Employees and customers use an enterprise's information assets differently.
Some use it to carry out their daily tasks on software applications where others might need data or information stored in the company's repositories for peculiar purposes. In any case, it's essential to regulate their access permissions on information assets to maintain security and adhere to compliance requirements.
Now, whenever an access request is made to the IT administrator, manually checking all attributes and clearances to grant access might consume a lot of time. If the IT admin supplies the access credentials personally to a user, it might be prone to internal security risks.
To avoid such situations, enterprises use user provisioning tools to create, manage, and monitor users' access privileges. These tools use automation to streamline user account creation and regulate rights, making it easier for the IT administrator to manage their organization's identity and access management program.
Not only does it save time and money, but it also helps the leadership gain visibility of identity and access permissions granted to different users starting from onboarding till their exit.
What is user provisioning?
User provisioning is a digital identity and access management process that involves creating user accounts and giving them appropriate rights and permissions to access an organization's resources.
Also known as user account provisioning, this process involves ensuring that user accounts are created, given appropriate privileges, managed, and monitored throughout a user's lifecycle in an organization.
It starts when new users are onboarded, where a new account is created for them with relevant access permissions. The account is managed and modified as they get promoted or transferred. Then, at the time of offboarding, the account is deactivated and deleted, which is a part of the user deprovisioning process.
What's the purpose of user provisioning and user deprovisioning?
The purpose of user provisioning and deprovisioning can be explained through the following stages in a user's lifecycle:
Onboarding: New hires need their user profiles set up with permissions relevant to their role and hierarchical position. It helps them perform their tasks application, use information assets effectively, and ramp up with the new processes in a frictionless way. It involves creating new user accounts, setting up an email account, granting access to applications, data repository, group memberships, and more.
Promotion: User permissions and rights might change when people move into a new role. User provisioning enables them to make a smooth transition by giving them relevant access rights. For example, when an IT specialist is promoted to a managerial role, they'd need access to a new set of tools, which helps them gain visibility over the entire team.
One-off access: There may be situations where teams onboard contractual users who might need temporary access to emails or other assets. You need to ensure that one-off user provisioning is managed quickly, and once the one-off event is finished, deprovisioning should be immediately implemented.
Offboarding: When an employee leaves an enterprise, their user account should be disabled quickly, and after a pre-decided period, it should be removed from the system. Providing access to former employees may put your security construct at risk and is not advisable.
Support or technical issues: If a new employee forgets their password or they encounter a problem in their account, such user accounts will have to be provisioned again. After this, the old account of the same user should be disabled and removed.
Overall, user provisioning plays a crucial role in managing user accounts and their right within an enterprise while ensuring that compliance standards (like HIPAA) are adequately met.
The purpose of user provisioning in an organization can be better explained by the capabilities that it offers.
- Enhances efficiency in security administration: User provisioning system reduces the amount of time required to set up and update system access controls while providing capabilities to update access permissions or suspend a user temporarily. It allows security administration staff to save a lot of time and enables them to work on other tasks to enhance the security administration function.
- Offers role-based system access: It's difficult to predict which systems a user may access without having an individual to monitor the usage. It's a common problem in user access setup that user provisioning solutions solve. The solution ensures that access permissions are granted solely based on the user's role or job title in the organization.
- Facilitates time-saving auditing: User provisioning systems have a centralized repository of all user access data and information on active and inactive users, enabling legal authorities to conduct audits efficiently. Furthermore, automated user provisioning systems offer capabilities to conduct audits in less time (a few hours) compared to the traditional methods where it could take days to finish it.
- Improves user experience: User provisioning systems automate user access setup and enable them to ramp up quickly in a new environment, saving a lot of time. This enhances the user experience considerably and reduces the number of calls that the help desk gets for providing access to different applications.
- Allows integration with single sign-on (SSO): User provisioning systems can be integrated with SSO provided that both have the same vendor. It saves a substantial amount of security administration time and reduces manual errors.
- Increases help desk efficiency: Large volumes of access requests made to the help desk cause delays and impact user satisfaction. With user provisioning, users get appropriate system access immediately, which minimizes the request made to support, and allows them to focus on high priority issues.
