A well-executed production schedule relieves the burden of the production manager. It also drives operational excellence, smoothes the supply chain road, and benefits end users, creating happy, loyal customers.
While production scheduling has traditionally relied on manual processes and spreadsheets, nowadays, solutions such as advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software are used to refine operations. They offer powerful features like real-time data analysis, automated calculations, and visualization tools that help you make informed decisions swiftly.
What is production scheduling?
Production scheduling is the process of creating a detailed plan that organizes and defines manufacturing workflow for a given period. Production managers allocate labor and resources, determine the flow of tasks, and establish timelines to optimize the overall production process, all thanks to production scheduling. The ultimate goal is to balance production capacity, minimize production costs, increase resources, and ensure on-time delivery.
From raw materials to finished products, efficient scheduling is at the heart of successful production. If you’re ready to learn more about boosting your production process, read on.
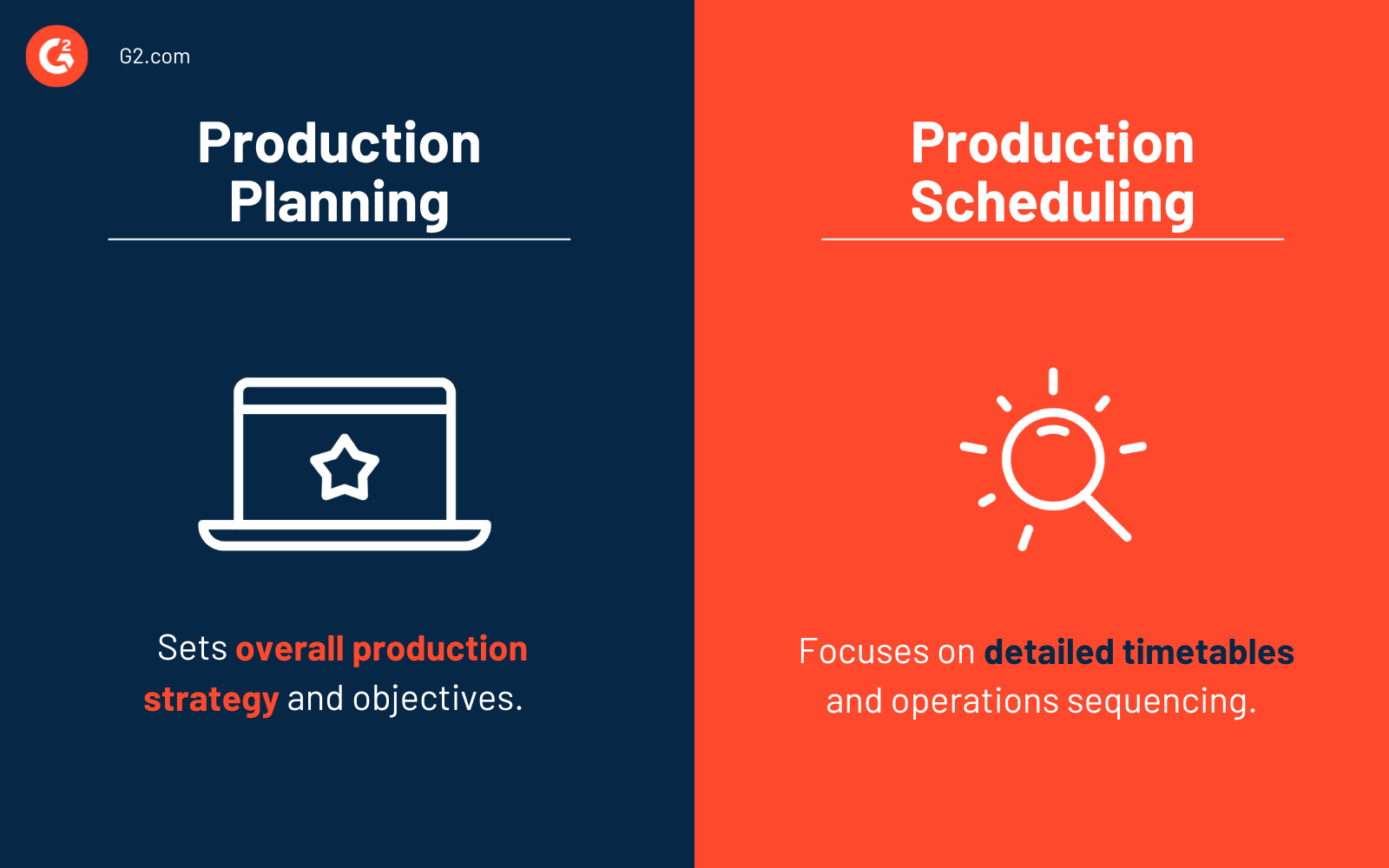
Production planning and scheduling
Production planning and scheduling serve different purposes, even though they sound similar. Production planning sets the goals and directions for an extended period of time, and production scheduling translates those goals into a sequence of tasks within a shorter period.
