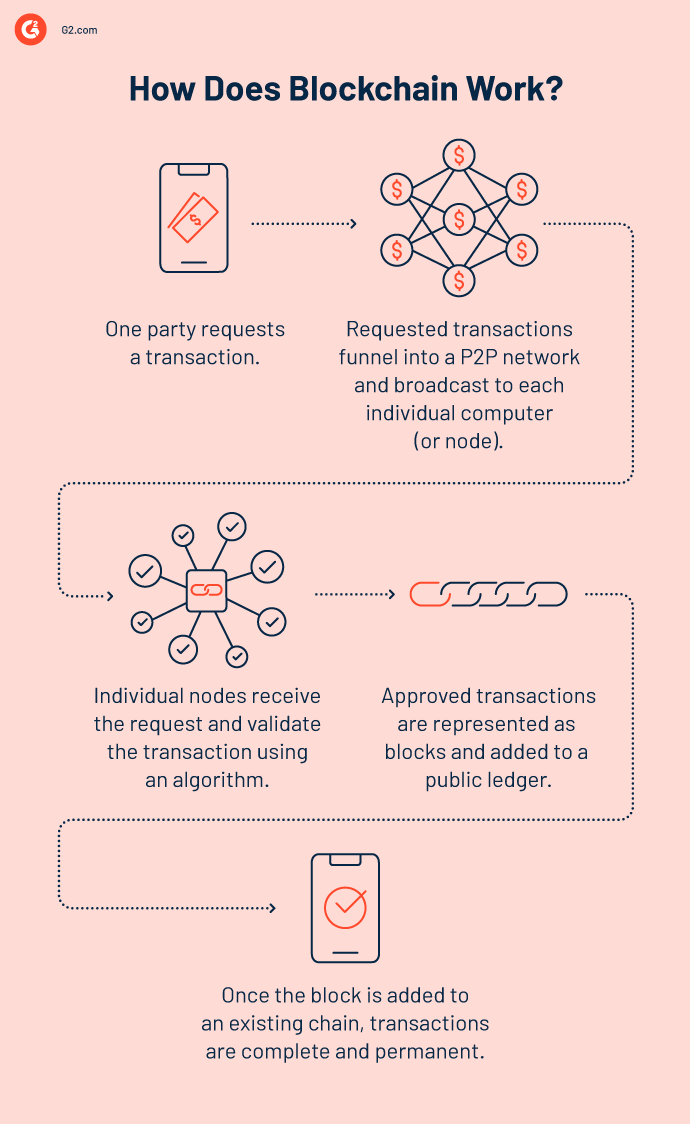
Krypto-Transaktionen gehen zuerst in einen Speicherpool oder Mempool, der unbestätigte Transaktionsdaten speichert. Ein Mining-Knoten sammelt diese Transaktionen und kombiniert sie zu einem temporären Kandidatenblock.
Nun überprüft ein Miner diese Kandidatenblöcke, um gültige Transaktionen zu finden und sie in Blöcke zu organisieren. Kurz gesagt, Transaktionen werden nach der Validierung Teil der Blockchain.
Auf technischer Ebene verwendet die Kryptowährungs-Mining-Technologie die Rechenleistung eines Computers, um den gesamten Prozess zu erleichtern. Der einzige Weg, einen Block zur Kette hinzuzufügen, besteht darin, einen kryptografischen Hash oder eine Funktion zu identifizieren, die mit dem neuesten Block übereinstimmt.
Der Hash kommt in einer 64-stelligen hexadezimalen Zahl innerhalb einer alphanumerischen Zeichenfolge. Miner führen also keine superkomplexen mathematischen Gleichungen durch. Sie führen Gleichungen aus, um diese Sequenz schnell zu erraten.
Der einzige praktikable Weg, um zu einem Hash zu gelangen, der den richtigen Kriterien entspricht, besteht darin, einfach so viele Hashes wie möglich zu berechnen und zu warten, bis Sie eine Übereinstimmung finden. Miner können einen neuen Block bilden, sobald sie den richtigen Hash gefunden haben.
Komponenten eines Krypto-Mining-Rigs
Ein Krypto-Mining-Rig ist ein maßgeschneiderter Personal Computer mit Hochleistungs-GPUs. Es besteht aus den folgenden Komponenten:
- Motherboard: Gewährleistet die Konnektivität zwischen Hardwarekomponenten
- CPU: Fungiert als Gehirn eines Computers
- Random-Access Memory (RAM): Bestimmt die Mining-Leistung abhängig von seiner Größe
- Netzteil (PSU): Reguliert die Stromversorgung aller Mining-Komponenten
- PCIe-Riser-Kabel: Erweitert die GPU-Verbindung zum Motherboard
- Grafikkarten: Reduzieren die Mining-Kosten, indem sie ein System stabil halten, den Stromverbrauch senken und den PC kühlen
Möchten Sie mehr über Krypto-Mining-Software erfahren? Erkunden Sie Kryptowährungs-Mining Produkte.
Arten von Kryptowährungs-Mining-Methoden
Miner verwenden spezialisierte Computereinheiten, um komplexe kryptografische Gleichungen zu lösen und eine Findergebühr und andere Belohnungen zu verdienen. Der Prozess und die Methoden des Kryptowährungs-Minings können je nach verwendeter Technologie und angewandten Strategien unterschieden werden.