The absence of a proper user provisioning process may cause unnecessary confusion when new users come in as they would be blind sighted to end-user objects that are crucial for their role. On the flip side, allocating these access rights manually would give rise to redundancies in an IT admins work, as they are swamped with a variety of other tasks. It would impact the efficiency of both sides – admins and new users.
Another need that user provisioning satiates is maintaining protection over the information assets. You cannot expose your assets openly to everyone in the enterprise; it will put up a bold question mark on your security and compliance standards. For any good identify and access management programs, it's essential to have systematic protection over information and applications that work with the enterprise's data.
User provisioning and user deprovisioning are a part of the identity and access management (IAM) program and cater to such needs effectively by managing and monitoring access rights and privileges of different users.
Want to learn more about User Provisioning and Governance Tools? Explore User Provisioning and Governance Tools products.
Types of user provisioning
There are four significant types of user provisioning:
- Self-service account provisioning: enables users to participate in a few parts of the provisioning process to help IT admins save time. For example, users are solely responsible for changing and managing their passwords.
- Discretionary account provisioning: involves IT administrators solely deciding a user's access to multiple applications and information. Although it's common in small companies, it can create a hassle when done manually in large enterprises.
- Workflow-based account provisioning: requires approvals from leadership to grant access to information or applications. Permissions are given based on the needs and requirements of a user.
- Automated account provisioning: involves managing user accounts based on a predefined set of rules through a centralized user provisioning tool. It enables the admin to closely monitor user accounts and permissions without spending too much time. The software slices the manual process's redundancies, but there would be some instances where admins may need to engage.
How to implement a user provisioning process
To implement a user provisioning process in your enterprise, here is a step-by-step guide that will help you understand the complete implementation process.
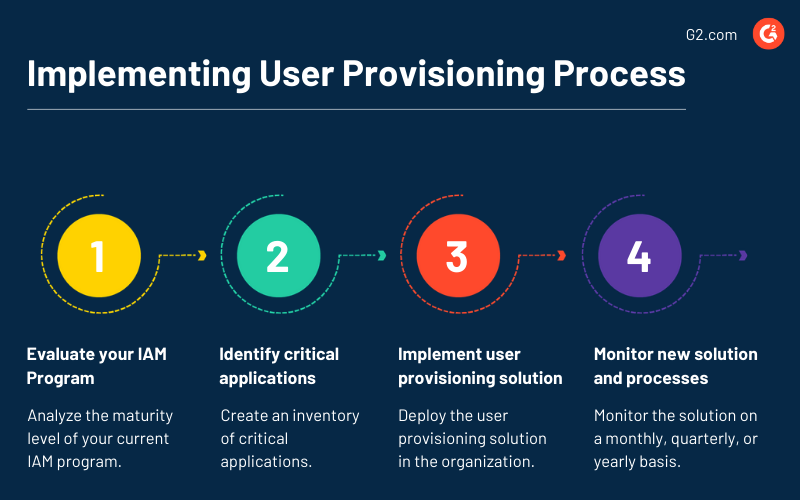
Evaluate your identity and access management program
The first step toward implementing a user provisioning process is to identify and analyze the maturity level of your current IAM program. Take a deep dive into understanding how your team sees user provisioning and their responsibilities associated with it. Your IT team must have a comprehensive understanding of the topic, as they would be the ones to implement it.
Tip: Want to know more? Here's your detailed guide to IT management.
Next, scrutinize processes in your enterprise. Find out the gaps you need to fill in the end-to-end process lifecycle catering to creating, managing, monitoring, disabling, and deleting user accounts. Take user experience feedback and check how the present IAM program helps users scale-up their productivity and efficiency. Identify the areas where you can improve with user provisioning.
Also, check the present technology that supports your IAM program from a security and usability standpoint. Last, build a business case of implementing a new user provisioning solution. As you would need resources and budget to do it, it's advisable to develop a strong business case that serves your organization's risk management and cost-saving motive.
