In legacy IT environments, network glitches and performance lags often required manual escalation to system administrators.
When organisations operate on a distributed database architecture, it creates chaos for internal team members. The inability to track service requests, version modifications, and resource allocation is a recipe for a complete IT crash.
Today, hyperconverged appliances offer a modern alternative: they track resource usage, optimize performance, and eliminate legacy IT silos.
To address previous IT silos and delayed resolutions, many IT teams now rely on hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) solutions to modernize their data center networks and scale for business continuity and availability.
Let’s explore HCI appliances in-depth and learn more about their features that help scale IT efficiently.
What is a hyperconverged appliance?
A hyperconverged appliance is a pre-configured device that combines storage, computing, and networking into a single system. It simplifies data center management by eliminating the need for separate infrastructure components. These appliances scale easily and are managed through a unified interface.
In legacy data centers, storage, compute, and servers existed as siloed components, contributing to lower power efficiency.
By consolidating these components in a hyperconverged appliance, data centers can more efficiently balance loads across all infrastructure components.
TLDR: Everything you should know about a hyperconverged appliance
- What is a hyperconverged appliance? A hyperconverged appliance is a software-defined unit that combines compute, storage, and networking in one scalable platform.
- Why are HCI appliances important for modern IT? They reduce operational complexity, lower costs, and deliver high performance for mission-critical workloads and hybrid environments.
- What features define HCI appliances? They include flash storage, flexible hypervisors, out-of-band management, end-to-end I/O control, linear scalability, and vendor-supported integration.
- Where are hyperconverged appliances typically used? Ideal for business continuity, virtual desktop infrastructure, remote office/edge deployments, and “cloud-in-a-box” rollouts with fast provisioning.
- What benefits do HCI appliances offer over traditional setups? Centralized operations, hybrid-cloud readiness, automated lifecycle management, and reduced total cost of ownership (TCO).
- What challenges should you consider? Traditional clustered deployments may require on-site staffing and complex orchestration. Dual-node systems can help eliminate downtime risks.
- How should you evaluate HCI for your data center? Assess your scalability needs, IT skillsets, and ROI goals to find the right appliance that balances flexibility, performance, and support.
With a hyperconverged appliance, not only can you view your SaaS optimization metric, but you can also maintain data archives, automate data warehousing, and ensure real-time updates across your system networks.
Hyperconverged appliances vs. traditional infrastructure
Hyperconverged appliances combine compute, storage, and networking into one unified system, while traditional infrastructure keeps each component separate, siloed, and independently managed.

Hyperconverged appliances serve as the physical building blocks of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI). They consolidate the core data center infrastructure, compute, storage, networking, and virtualization into a modular, software-defined unit. This integration simplifies deployment, accelerates provisioning, and streamlines management through a centralized interface. Organizations can scale linearly by adding nodes without overhauling the architecture, making HCI ideal for dynamic workloads, edge environments, and fast-growing teams.
In contrast, traditional infrastructure relies on separate compute servers, storage arrays (like storage area networks or NAS), and networking gear, often from multiple vendors. Each component requires dedicated configuration, support, and lifecycle management. Scaling this model is slower and costlier, often involving complex hardware upgrades and increased physical footprint. The result is higher operational overhead, more integration points, and slower time to value.
If you're looking to reduce complexity, accelerate scalability, and future-proof your infrastructure, hyperconverged appliances offer a streamlined alternative to traditional data centers' fragmented, high-maintenance model.
Want to learn more about Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) Solutions ? Explore Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) Solutions products.
What are the key features of a hyperconverged appliance?
Not all hyperconverged appliances are created equal. The right feature set depends on your workloads, performance needs, and growth plans.
Whether you're powering high-performance analytics or virtual desktops, here’s a breakdown of the most critical HCI appliance features to look for:
- Flash and NVMe storage support: Many HCI appliances offer all-flash arrays or NVMe-based storage for ultra-fast read/write speeds, ideal for latency-sensitive, high-throughput workloads like real-time analytics or transactional databases.
- Hypervisor flexibility: For broader compatibility, choose from hosted hypervisors (e.g., on Linux or Windows) or go with bare-metal virtualization (e.g., VMware ESXi) for tighter resource control in high-performance environments.