If we compared the two processes to traveling, production planning would be akin to planning the trip, focusing on the overall itinerary, destination, and resources required to complete the journey. Production scheduling, on the other hand, is analogous to executing the trip. Scheduling flights, arranging accommodation, planning activities, timing the trip, and sending invitations.
Production planning
Production planning is the big-picture strategy that deals with what needs to be produced, when it needs to be produced, and how much of it needs to be produced. It’s more focused on production targets and long-term strategic decisions than production scheduling.
The plans entail a high-level roadmap wherein managers set targets by analyzing forecasts, assessing inventory levels, and considering factors such as market demand, resource availability, and production capacity.
Production scheduling
All of the tactical and detailed processes of specifying the sequence and timing of tasks fall under the umbrella of production scheduling. It concentrates on short-term execution and upcycles production plans into actionable steps, delving into the details of how and when. A comprehensive schedule that outlines when each task will be performed has to factor in production requirements, available resources, task dependencies, constraints, and timelines.
Essentially both planning and scheduling functions are required for increasing production efficiency. Harmonizing these two processes ensures the timely delivery of high-quality products.
Want to learn more about Distribution ERP Software? Explore Distribution ERP products.
The importance of production scheduling in manufacturing
The weight that production scheduling carries in a manufacturing setup can’t be overstated. If you’re looking to operate more smoothly than you are right now, take time to make an effective production schedule, and it’ll practically do the heavy lifting for you.
Imagine you’re running a successful snacks business and your products are doing great on the market. There’s a surge in consumer demand, and now all you’ve got to do is match the demand to supply. Right? Right. But…
Without a plan and schedule in place, you’ve got suggestions for deadlines, uneven distribution of resources and workers, and no record of the production process. The conclusion? Your customers are left waiting for products that don’t seem to materialize. That can’t be good.
Now let’s see how production scheduling saves the day.
First and foremost, using a schedule you guarantee optimal resource utilization. Correctly allocating machinery, equipment, and personnel reduces idle time and maximizes productivity.
Production scheduling also enables efficient inventory management for you to plan and coordinate your material requirements. With a carefully drafted schedule made by analyzing market forecasts, order patterns, and delivery timelines, you’re better positioned to meet customers’ expectations. Your product is ready to hit the shelves again, deliveries are done on time, and as a result, customer satisfaction soars!
You’ll also build a foundation for continuous improvement when you turn to production scheduling. By monitoring performance and analyzing data, you can make adjustments to run optimal operations.
Production scheduling methods
Capacity planning and forward and backward scheduling are commonly used to optimize operations. They play a key role in determining the order and timing of production activities, which establishes the factory production flow and reduces waste. The method that works best for you will depend on factors like the complexity of the product, resource availability, dependencies, and lead time.
The right combination of production scheduling methods simplifies the production process, increases customer satisfaction, and drives success.
1. Capacity planning
This method involves evaluating the capacity of key resources, such as labor, machinery, and facilities, and aligning it with the expected demand. Matching resources with production requirements bypasses bottlenecks, optimizes resource utilization, and maintains an overall balance in the production process.