Prozesse konzentrieren sich auf die Computerkomponenten, die für den Mining-Prozess verwendet werden, während sich Methoden auf die tatsächlichen Techniken konzentrieren, die verwendet werden, um Belohnungen zu gewinnen.
Sie können Krypto-Mining-Prozesse oder -Methoden nach Ihrem Belieben durchlaufen.
Kryptowährungs-Mining-Prozesse
Miner verwenden eine der folgenden drei Computerkomponenten, um Kryptowährungen zu minen.
1. CPU-Mining
CPU-Mining war die erste Art des Krypto-Minings und basierte auf Prozessoren, um Währungen zu minen. Diese Methode erforderte viel Rechenleistung und ordnungsgemäße Kühlung und war nicht sehr kosteneffektiv.
Miner hatten Schwierigkeiten, Transaktionen mit CPU-Mining zu validieren, da es extrem langsam war. Die durchschnittliche Hash-Rate (misst die Rechenleistung, die ein Kryptowährungsnetzwerk benötigt, um Blockchain-Transaktionen zu verarbeiten) des CPU-Minings liegt bei etwa 0,7MH/sec.
2. GPU-Mining
GPU-Mining basiert auf Grafikkarten, um verschiedene Kryptowährungen zu minen. Seine Flexibilität ermöglicht es Ihnen, zwischen Währungen in einem bärischen oder bullischen Markt zu wechseln. GPU-Mining-Rigs sind aufgrund ihrer Effizienz und Erschwinglichkeit ziemlich beliebt.
GPU-Mining erfordert mehr Energiequellen als ASIC-Rigs, und deshalb dauert es eine Weile, bis Miner die anfängliche Investition wieder hereinholen.
3. ASIC-Mining
ASIC-Mining verwendet spezielle Geräte, die eine einzige Aufgabe mit spezifischen Algorithmen ausführen. Da diese Geräte leistungsstarke Chips enthalten, übertreffen sie leicht GPU- und CPU-Mining.
Krypto-Miner, die sich für ASIC-Mining entscheiden, können nur Algorithmen minen, die für ASIC entwickelt wurden. Viele Kryptowährungsentwickler nutzen diese Einschränkung, um die Netzwerkdezentralisierung sicherzustellen.
Kryptowährungs-Mining-Methoden
Kryptowährungs-Miner, die nicht tief in das technische Know-how eintauchen möchten, verwenden eine dieser drei Methoden, um Kryptowährungen zu minen.
1. Solo-Mining
Beim Solo-Mining oder individuellen Mining minen Solo-Miner Kryptowährung auf eigene Faust. Sie führen den Mining-Prozess unabhängig durch und sind nicht auf Unterstützung Dritter angewiesen. Solo-Miner erhalten große Anreize für die Blockentdeckung in ihren nativen Krypto-Clients mit individuellen Mining-Computern.
Der Erfolg des Solo-Minings hängt von der Hardware-Hash-Kapazität und der gesamten Netzwerk-Hash-Rate ab. Solo-Miner müssen geduldig sein, da es länger dauern kann, komplexe Blockdaten zu lösen und eine neue Münze freizuschalten.
Allerdings kann Solo-Mining auf lange Sicht profitabler sein als Pool-Mining. Krypto-Wertschwankungen und Stromverbrauchskosten beeinflussen auch die Rentabilität des Solo-Minings.
2. Pool-Mining
Nicht jeder hat tiefe Taschen, um in Solo-Mining zu investieren. Deshalb haben Krypto-Miner einen Weg gefunden, ihre Rechenleistung und Ressourcen zu teilen, um die Chancen auf das Finden von Blöcken zu verbessern. Diese Gruppen von Individuen werden Pool-Miner genannt, und der Prozess wird Pool-Mining genannt.
Mining-Pools kombinieren die Hash-Leistung einzelner Miner, um Ausgaben zu generieren, die großen Mining-Farmen ähneln. Pool-Miner erhalten proportionale Blockbelohnungen basierend auf ihrem Beitragsprozentsatz und nur nach Einreichung eines Proof-of-Work (PoW) von Transaktionen. Der Schlüssel zu erfolgreichem Pool-Mining ist es, während einer Pool-Mining-Runde mehr Hash-Leistung bereitzustellen.
3. Cloud-Mining
Cloud-Mining beinhaltet das Mieten von Rechenleistung von Cloud-Mining-Anbietern. Diese Drittanbieter-Rechenzentren verkaufen oder bieten Hashing-Leistung zur Miete für das Mining digitaler Währungen an. Sie hosten Mining-Ausrüstung und berechnen Ihnen einen Anteil an den Erlösen.
Cloud-Mining ist riskant, da es Chancen auf direkte Betrügereien oder keine Gewinne während der Vertragslaufzeit gibt. Seien Sie vorsichtig, wenn Sie in Cloud-Mining investieren, denn wenn es nicht Ihre Mining-Hardware ist, ist es nicht Ihre Belohnung.
Entwicklung des Krypto-Minings
Nach der Veröffentlichung des Papiers Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System im Jahr 2008 veröffentlichte Satoshi Nakamoto 2009 die erste Bitcoin-Software. Damit begann das Krypto-Mining offiziell.