Identify the most critical applications and initiate a pilot program
Once you have a business case that aligns with your company's standards, the next step is to create an inventory of applications. You can collaborate with a cybersecurity expert to identify the critical application, which can collapse the security construct and lead to data breaches when hacked.
Define the scope (users or systems) of your program in addition to the timeline in which it would be conducted. It's advisable to place a success metric (time savings, cost-saving, etc.) in place that you can track in the program's timeframe.
Make a note of the benefits and challenges you observed while implementing the pilot program, which can train others later.
Implement the user provisioning solution
There are a variety of factors that you should consider to implement the user provisioning solution successfully in an organization.
1. Access standards and process for existing users
Implementing a user provisioning system provides an opportunity to revamp your existing business processes for better outcomes. You should map out the complete business process to create, manage, monitor, and delete user accounts before listing your requirements from the system.
Once you’ve done that, you should develop the business process, where you can bridge the gaps with the user provisioning system and gain suitable outcomes from implementation.
2. Participation of end-users
For user provisioning systems, end users are generally, security team, IT administrators, customer support, or system administrators. It's important that all end users participate in reviewing the implementation of the new system.
You should also inform the security teams and other end users about the new business processes, as it would make them aware of how they'll be using the new system. There should be proper training on using the new user provisioning system and business processes associated with it.
3. Resource planning
Implementation of user provisioning solutions will need both technical and business resources.
You'd need to appoint professionals in the following roles:
- Project manager: to manage and support the organization's vendor activities. It's advisable to have a project manager with a strong background in security.
- Analyst: to present the requirements of end-users.
- Technical lead: to gain a strong understanding of the solution.
- System administrator: to manage infrastructure.
- Database administrator: to manage databases.
- HR analyst: to support the development and testing of trigger files.
4. Moving toward deployment
To deploy the user provisioning solution, you should prepare a checklist with an outline of all tasks required by the vendor and the organization. Hold status meetings to ensure everything is on schedule and all end-users are prepared to go live.
Also, ensure that the new user provisioning solution is adopted, and slowly retire the existing system, as deployment won't be successful if users do not use the new system.
5. Ensuring support
Regardless of all your testing, some issues might arise after deployment. To ensure that these are properly resolved, make sure your project manager and analyst are available in the first fifteen to thirty days.
Organizations should plan using the user provisioning solution vendor for post-go-live support. But if the organization plans on supporting everything, they must engage the development teams in the lifecycle of project implementation.
Monitor the new solution and processes
Once you have implemented the user provisioning solution in the organization, make sure you monitor it on a monthly, quarterly, or yearly basis. Track the number of user provisioning requests handled, the time required to address such requests, internal audit findings, and user experience level to improve the process continually.
Top 5 user provisioning software solutions
User provisioning software allows administrators to use a centralized system to maintain and manage user access to IT applications. It helps them to use the information in these systems to automate multiple tasks like creating user accounts, modifying, or deleting throughout the changes in the user's lifecycle.
To qualify as user provisioning and governance tools, a product must:
- Store accessible identity information on its infrastructure
- Provide relevant administrator tools to define access requirements.
- Use automation in processes related to identity administration.
- Protect security information with security and authentication features.
* Below are the five leading user provisioning software from G2's Fall 2020 Grid® Report. Some reviews may be edited for clarity.
1. Okta
Okta provides identity and access management solutions that harness the power of the cloud and enable people to access applications on any device while ensuring the vigorous enforcement of security policies.
What uses like:
"Okta is an exceptionally adaptable platform for managing several aspects of personality to SaaS and on-premises applications. Okta is an excessively straightforward authentication arrangement from an end-user point of view. You get the chance to integrate Single sign-on, and it automatically stores your credentials and logs you on once you are authenticated through their portal. We have integrated Okta with a large portion of our apps.
With multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled, you have to download the Okta app on your telephone and accept the push to login. SaaS Model is easy to manage and support the most utilized applications from access management and catalog integration viewpoint. The UI and capabilities are light years ahead of the competition. I have never had any login or 2FA issues with Okta. Our clients save minutes every day, not, at this point, composing and re-composing their catalog password."
- Okta Review, Lucas J.