- Infinite capacity planning is used for production processes with no resource limitations or potential bottlenecks. It’s the right method for you if there are fewer stock-keeping units (SKUs) but a high volume.
- Finite capacity planning is for production processes with limited resources, like staff, machines, and workstations.
2. Forward and backward scheduling
Production managers use both forward and backward scheduling processes to determine the order and timing of operations.
- Forward scheduling generates a plan by organizing tasks chronologically, starting from the present. It determines each task's start and end dates based on their duration and dependencies. Forward scheduling focuses on meeting customer delivery dates. It works well when lead times are consistent, and there are no resource constraints.
- Backward scheduling focuses on the desired delivery date and backtracks to determine the start date. It considers the timing for each task, ensuring that production activities are completed promptly to meet the desired delivery date. Backward scheduling is particularly useful when strict deadlines or complex dependencies between tasks exist.
3. Just-in-time
Just-in-time, or JIT, aims to synchronize production and delivery schedules with customer demand to minimize inventory levels and waste. It follows a demand-driven approach and promotes lean manufacturing practices. Successful JIT scheduling requires reliable supply chain coordination because materials and components are received as needed. It’s a good approach for businesses with fluctuating consumer demand as it offers flexibility and responsiveness to market changes.
4. First come, first serve
FCFS scheduling takes care of tasks based on their arrival order. The sequential approach treats all tasks equally and doesn’t prioritize based on urgency, complexity, or any other criteria. It's an easy-to-implement approach but may prove inefficient when the longer ones delay shorter tasks. FCFS is more suitable for tasks with no time constraints or dependencies.
Production scheduling steps
To make an effective production schedule that enhances your operations, you must follow a series of carefully curated steps. Each plays a vital role in ensuring that production activities are organized, resources are optimized, and consumer demands are met.
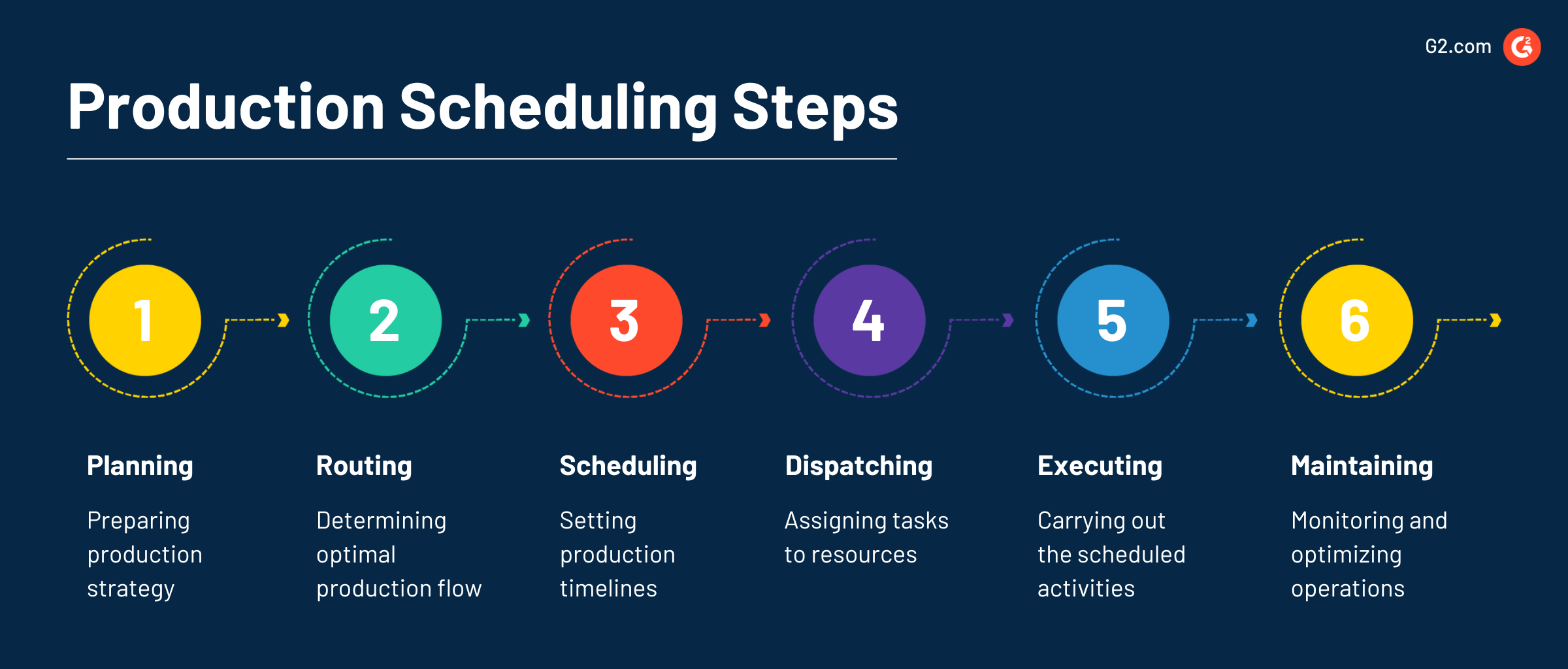
1. Planning
The planning phase provides a framework for subsequent scheduling activities. It involves forecasting consumer demand, analyzing historical data, and establishing production goals. It also takes into consideration factors like lead time, capacity constraints, and resource availability. Planning can be static or dynamic depending on the assumption that the production journey goes according to schedule without any changes.
2. Routing
Routing determines the best path a product will take through the production process. You or one of your staff has to identify the specific operations and workstations required to transform raw materials into finished products. This process minimizes unnecessary movements and cuts down on lead time.