Bitcoin gewann schnell an Popularität, da Menschen Interesse an der Währungsdezentralisierung und einer von der Regierung unabhängigen Wirtschaft zeigten. Dieses Interesse führte dazu, dass Bitcoin-Enthusiasten Knoten erstellten, neue Bitcoins mineten und das Netzwerk sicherten.
Ein Personal Computer mit einem Intel Core i7-Prozessor konnte 2009 etwa 50 Bitcoins pro Tag minen. Damals war ein Bitcoin 0,08 $ wert, und Bitcoin-Miner zahlten mehr für den Strom, als sie durch Bitcoin-Transaktionen verdienen konnten.
Die Schwierigkeit des Bitcoin-Netzwerks, Kryptowährungen mit Personal Computern (PCs) zu minen, führte zu den High-End-Grafikkarten. Miner begannen 2010, Grafikprozessoren (GPUs) zum Minen von Bitcoins zu verwenden. GPUs ermöglichten es ihnen, kryptografische Hashes schneller zu verarbeiten als zentrale Verarbeitungseinheiten (CPUs). GPU-Mining-Rigs bestanden aus einem CPU-Prozessor, einem Motherboard und sechs High-End-Grafikkarten.
Im Jahr 2011 begannen Miner nach GPU-Alternativen mit geringerem Stromverbrauch zu suchen. Sie stießen auf feldprogrammierbare Gate-Arrays (FPGAs), die Bitcoins doppelt so schnell minen konnten wie die hochwertigste GPU. Allerdings erfordern FPGAs Software- und Hardwarekonfiguration und -anpassung, um effizient Münzen zu minen.
Die arbeitsintensive Natur von FPGAs veranlasste Miner, nach neuen Maschinen zu suchen, die keine Umnutzung von Software- und Hardwareparametern erforderten. Diese Suche endete, als Canaan Creative, ein in China ansässiger Computerhardwarehersteller, 2013 anwendungsspezifische integrierte Schaltungen (ASICs) auf den Markt brachte. Im Gegensatz zu FPGAs, GPUs und CPUs minen ASICs nur Bitcoin und tragen zu höheren Effizienzgewinnen bei.
Bitmain und MicroBT brachten später ASIC-Bitcoin-Mining-Geräte mit fortschrittlicher Hardware auf den Markt. Seit ihrer Einführung haben ASIC-Chips im Laufe der Zeit eine stetige Größenreduzierung erfahren.
Krypto-Mining-Konsensalgorithmen
Krypto-Miner verwenden Netzwerk-Konsensregeln, um legitime Transaktionen zu validieren und unehrliche Miner zu eliminieren. Legitime Transaktionen haben ausreichende Krypto-Wallet-Salden, um ausgehende Transaktionen zu finanzieren.
Diese fehlertoleranten Konsensprotokolle oder -algorithmen verhindern wirtschaftliche Angriffe und helfen verteilten Prozessen, sich auf einen einzigen Datenwert zu einigen.
Arten von Kryptowährungs-Konsensalgorithmen:
- Proof of Work (PoW) basiert auf dem Nachweis des Aufwands für Rechenleistung, um böswillige Nutzung von Rechenleistung und Doppelausgaben (die mehrfache Verwendung eines einzelnen digitalen Tokens) zu verhindern. Cynthia Dwork und Moni Naor erfanden das PoW-Konzept 1993, um Denial-of-Service (DoS)-Angriffe zu bekämpfen. Der Begriff erlangte jedoch Popularität, nachdem Markus Jakobsson und Ari Juels ihn in einem Papier von 1999 formalisierten.
- Proof of Stake (PoS) fordert Knoten auf, Mittel zu binden und einen wirtschaftlichen Anteil am Netzwerk zu haben, um die Chance zu haben, das nächste kryptografische Puzzle zu lösen. Sunny King und Scott Nadal waren die ersten, die ein PoS-System auf der Peercoin-Blockchain im Jahr 2012 verwendeten.
- Proof of Activity (PoA) kombiniert PoW-Mining, um Blöcke zu finden, und PoS-Mining, um diese neu gefundenen Blöcke zu validieren. Litecoin-Gründer Charlie Lee schlug PoA-Mining in einem BitCoin-Forum-Thread im Jahr 2012 vor.
- Proof of Capacity (PoC) bestimmt Mining-Rechte und validiert Transaktionen basierend auf der Rechenleistung der Mining-Geräte. Dziembowski et al. formulierten das PoC-Konzept im Jahr 2013.
- Proof of Spacetime (PoSt) ist dem PoC-Konzept nahe, ermöglicht es Teilnehmern jedoch, die Zuweisung von Speicherkapazität an ein Netzwerk über die Zeit nachzuweisen. Tal Moran und Ilan Orlov schlugen das PoSt-Konzept vor, da sie glaubten, dass Speicher ein rationaler Beweis für Raum und Zeit wäre.
- Proof of Burn (PoB) adressiert Energieverbrauchsprobleme, indem Krypto-Münzen an nicht ausgebbare Adressen ohne private Schlüssel gesendet werden. Counterparty (XCP) war die erste, die PoB implementierte, um die Blockchain im Jahr 2014 zu sichern.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) ermöglicht es Teilnehmern, Münzen auszugeben, um für Delegierte zu stimmen. Die gewählten Vertreter treffen Entscheidungen, die für das gesamte Netzwerk gelten. Dan Larimer erstellte und implementierte DPoS in der Bitshares-Blockchain im Jahr 2013.