What users dislike:
"There is nothing that is troublesome. The interface sometimes can be tricky, but the product is always evolving, and a lot of UX has already been fixed and is now very usable."
- Okta Review, Xavier R.
2. JumpCloud
JumpCloud securely manages users and their systems while providing access to cloud and multiple on-premise resources. Leveraging cloud-based directory services, IT organizations can choose the best IT resources to enable users to be as productive as possible.
What users like:
"JumpCloud is an excellent user management tool that allows you to extend your current identity provider infrastructure to your end-users. With our remote rollout, JumpCloud quickly allowed us to deploy password protection with encryption and native 2FA. We now have an almost 100% remote workforce, and we rest easy knowing our users are protected and secure.
The policies are useful to ensure that users are installing updates, have appropriate screen locks, and enforce Bitlocker encryption with the recovery keep available in the UI. We also integrated with Duo for a super easy 2FA rollout."
- JumpCloud Review, Tyler D.
What users dislike:
"I don't have a lot of complaints as it's good software. I would like to see an easier way to switch between my normal user account and my admin account for administering JumpCloud itself. Easy enough to have another browser opened, but that's one more thing I have to do."
- JumpCloud Review, Tim R.
3. Rippling
Rippling provides an all-in-one solution to manage a company's payroll, benefits, HR, and IT. It helps you bring all employee systems and data together and automates workflows to save time.
What users like:
"I'm quite happy with how quickly the website loads and how easy it is to access any information related to my pay, position, or medical coverage. Even setting up insurance-related matters only took but a few minutes. By far, much better than ADP use at my wife's current company and my previous companies. This is the first portal I've used that has an HR function as well, which I love since I would normally have to request this information and associated documents via phone or email."
- Rippling Review, Daniel V.
What users dislike:
"There's very little I dislike about Rippling. One thing that I do dislike is that in certain parts of the site, such as the page for integrating other applications into Rippling, the icons can appear a little overwhelming, and it's somewhat unclear how the integration works with Rippling, especially with so many different options."
- Rippling Review, Matthew T.
4. OneLogin
OneLogin is a simplified identity management solution that provides a secure, one-click access for employees, customers, and partners. It works with all device types, cloud, and on-premises applications. Also, it enables IT identity policy enforcement and instantly disables app access for employees who leave or change roles in real time by removing them from Active Directory.
What users like:
"Great support, documentation, and resources are available. OneLogin's account support team is on top of checking in on us to ensure everything continues to go smoothly with quarterly meetings. During these meetings, they go over our OneLogin account and keep us up to date on what OneLogin has planned for future releases. They go over any support tickets we have submitted and answer any questions we might have. We appreciate all of their communication; it's top-notch."
- OneLogin Review, Jon D.
What users dislike:
"On the user side, OneLogin does require a modicum of computer literacy, which can lead to support issues with users who are less technologically advanced. The required use of an extension presents an issue when we're supporting parents who use work provided laptops, as a lot of the time extension downloads are restricted for them."
- OneLogin Review, Christian W.
5. Auth0
Auth0 provides a simple platform that enables easy authentication, authorization, and secure access for applications, devices, and end-users. It makes user account management work for everyone with its extensible and expert-level solution that security and development teams appreciate. Security and development teams rely on its simplicity, extensibility, and expertise to make identity management easy for everyone.
What users like:
"The quickstarts are good. It gives you a good point to work from, and the articles and API explorer allow you the chance to test drive some of the capabilities of the libraries."
- Auth0 Review, Domanic S.
What users dislike:
"Sometimes, the UI seems cluttered as it is difficult to find something. Like, navigating to different tabs while it should be visible at the current tab only."
- Auth0 Review, Kamal W.
Protect your information assets from unauthorized access
Employ user provisioning to onboard or offboard users to save time and add a robust security layer around your information assets. It will help you expedite the process and focus on tasks that are crucial from the security standpoint.
Now that you have provisioned user accounts with access to the system and software, it's advisable to ensure that these software are used effectively for every dime you spend on them.
Learn more about how to manage software assets at your business and avoid costly mistakes.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.