3. Scheduling
Scheduling creates a precise timeline for production activities. This core step factors in task durations, task dependencies, resource availability, and production priorities. Determining the right task sequencing ensures production activities are executed in the most efficient and logical order. The three different types of schedules are:
- Master production schedule (MPS): a full-scale plan made for a specific time frame, detailing the requirements for manufacturing a product. It considers aspects such as budget, resources, and routing.
- Manufacturing schedule: a production plan that solely focuses on routing to detail the steps required to build finished products.
- Retail operations schedule: similar to MPS, except it’s specific to retail products.
%20Template.png)
Source: SoftwareConnect
4. Dispatching
Once the schedule is established, dispatch communicates the plan to appropriate personnel and workstations. Tasks and their necessary instructions are assigned, ensuring that resources and materials are available. Another important aspect of dispatching is guaranteeing that everyone involved is aware of their responsibilities and capable of executing their assigned tasks.
5. Executing
Executing concerns actual implementation, carrying out assigned tasks, operating machinery, assembling products, and performing quality control checks. During execution, you must monitor progress, address any unforeseen issues, and make sure tasks are completed according to the predetermined schedule.
6. Maintaining
The final step is maintenance to evaluate the production process. It takes into account the schedule performance, production data, bottlenecks, and corrective actions.
Production schedule optimization
Optimizing is a critical step toward enhancing operational efficiency and improving overall output. Consider incorporating the following factors into your approach to unlock the full potential of the production scheduling process.
- Embrace the concept of dynamic scheduling. This agile approach lets you respond swiftly to disruptions, prioritize urgent orders, optimize resource allocation, and make real-time adjustments based on changing conditions. Dynamic scheduling empowers you to maintain flexibility and adaptability in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
- Effective work-in-progress (WIP) control ensures smooth production flow. Carefully label tasks by urgency so priorities are set straight, and production is completed without disruption.
- Prioritize on-time deliveries by incorporating order fulfillment deadlines and customer commitments into your scheduling process to enhance consumer satisfaction and maintain strong relationships.
- Inventory and supply management helps you synchronize production with supply chain dynamics. By accurately forecasting demand, coordinating with suppliers, and implementing JIT principles, you can minimize inventory carrying costs, reduce stockouts, and ensure the availability of materials.