Wie man Kryptowährung minet: Schritt für Schritt
Da Sie nun eine grobe Vorstellung davon haben, wie Krypto-Mining funktioniert, werfen wir einen detaillierten Blick auf jede Phase des Prozesses.
Transaktions-Hashing
Der erste Schritt des Krypto-Minings besteht darin, eine Hash-Funktion zu verwenden, um ausstehende Transaktionen aus dem Speicherpool einzureichen. Jede Transaktionseinreichung erzeugt einen festen Ausgabe-Hash, der als Transaktionsidentifikator fungiert. Ein Miner fügt auch eine benutzerdefinierte Transaktion hinzu, um auf die Blockbelohnung zuzugreifen.
Merkle-Baum-Erstellung
Ein Merkle-Baum oder Hash-Baum überprüft die Inhalte der Datenstruktur, indem er Transaktions-Hashes in Paare organisiert. Er kennzeichnet Knoten mit dem kryptografischen Hash des Datenblocks und innere Knoten mit dem Hash ihres Kindknoten-Labels.
Neue Hash-Ausgaben durchlaufen nach jeder Transaktion Hashes, bis ein einzelner Hash (auch bekannt als Root-Hash oder Merkle-Root), der die vorherigen Hashes repräsentiert, erstellt wird.
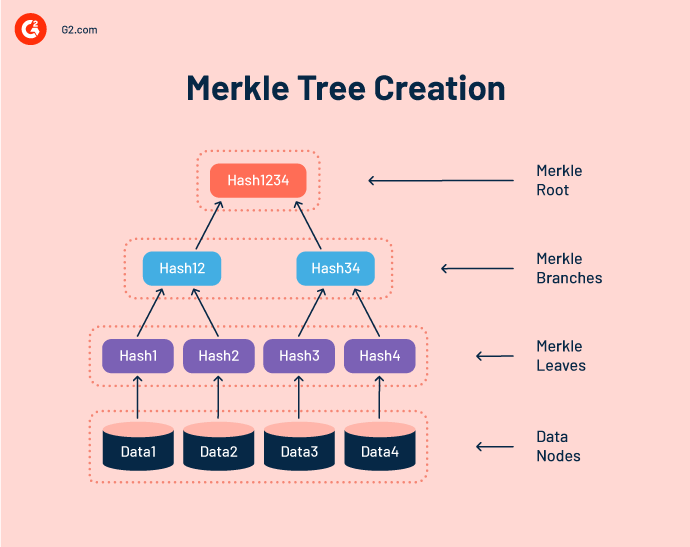
Entdeckung eines gültigen Block-Headers
Ein Block-Header hilft Minern, einen einzelnen Block mit einem eindeutigen Hash zu identifizieren. Miner kombinieren den Root-Hash des Kandidatenblocks, den Hash des vorherigen Blocks und eine einmalig verwendete Zahl (Nonce), um einen gültigen Hash zu erstellen.
Das Protokoll entscheidet den Zielwert, der höher sein sollte als die Ausgabe, damit der Block-Hash korrekt ist. Miner ändern den Nonce-Wert mehrmals, da sie die anderen beiden Komponenten nicht ändern können.
Die Mining-Schwierigkeit zeigt ein komplexes kryptografisches Puzzle an. Je länger es dauert, den korrekten Block-Hash zu finden, desto höher ist die Schwierigkeit. Die Mining-Schwierigkeit hängt auch von der Anzahl der Miner in einem Krypto-Netzwerk ab.
Block-Hash-Verifizierung
In diesem Stadium senden Miner die neu gefundenen Blöcke an Peer-Miner zur Hash-Verifizierung. Die Peer-Mining-Knoten verwenden einen sicheren Hash-Algorithmus 256 (SHA-256), um die Datenintegrität zu überprüfen und Hash-Probleme und Manipulationen zu identifizieren.
SHA-256-Bit (32 Bytes) Hash-Wert-Beispiel:
Daten:
G2 ist, wo Sie für Software hingehen
SHA-256-Hash: 37b57cca30f0f9df5d9a0654e1cb7efeba86f36b61c6836a8b6e43e61b61c358
Sie können gehashte Daten ohne Schlüssel nicht lesen. Ein Brute-Force-Angriff benötigt 2256 Versuche, um die ursprünglichen Daten zu generieren. SHA-256 ist eine der sichersten Hash-Funktionen. Die US-Regierung verwendet es, um sensible Daten zu schützen.
Blockbestätigung und Veröffentlichung
Sobald Peer-Miner einen Konsens über einen Block erreicht haben und ihn verifiziert haben, wird ein Kandidatenblock zu einem bestätigten Block. Dieser neue Block wird am Ende einer Blockchain hinzugefügt. Wenn Miner den Kandidatenblock-Hash nicht validieren können, verwerfen sie den Kandidatenblock – ein erfolgloser Versuch für einen Miner.
Kryptomining-Malware
Erinnern Sie sich an Mike Judges Kultklassiker Office Space?
Unzufriedene Mitarbeiter installieren bösartige Software auf dem Computer ihres Arbeitgebers, um Bruchteile von Cent von jeder Transaktion abzuzweigen. Die Begründung war, dass Banken und Arbeitgeber solche kleinen Beträge nicht bemerken würden. Kryptomining-Malware verwendet eine ähnliche Technik und faule CPU-Zyklen, um digitale Münzen abzuzapfen und zu minen.