- Out-of-band management: Maintain full administrative access to your infrastructure, even when the main network is down. Perfect for remote support and edge deployments, out-of-band management allows secure access via dedicated hardware paths.
- Workload-optimized memory: HCI nodes can be configured with high-capacity RAM to support in-memory computing needs, such as real-time dashboards, caching layers, or large-scale virtual desktop environments.
- Linear scalability: Add nodes as needed without redesigning your architecture. HCI is built for environments that scale horizontally, ensuring performance grows in step with compute and storage needs.
- Integrated vendor support & flexibility: Most appliances are sold as turnkey bundles with end-to-end vendor support, but you can still tailor configurations (CPU, RAM, storage, network) to fit your IT footprint.
- High availability built-in: HCI systems are designed with native failover and redundancy, enabling continuous uptime even during hardware or node failures. Vendors like Nutanix and Dell VxRail are known for robust HA capabilities.
- OS-level native integration: Some architectures offer deep Windows integration, embedding directly at the kernel level to eliminate VM overhead and streamline management.
- Granular I/O and QoS control: Fine-tune application performance with Quality of Service (QoS) settings. Allocate bandwidth and I/O resources per virtual machine to prioritize mission-critical apps and workloads.
- Elastic pay-as-you-grow scaling: Many modern HCI appliances support incremental scaling without 3-way replication, improving CPU efficiency and minimizing storage waste. This makes expanding your infrastructure less costly and more agile.
Also, there’s no one-size-fits-all HCI vendor; your ideal solution depends on your existing infrastructure, operational goals, and scalability needs.
Where are hyperconverged appliances used? (with industry examples)
Hyperconverged appliances aren’t just infrastructure upgrades; they’re enablers of agility across industries.
From healthcare to manufacturing to financial services, organizations rely on HCI to deliver performance, uptime, and scalability without complexity. Below are the most common and high-impact use cases, now expanded with vertical-specific examples:
- Business continuity for critical applications. HCI platforms deliver built-in high availability and data redundancy, making them ideal for finance and healthcare environments where application downtime can mean regulatory penalties or patient risk. By unifying storage, compute, and network layers, HCI minimizes failure points and ensures uninterrupted service during hardware or software issues.
- Remote Office, Branch Office (ROBO), and edge deployments: For industries like retail, logistics, and oil & gas, hyperconverged appliances offer lightweight, self-contained units that can run in remote or rugged environments. These deployments often have no on-site IT teams, so centralized management and out-of-band access are critical for consistency and uptime across geographies.
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Educational institutions and enterprise IT departments use HCI to host secure, high-performance VDI environments. With support for hundreds of virtual desktops per appliance, schools, hospitals, and call centers can rapidly deploy or scale desktops while maintaining centralized policy and security control.
- Cloud-in-a-Box deployments: Fast-growing companies in startups or software development often use HCI appliances to stand up private clouds or test environments in under a day. Preconfigured hardware and software bundles make it possible to deploy new workloads or migrate legacy systems without multi-week infrastructure planning.
- Disaster recovery & data replication: Organizations with compliance mandates (e.g., legal or insurance sectors) use HCI for built-in replication and backup. This supports geographically distributed failover strategies without requiring third-party software or separate disaster recovery hardware.
Many organizations begin with a single use case, like VDI or edge deployments, and expand HCI across the enterprise once the time-saving and performance benefits become clear.
What are the benefits of hyperconverged appliances?
Below are some notable benefits of HCI appliances.
- Hybrid-cloud ready: HCI appliances offer a complete, turnkey, and automated solution in hybrid cloud environments. They make it easier to deploy applications quickly.
- Managing operations consistently. It delivers a consistent operational experience from core to edge to cloud through full-stack integration and automated lifecycle management.
- Ensuring powerful performance. It allows businesses to manage workloads while ensuring the reliable performance of applications like SAP or Oracle that are critical to business applications.
- Modernizing the data center. It offers automation, operational processes orchestration, and lifecycle management to drive rapid IT transformation and management.
“We use hyperconverged appliances for virtualization and disaster recovery. They're perfect for disaster recovery because of built-in backup and replication tools. We've also used them in dev and testing environments where spinning up resources quickly is key.”
Matthew Lam
Full-Stack Developer at Penfriend
What are the challenges of traditionally clustered HCI appliances?