- Regular equipment and facility maintenance are vital for uninterrupted production. Implement preventive or predictive maintenance programs to minimize breakdowns and unplanned downtime. By proactively addressing maintenance needs, you create a more reliable production environment.
- Take advantage of the power of production scheduling software. These sophisticated tools automate scheduling processes and provide data-driven insights. You’ll gain the ability to generate optimized schedules quickly, factor in complex variables, and achieve a higher level of efficiency and precision.
Production scheduling tools
Production scheduling tools provide a clear view of the project's progress so you can track the status and deviation at any point in time. Bar charts and Gantt charts are commonly used visual tools. Teams rely on them to represent and communicate project timelines, tasks, and dependencies. While not standalone, production scheduling tools are often utilized within scheduling software or project management systems to handle timetables effectively.
Bar chart
Bar charts, also called activity charts or milestone charts, display tasks as horizontal bars on a time axis. Each bar represents a specific task or activity, and its length corresponds to the duration of that task. Bar charts are useful for visualizing the sequence and timing of tasks, identifying overlapping activities, and determining critical paths.
Gantt charts
Gantt charts are a more advanced and comprehensive version of bar charts. They enable project managers to schedule and monitor activities, allocate resources, track progress, and identify potential bottlenecks or delays over a certain time period. It shows tasks as horizontal bars, but also as vertical lines or arrows to indicate dependencies between tasks. Linked below are some Microsoft Excel templates you can use.
Source: Microsoft
Production scheduling template
When you create your production schedule, include relevant fields that capture the necessary information for monitoring all production activities. Specific requirements may vary based on the industry and organization’s needs, but some commonly included fields are: order/job number, product/item, quantity, start and end date, work center and machinery, lead time, status, operator/assigned employee, and additional notes and comments.
Other points you should remember:
- Keep the schedule simple and easy to understand.
- Prioritize critical information such as product type, quantity, and order.
- Use color coding to visually differentiate fields.
- Update and review the schedule regularly to ensure accuracy and reflect changes.
- Allow some room to accommodate variations.
You can use this example of production scheduling as a jumping-off point. It gives you enough guidance to create a schedule that works specifically for you and your teams.
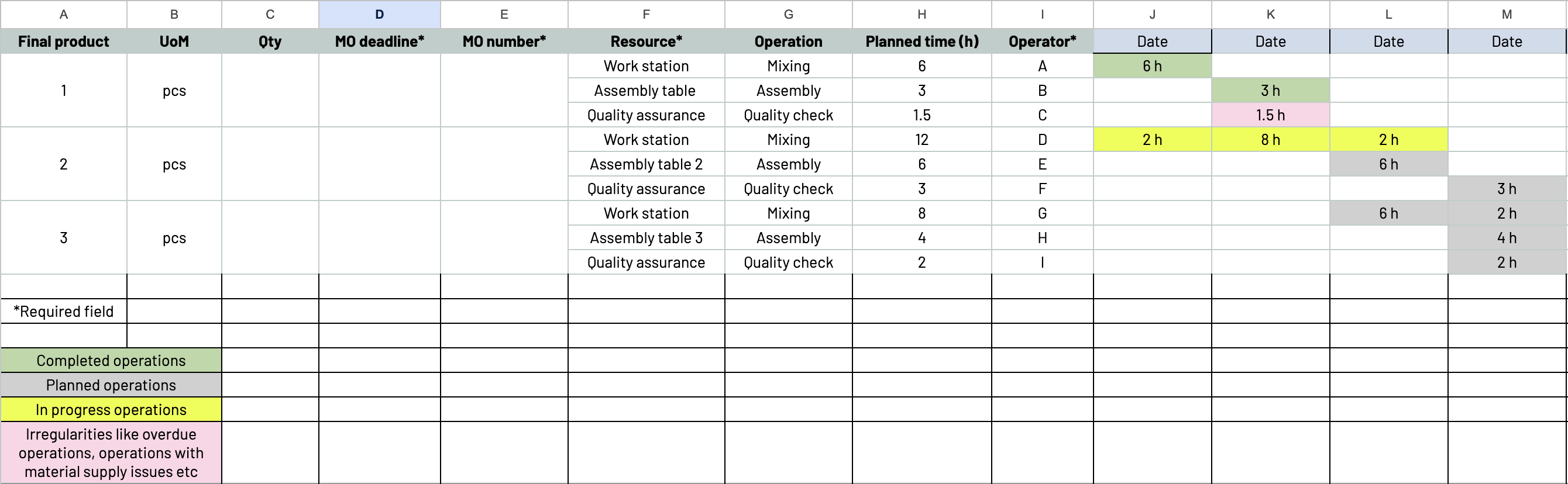
Source: Katana
Benefits of production scheduling
The benefits of production scheduling are many, influencing a company’s every aspect. From the best use of resources to customer satisfaction, it helps you plan and execute production activities. Not only that, it also provides you with a framework to use when things deviate from their expected course, equipping you with the right knowledge to handle unforeseen circumstances.