Bösartiges Krypto-Mining, oder Kryptojacking, verwendet Webbrowser-Downloads oder Mobile Apps, um die Ressourcen eines Rechengeräts zu übernehmen. Diese Krypto-Miner nutzen die Rechenleistung der Opfer, um Kryptowährungen zu minen oder zu stehlen. Infolgedessen erleben Gerätebesitzer Systemleistungsverlangsamungen, erhöhte Prozessor-Auslastung, überhitzte Computer und höhere Stromrechnungen.
332,3 Millionen
Kryptojacking-Angriffe ereigneten sich in der ersten Hälfte des Jahres 2023.
Quelle: SonicWall
Kryptomining-Angriffe wurden mit dem Aufstieg der Popularität von Kryptowährungen im Jahr 2017 verbreitet. Der bekannteste war Coinhive, das 2017 einen neuen Kryptowährungs-Mining-Service veröffentlichte. Coinhive-Kunden konnten JavaScript (JS)-Codierungszeilen auf ihrer Website platzieren, um die CPU-Leistung der Besucher zum Minen von Währungen zu nutzen.
Kryptojacking-Beispiele:
- Prometei ist ein Kryptowährungs-Botnetz, das Geräte infizierte, um Monero-Kryptowährung im Jahr 2016 zu minen und später 2021 Microsoft Exchange-Schwachstellen ausnutzte.
- PowerGhost verwendet Spear-Phishing, um sich im System festzusetzen, Windows-Anmeldeinformationen zu stehlen und konkurrierende Krypto-Miner zu deaktivieren.
- Graboid ist der erste bekannte Krypto-Mining-Wurm, der nicht authentifizierte Docker-Engine-Bereitstellungen nutzte, um sich zu verbreiten und Container zu infizieren.
- MinerGate-Malware erkennt Mausbewegungen, um Mining-Aktivitäten auszusetzen und das Opfer nicht zu alarmieren.
- BadShell verlässt sich auf dateilose Techniken, um legitime Windows-Prozesse zu verbergen und Kryptowährungen zu minen.
- Facexworm verwendet eine Chrome-Erweiterung, um bösartige Dateien über Facebook Messenger zu verbreiten, Computer zu infizieren und Anmeldeinformationen zu stehlen.
- WinstarNssmMiner bringt Computer zum Absturz, indem es einen svchost.exe-Prozess startet und ihm CriticalProcess zuweist.
Der beste Weg, sich vor solchen bösartigen Angriffen zu schützen, ist die Verwendung zuverlässiger Blockchain-Sicherheitssoftware. Sie hilft Ihnen, Krypto-Ökosysteme zu analysieren, potenzielle Bedrohungen zu identifizieren, Risiken zu bewerten und digitale Vermögenswerte zu schützen.
Achten Sie auch darauf, ob der Besuch einer bestimmten Website die CPU-Auslastung erhöht. Vermeiden Sie das automatische Laden der vorherigen Browsersitzung beim Neustart Ihres Computers.
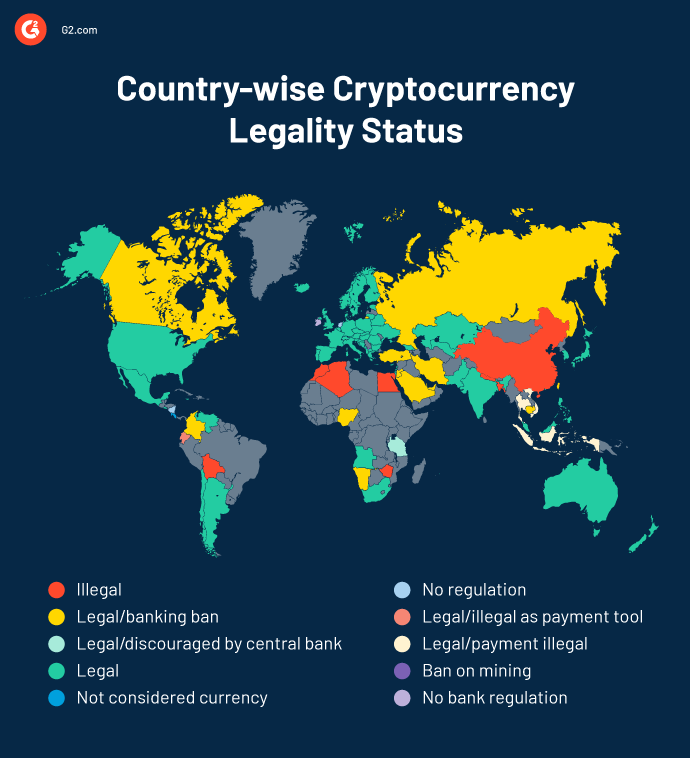
Ist das Mining von Kryptowährungen legal?
Ja, aber es hängt auch von Ihrem geografischen Standort ab und davon, ob Sie legal Kryptos minen. Die meisten Länder haben noch keine Kryptowährungsgesetze erlassen, um Krypto-Mining und -Transaktionen zu regeln.
Krypto-Mining-Steuern
Der steigende Wert von Bitcoin, Ethereum und anderen digitalen Währungen hat Fragen zu Kryptowährungssteuern bei Krypto-Händlern und Minern aufgeworfen.
Wie werden Kryptowährungen besteuert? Kryptowährungen sind Kapitalanlagen und erhalten eine ähnliche steuerliche Behandlung wie Aktien. Daher führen Krypto-Einnahmen aus der Wertsteigerung von Krypto-Assets zu einer Steuerschuld. Sie können diese Verbindlichkeiten jedoch durch die Angabe von Kapitalverlusten ausgleichen.
Der Internal Revenue Service (IRS) veröffentlichte IRS Notice 2014-21, um die Steuerschuld von Krypto-Beständen, -Transaktionen und -Investitionen zu bewerten. Der IRS verlangt, dass Sie Einnahmen oder Gewinne aus den folgenden Aktivitäten melden:
- Virtueller Währungsaustausch
- Empfang von Airdrop-Token
- Verkauf von Kryptowährungen gegen Bargeld
- Kryptowährungs-Mining oder -Staking
- Erhaltene Kryptowährungszahlungen
- Händlerzahlungen mit Krypto-Debitkarten oder Kryptowährungen
Die folgenden Krypto-Transaktionen fallen jedoch unter nicht steuerpflichtige Krypto-Aktivitäten:
- Kauf und Halten von Kryptowährungen
- Übertragung von Kryptowährungen zwischen Wallets
- Steuerlich absetzbare Kryptowährungs-Spenden
- Kryptowährungs-Schenkungen, ausgenommen große Geschenke
Vorteile des Krypto-Minings
Ob Sie Bitcoin minen oder planen, andere Kryptowährungen zu minen, Sie haben immer die vollständige Kontrolle über digitale Vermögenswerte, solange Sie keine privaten Schlüssel verlieren. Hier sind einige weitere Vorteile des Krypto-Minings:
- Keine gefälschte Transaktion kann auftreten, da die Blockchain-Technologie keine Änderungen nach der Aufzeichnung eines Transaktionseintrags zulässt.
- Niedrigere Gebühren als bei traditionellen Banken ermöglichen es Minern, Transaktionen effizient zu verarbeiten und sogar grenzüberschreitende Zahlungen zu tätigen.
- Die Push-and-Pull-Methode sichert Ihre Identität besser als Radiofrequenz-Identifikationskarten (RFID) und reduziert die Wahrscheinlichkeit von Identitätsdiebstahl.
- Vollständige Kontrolle über Geld ist ein weiterer Vorteil des Krypto-Minings, der es Minern ermöglicht, ihre Krypto-Assets frei zu nutzen.
Probleme beim Kryptowährungs-Mining
Das Kryptowährungs-Mining hat seine Herausforderungen, genau wie jede andere Bergbauindustrie, trotz all dieser Vorteile. Nachfolgend sind einige dieser Herausforderungen aufgeführt.
Hohe Krypto-Konkurrenz
Das Krypto-Mining ist hochgradig wettbewerbsfähig, da die Mining-Schwierigkeit mit jedem Hash zunimmt. Diese Hash-Level-Schwierigkeit hält einen stetigen Fluss neuer Blöcke aufrecht. Je komplexer die Berechnungen, desto mehr Rechenleistung benötigen Sie, um sie zu lösen.
Deshalb ist es herausfordernd, das Krypto-Mining als Hobby fortzusetzen. Und dann gibt es harte Grenzen für die Zirkulation. Zum Beispiel wird die Bitcoin-Blockchain insgesamt nur 21 Millionen Münzen haben, um Inflation zu verhindern.
Zugang zu Hardware
Sie benötigen die schnellste und fortschrittlichste Technologie, um die geringste Chance zu haben, beim Mining von Kryptos einen Gewinn zu erzielen. Aber Sie können nicht einfach die schnellsten Chips bestellen, weil das Angebot begrenzt ist.
Bitmain und MicroBT sind zwei chinesische Hersteller mit dem Löwenanteil am Bitcoin-Mining-Hardwaremarkt. Aber sie produzieren Chips nur zu bestimmten Zeiten des Jahres, und enge Lieferungen führen zu häufigen Ausverkäufen. Um mit dem Mining zu beginnen, müssen Sie Vorausbestellungen aufgeben und die Fähigkeit haben, mit dem Mining Geld zu verdienen.
Energieverbrauch von Kryptowährungen
Die teure Natur von Krypto-Mining-Operationen ist vielleicht die größte Barriere für viele. Ihre Fähigkeit, neue Blöcke zu erstellen, hängt von Ihrer Rechenenergie und der Hardwarestärke ab.
Die enorme Energie, die Sie benötigen, um die Hardware zu betreiben, trägt zu den Stromkosten und dem Klimawandel bei. Aus diesem Grund fühlt sich die globale Miner-Community verpflichtet, den globalen Einfluss von Treibhausgasemissionen und Energieverbrauch anzugehen.
Konsolidierung von Minern
Das Krypto-Mining leidet unter der Konsolidierung von Minern in verschiedenen Regionen weltweit. Krypto-Miner wählen normalerweise Gebiete mit günstigen Stromkosten und kaltem Klima, da beides die Stromkosten senkt und ihnen hilft, mehr Gewinn zu erzielen.