- Effective inventory management. By aligning production schedules with demand forecasts, you take full advantage of inventory levels and avoid excess or dead stock. A good schedule also reduces inventory holding costs, further improving turnover and cash flow.
- Reduced lead time. Your customers have to get their products on time if you want to stay competitive in the market. By sequencing tasks and activities most efficiently, you reduce the time it takes to make the final product. This agility enables you to respond quickly to customer orders and adapt to market changes.
- Optimal resource utilization. This is simply a major benefit of production scheduling that has been stated multiple times throughout this article and yet not said enough. By careful planning and analysis, you ensure that resources like labor, machinery, materials, and facilities are only used as required.
- Cost savings. Having a production schedule lets you identify the least expensive way to transform raw materials into final products. Saving money is an outcome of using the most cost-effective material, labor, and transport.
- Increased customer satisfaction. The end goal of any business is to make its customers happy, and meeting delivery deadlines maintains positive consumer relationships. Managing your manufacturing and operations via production scheduling allows you to fulfill orders on time.
- Improved project management. Production scheduling provides a clear roadmap for completing production so you’re able to effectively allocate resources, track milestones, and get all your projects completed on time and within budget. It also promotes better visibility and coordination across teams so everyone is aligned about timelines, tasks, and dependencies.
Challenges of production scheduling
Production scheduling offers numerous benefits, but nothing comes without its challenges. Issues with effectively managing and perfecting production schedules are common. But it’s easy to overcome these problems once you’ve properly understood them, so let’s dive right in and look at some issues you might face.
- Inaccurate demand forecasting. Forecasting customer demand with precision challenges you because of changing market dynamics, evolving customer preferences, and unpredictable factors. Imprecise demand planning and forecasts lead to overproduction or stockouts, disrupting the production schedule. You must continuously improve demand forecasting techniques by studying historical data and market insights and collaborating with sales and marketing teams to enhance accuracy.
- Insufficient capacity planning. Inadequate capacity planning can result in imbalanced workloads, resource constraints, and missed production targets. You must carefully assess production capabilities by considering equipment capacity, labor availability, and production cycle.
- Limited resources. Limited resources negatively affect production efficiency, lead times, and overall productivity. Matching the production demand with available resources requires careful planning.
- Poor material planning. Inefficient material planning causes delays, production stoppages, or excess inventory. You have to learn to forecast material requirements accurately, consider lead times, and coordinate with procurement teams to ensure the timely availability of materials. Proper material planning minimizes disruptions and supports smooth production.
- Lack of flexibility. Rigidity in scheduling makes it hard to respond to unexpected changes, rush orders, or interruptions. You should build flexibility into the scheduling process by allowing buffer times, reserving space capacity, or implementing agile production techniques.
- Ignoring feedback. Failing to incorporate feedback from production teams, operators, or quality control personnel hinders the optimization of production scheduling. Regularly gathering feedback and engaging in improvement initiatives helps identify scheduling issues that need fine-tuning.