Gemeinschaften mit hohen Konsolidierungsgraden von Minern sind wahrscheinlich wirtschaftlich instabil, wenn Mining-Operationen ins Stocken geraten. Dieses Problem der langfristigen wirtschaftlichen Lebensfähigkeit ist ein Anliegen, da Kryptowährungspreise durch Marktspekulationen und nicht durch Angebot und Nachfrage schwanken.
Schwankendes Einkommen der Miner
Nicht jeder kann mit dem Mining von Kryptowährungen Geld verdienen. Krypto-Operationen erfordern eine Anfangsinvestition und erhebliche Betriebskosten jeden Monat. Der Kryptowährungspreis muss hoch sein, damit Miner diese Kosten decken und einen Gewinn erzielen können. Schwankungen in der Marktkapitalisierung von Kryptowährungen bedrohen das Einkommen der Miner und die Betriebskostenrendite (ROI).
Investieren vs. Handeln vs. Mining vs. Kauf von Krypto
In Kryptowährungen zu investieren bedeutet, Krypto-Assets zu kaufen und in Krypto-Fonds oder Unternehmen zu investieren.
Häufige Krypto-Investitionsstrategien:
- Hold on for dear life (HODL) bedeutet, Kryptowährungen für immer zu kaufen und zu halten, in der Hoffnung, dass ihre Preise in der Zukunft steigen werden.
- Dollar-Cost-Averaging beinhaltet das Investieren kleinerer Beträge in ein digitales Asset in regelmäßigen Abständen.
- Marktkapitalisierungsgewichtetes Portfolio bezieht sich auf das Übergewicht eines digitalen Assets und das monatliche oder vierteljährliche Rebalancing des Portfolios.
Krypto-Handel beinhaltet häufige Transaktionen, einschließlich Kauf und Verkauf. Krypto-Händler zielen darauf ab, mehr Renditen aus Kursschwankungen zu erzielen als beim Buy-and-Hold-Investing.
Häufige Krypto-Handelsstrategien:
- Day-Trading versucht, durch den Kauf und Verkauf von Kryptowährungen innerhalb eines einzigen Tages Gewinne zu erzielen.
- Swing-Trading sucht nach größeren Zyklusverschiebungsmustern, um Krypto-Assets zu kaufen und zu verkaufen.
- Positionstrading analysiert langfristige Trends, bevor Kryptowährungen verkauft werden.
- Scalping erzielt kumulative kleine Gewinne durch den Handel mit kleinen Preisbewegungen.
Krypto minen bedeutet, Transaktionen auf einem Blockchain-Ledger zu verifizieren und neue digitale Währungseinheiten zu erstellen. Krypto-Miner verlassen sich auf Rechenleistung, um Transaktionen zu validieren und neue Blöcke zu finden.
Krypto kaufen bedeutet, digitale Währungen von Kryptowährungsbörsen oder anderen Personen zu kaufen. Nach dem Kauf dieser Währungen können Sie sie entweder mit Kryptowährungsverwaltungssoftware speichern oder handeln oder investieren.
Kryptowährungs-Mining-Software
Ob Sie neu im Krypto-Mining sind oder ein Profi, Sie benötigen die beste Kryptowährungs-Mining-Software, um Währungen effizient zu minen und Blöcke zu finden. Lassen Sie die Software die schwere Arbeit erledigen, während Sie sich auf das Lösen komplexer Krypto-Rätsel konzentrieren.
Um in diese Kategorie aufgenommen zu werden, muss ein Softwareprodukt:
- Ressourcen zum Minen zuweisen
- Währungen mit GPU oder CPU minen
- Mining-Hardware und Blockchain verbinden
*Nachfolgend sind die Top 5 führenden Kryptowährungs-Mining-Softwarelösungen aus dem G2 Spring 2024 Grid® Report aufgeführt. Einige Bewertungen können zur Klarheit bearbeitet worden sein.
1. ECOS DeFi
ECOS DeFi ist eine Krypto-Investitionsplattform, die es Ihnen ermöglicht, Krypto-Portfolios zu erstellen, Krypto zu tauschen und auch zu minen.
Was Benutzer am meisten mögen:
„Es ist eine All-in-One-Lösung für sowohl Cloud-Mining als auch Krypto-Investitionen. Zuverlässiger Dienstleister in einer Ära von Betrügern. Vielfalt an Verträgen für alle Budgets verfügbar.“
- ECOS DeFi Review, Capt. Inderdeep D.
Was Benutzer nicht mögen:
„Ich würde gerne kleinere Wertverträge sehen, damit es einfacher für Menschen ist, ins Mining einzusteigen, ohne zu viel ausgeben zu müssen."
- ECOS DeFi Review, Jacques Z.
2. NiceHash
NiceHash ist eine führende Plattform für Kryptowährungshandel und -mining. Hash-Power-Käufer, Krypto-Miner und Händler nutzen diese Plattform regelmäßig.
Was Benutzer am meisten mögen:
„Das Interessanteste und Praktischste an NiceHash ist, dass es Ihnen ermöglicht, auf zwei Arten zu interagieren. Als Käufer können Sie die Mining-Dienste anderer Plattformen oder Algorithmen von verschiedenen Anbietern anfordern. Diese Fähigkeit hilft Käufern zu sparen, da sie kein Kapital in Mining-Hardware investieren. Sie mieten die "Hashing"-Rechenleistung Ihrer Online-Plattform.“
- NiceHash Review, Jesús A.
Was Benutzer nicht mögen:
„Es ist schmerzhaft, abzuheben, und Sie müssen einen umständlichen Prozess durchlaufen, um ein Konto zu verifizieren, insbesondere wenn Sie eine Weile inaktiv waren, wie ich es war. Der Support ist langsam.“
- NiceHash Review, John S.
3. Cudo Miner
Cudo Miner bietet eine Mischung aus Einfachheit, Effizienz und fortschrittlichen Funktionen. Sein automatisiertes Gewinnumschalten und Echtzeitanalysen ermöglichen es Ihnen, Ihr Mining-Potenzial mit minimalem Aufwand zu maximieren.
Was Benutzer am meisten mögen:
"Cudo Miner zeichnet sich durch seine benutzerfreundliche Oberfläche und automatisierte Gewinnoptimierung aus, die das Kryptowährungs-Mining für Benutzer aller Erfahrungsstufen zugänglich und lukrativ macht. Das Engagement der Software für aktive Entwicklung und Sicherheit erhöht ihre Attraktivität in der wettbewerbsintensiven Mining-Landschaft weiter."
- Cudo Miners Review, Akash K.
Was Benutzer nicht mögen:
"Es ist nicht für Anfänger geeignet. Wenn Sie Geld verdienen möchten, ist es keine Option. Begrenzte Zahlungsmethoden machen Kryptex zu einer bevorzugten Wahl."
- Cudo Miner Review, Lisa H.
4. Kryptex
Kryptex verwandelt Ihren Computer in eine zuverlässige Krypto-Mining-Maschine, egal ob Sie ein Anfänger oder ein erfahrener Miner sind. Mit der neuesten Technologie und einem benutzerzentrierten Ansatz stellt Kryptex sicher, dass Sie Ihre Mining-Gewinne mit minimalem Aufwand maximieren können.
Was Benutzer am meisten mögen:
"Ich habe Kryptex für CPU- und GPU-Mining verwendet und fand es sehr hilfreich, um das Beste aus der Hardware herauszuholen. Es ist eine sehr leichte und einfach zu bedienende Anwendung mit den richtigen Überwachungs- und Konfigurationsparametern."
- Kryptex Review, Muhammad Daud S.
Was Benutzer nicht mögen:
"Die Dinge, die ich an Kryptex nicht mag, sind, dass es die Lite-Version nicht auf einer GPU ausführen kann. Auch die Lite-Version hängt manchmal und stürzt ab. Außerdem kann die Software nur zum Mining von Bitcoin und nicht von anderen Kryptowährungen verwendet werden. Abgesehen davon ist die Software gut gebaut, und das Mining ist einfach und unkompliziert. Die Auszahlung ist etwas niedrig, aber ansonsten ist die Software einfach zu bedienen."
- Kryptex Review, Rimsha S.
5. Salad
Salad ermöglicht es Benutzern, Belohnungen zu verdienen, indem sie ungenutzte Rechenleistung nutzen. Die Plattform verlässt sich auf die Ethereum-Blockchain, um Benutzern das Teilen von Rechenressourcen zu ermöglichen.
Was Benutzer am meisten mögen:
„Ich mag, wie Salad Ihre ungenutzten PC-Ressourcen nutzt, sodass Sie sich keine Sorgen machen müssen, dass es läuft, während Sie etwas ressourcenintensives tun. Dieses Programm hat es mir ermöglicht, Freunden Geschenke zu machen, und es hat mir auch ermöglicht, mich selbst zu belohnen.“
- Salad Review, Joseph K.
Was Benutzer nicht mögen:
„Manchmal liefert die Plattform Schlüssel nicht rechtzeitig. Obwohl ihr Support-Team die Schlüssel später bereitstellt, ist ihr Team während der Ferienzeit nicht vorhanden. Und es dauert einige Zeit, bis Ihre feststeckenden Schlüssel geliefert werden.“
- Salad Review, Karan P.
Die Zukunft des Krypto-Minings
Das Mining von Krypto-Assets bedeutet, mehr Strom als je zuvor zu verbrauchen. In Kombination mit dem globalen Chipmangel und den Vorschriften scheint die Zukunft für Krypto-Miner wild zu sein.
Es werden mehr saubere Energieinitiativen entstehen, um die Krypto-Mining-Industrie zu unterstützen, mehr Arbeitsplätze im Bereich erneuerbare Energien zu schaffen und lokale Gemeinschaften zu unterstützen. Es gibt auch eine große Chance, Mining-Technologien zu verbessern, die weniger Strom benötigen, weniger Lärm erzeugen und weniger Platz benötigen.
Finden Sie die besten Kryptowährungs-Wallets, um Kryptowährungen auszugeben, zu handeln und zu empfangen.
Dieser Artikel wurde ursprünglich im Jahr 2022 veröffentlicht. Er wurde mit neuen Informationen aktualisiert.

Sudipto Paul
Sudipto Paul leads the SEO content team at G2 in India. He focuses on shaping SEO content strategies that drive high-intent referral traffic and ensure your brand is front-and-center as LLMs change the way buyers discover software. He also runs Content Strategy Insider, a newsletter where he regularly breaks down his insights on content and search. Want to connect? Say hi to him on LinkedIn.