- Lack of communication and collaboration. Insufficient communication among departments and stakeholders results in misalignment, misunderstandings, and scheduling conflicts. Establish clear communication channels, facilitate cross-functional collaboration, and ensure that information flows seamlessly across teams. Regular meetings, real-time updates, and collaborative decision-making processes are key to effective production scheduling.
Why do you need production scheduling software?
Production scheduling software revolutionizes how you plan and manage your production process. These specialized tools combine sophisticated algorithms, mathematical models, and real-time data analysis to generate effective and accurate schedules. Unlike spreadsheets, which are complex, time-consuming, and prone to human error, production scheduling software provides a centralized platform for scheduling, collaboration, and updates.
Everyone from shop floor workers to procurement personnel to production managers can use production scheduling solutions. They let you optimize resource allocation, minimize downtime, and meet customer demands with precision while saving time.
Advanced planning and scheduling software helps create accurate schedules, simplify operations, improve productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction. It utilizes algorithms and data analysis to make a workable schedule. APS also integrates with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems to automatically update data and optimize production plans.
To qualify for inclusion in G2’s advanced planning and scheduling category, a product must:
- Gather demand data from several systems
- Track raw material availability
- Identify production capacity
- Create demand and constraint-based production schedules
- Optimize schedules based on demand changes
- Convert production plans into schedules
- Deliver production plans and schedules for multiple locations
*Below are the top 5 leading advanced planning and scheduling software from G2’s Summer 2023 Grid® Report. Some reviews may be edited for clarity.
1. SAP S/4HANA Manufacturing solutions
SAP S/4 HANA Manufacturing solutions is an ERP suite that offers a range of modules and tailored solutions for various industries. Expect on-premise deployment, enterprise-wide collaboration, seamless digital manufacturing capabilities, real-time analytics, and detailed scheduling.
What users like best:
“I like the functionality to automate tasks and key processes. The digitalization of the entire supply chain management with great user interface and user experience is one of the best features of this product.”
- SAP S/4HANA Manufacturing solutions Review, Piyush C.
What users dislike:
“SAP S/4HANA requires a lot of customizations that can sometimes be a little complicated if you don’t have an internal SAP development team. You will need to outsource those implementations, which costs extra.”
- SAP S/4HANA Manufacturing solutions Review, Joao O.
2. Acumatica
Acumatica is a cloud-based ERP that offers integrated modules covering various aspects of a business, from finances to CRM. It caters to small and mid-market businesses, providing features like mobile access, flexibility, customization, scalability, and advanced analytics and reporting.
What users like best:
“Acumatica's industry modules make it easy to collaborate and share data across departments. The customizable tools require little to no coding, which makes it easier to manipulate large amounts of data. I'm also impressed by their commitment to constantly developing new product upgrades based on user suggestions in their forum – questions are always answered promptly! Acumatica provides an excellent all-in-one business solution.”
- Acumatica Review, Zeeshan I.
What users dislike:
“The only thing that I dislike about Acumatica is the format of the pages. I would prefer not to click on the bottom right corner of the page to go to the next page. I would rather it be like when I am printing my check run. The list is all there, and all I do is keep scrolling down till I find what I need. Or use the right side to scroll down. Having them in a page-like format instead of all available in a file that you can easily scroll through as a complete file is cumbersome.”
- Acumatica Review, Brenda P.
3. Katana Cloud Manufacturing
Katana Cloud Manufacturing offers a range of features for manufacturers, including live inventory management, real-time master planning, shop floor control, purchase order management, and sales order insights.
What users like best:
“The system is intuitive and user-friendly. I like the logical steps to build the initial material, product, and bill of materials data sets. The tutorial videos provide easy-to-follow, step-by-step guidance. Katana provides functionality to deal with highly customized products without the need to create product SKUs for every possible variant. Given the majority of my products are customized, this feature is extremely important to me. Easy integration with Shopify and Xero is also an important feature. And finally, the technical support and sales teams are super helpful and easily accessible.”
- Katana Cloud Manufacturing Review, Lorna B.
What users dislike:
“The price is high compared to others. If the program is closed, the data is not automatically saved. When you load a large amount of products to the inventory, it gets a little slow.”
- Katana Cloud Manufacturing Review, Mohit G.
4. GPS
GPS brings advanced planning and supply chain management (SCM) to manufacturers for help with production scheduling, material and resource planning, and collaboration with vendors and contractors.
What users like best:
“I keep track of vehicles, and get exact coordinates, which can be used to assist in any emergency. Also used to keep a check on drivers to ensure there is no delay in delivery.”
- GPS Review, Ritesh Y.
What users dislike:
“Occasional system glitches make it difficult to track at times.”
- GPS Review, Hanna A.
5. PlanetTogether
PlanetTogether's easy-to-use software helps manufacturers solve scheduling and capacity issues promptly to increase efficiency and drive manufacturing profitability. Some popular features include ultra-flex Gantts and boards, data synchronization, drag-and-drop rescheduling, and inventory optimization.
What users like best:
“I liked the attention they provided from the first contact. It showed they knew the subject and how to do the job very well. It has helped us in providing better customer service, compliance, and effectively planning inventory.”
- PlanetTogether Review, Arthur J.
What users dislike:
“PlanetTogether does not support Mac and mobile devices with different operating systems.”
- PlanetTogether Review, Gorinta M.
Production scheduling FAQs
Before we get to the conclusion, let’s address some common Qs about production scheduling and software selection.
Q: What are some production scheduling KPIs?
A: A few production scheduling key performance indicators (KPIs) to track include:
- Cost reduction
- Inventory turnover
- Production cycle time
- Order management
- Production service rate
- On-time deliveries
Q: What are the factors to consider when building a production schedule?
A: When creating a production schedule, you want to end up with a comprehensive and realistic framework. To get that, you must consider factors like production capacity, forecasting, inventory needs, specific raw materials requirements, supply chain status, equipment availability, operations management, and plant layout.
Q: How does production scheduling impact overall operational efficiency?
A: By reducing idle time, minimizing production bottlenecks, improving workflow, and enhancing resource utilization, production scheduling makes sure that the right material, labor, and equipment are available at the right time in the right quantities, leading to increased productivity, cost savings, and overall better performance.
Q: How can production scheduling help in reducing costs and maximizing profitability?
A: By optimizing resource allocation and minimizing idle time. It also reduces inventory holding costs by aligning production with demand and avoiding excess inventory. Improved production efficiency, reduced lead times, and enhanced customer satisfaction translate to increased sales and revenue.
Q: What are the core features of production scheduling software?
A: The core features include production scheduling, labor management, production tracking, inventory management, work order management, forecasting, analysis, and process optimization.
Q: Are there any free production scheduling software?
A: Multiple software solutions offer free trials and demos, including Katana Cloud Manufacturing and PlanetTogether.
Q: How do I choose the right software?
A: When selecting production scheduling software, keep the following things in mind:
- Understand your needs and look for software that fulfills them.
- Some software solutions specifically cater to medium or small businesses. The more specialized or customized the software is, the more expensive it becomes.
- Get a demo to check if the tool works for you before investing in it.
- Include people working in different production departments in the selection process.
- Check reviews about the product.
Schedule yourself for success
This is a call for all production managers to maximize their operational efficiency, surpass customer expectations, and thrive in the competitive manufacturing space. Unlock the full potential of your operations with advanced algorithms, real-time data analysis, and automation. Production scheduling is the backbone of a healthy production process, so embrace the right tools and tech and take your production scheduling to the next level.
An effective manufacturing setup demands coordination between internal as well as external partners like vendors. Check out how vendor management uplifts third-party collaborations to ensure smooth operations.

Harshita Tewari
Harshita is a Content Marketing Specialist at G2. She holds a Master’s degree in Biotechnology and has worked in the sales and marketing sector for food tech and travel startups. Currently, she specializes in writing content for the ERP persona, covering topics like energy management, IP management, process ERP, and vendor management. In her free time, she can be found snuggled up with her pets, writing poetry, or in the middle of a Netflix binge.