While hyperconverged infrastructure simplifies many aspects of IT operations, traditionally clustered HCI setups can introduce their own set of operational and financial challenges, especially for mid-sized organizations scaling quickly or operating in distributed environments.
- High dependence on on-site IT staff: Maintaining peak performance for clustered HCI often requires round-the-clock, in-house expertise, from server tuning to managing firmware updates. This can raise operational costs by up to 25%, particularly in industries where IT staffing is already lean or hard to recruit for remote sites.
- Complex data orchestration: In traditional HCI clusters, teams often need to manually configure network topologies, storage mapping, and replication paths. These setups are prone to errors and require frequent reconfiguration as workloads shift, slowing down deployment cycles and increasing troubleshooting time.
- Third-party add-on overload: Many legacy HCI deployments depend on external services for backup, disaster recovery, deduplication, or storage tiering. This creates integration overhead and inconsistent update cycles, pushing up both management complexity and software licensing costs.
- Hidden costs inflate total cost of ownership (TCO): When you combine hardware refresh cycles, support contracts, and layered services, the TCO of a traditional HCI cluster can exceed projections by 30–40% over five years, especially in environments with volatile workload demands or compliance-driven upgrades.
- Scaling isn't always modular: Some older HCI models require node upgrades in large, fixed increments. That means adding more compute or storage than you currently need, leading to resource waste and higher energy and licensing bills.
While HCI simplifies infrastructure management in theory, traditional clustering models can introduce complexity and cost creep, especially if you’re not working with modern, modular appliances that support incremental growth and automation.
Why do you need dual-clustered HCI appliances?
Some HCI appliances have a dual-node system that automatically switches over whenever the local area network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN) has any issue.
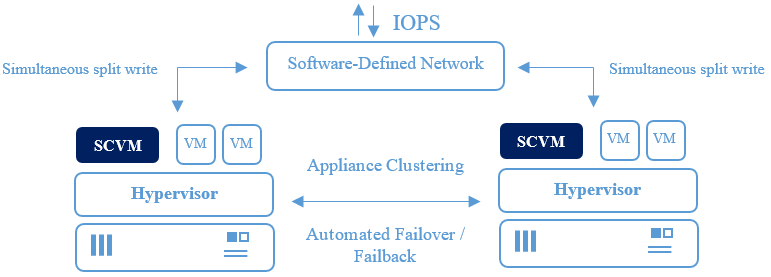
Source: StoneFly
The dual nodes keep data accessible without compromising downtime, making it a suitable HCI solution for enterprises that can’t risk downtime.
Dual-clustered HCI appliances minimize rack space, reduce hardware sprawl, and improve resilience by merging compute and storage into compact, redundant units
Using software-defined networking, such HCI appliances write on both nodes simultaneously, ensuring both HCI appliances have full copies of data.
The system automatically switches to another node whenever one node goes down for maintenance or due to adverse circumstances. This keeps the business running and helps avoid any service interruptions.
How to choose the right hyperconverged appliance (with evaluation checklist)
Choosing the right HCI appliance starts with aligning the technology to your unique IT goals. Here are the top considerations to guide your evaluation:
- Understand your primary use case: Start by identifying what your HCI appliance will actually power. Is it a VDI rollout for remote teams? A DR failover site? A mission-critical SQL workload? For example, a healthcare org running EMRs will need high availability and compliance-ready backup. In contrast, a retail chain deploying edge systems may prioritize remote manageability and compact hardware.
- Check for hypervisor compatibility and flexibility: Does your team have existing VMware licenses or a preference for Hyper-V? Some HCI vendors lock you into a proprietary hypervisor (e.g., Nutanix AHV), while others support multi-hypervisor environments. The right choice depends on your current virtualization strategy and how much flexibility you’ll need in the future.
- Evaluate scalability without overprovisioning: Look for an HCI platform that lets you scale compute, storage, and memory independently, or at least incrementally. Avoid platforms that force large, fixed-size node upgrades. This is especially important if your resource needs fluctuate or if you're planning a phased deployment across sites.
- Prioritize built-in data protection: Native snapshotting, replication, and backup tools should be included, not an afterthought. This is critical for disaster recovery, especially in industries like finance or legal, where uptime and compliance are non-negotiable. Ask if failover is automated or requires manual configuration.
- Assess the vendor’s support model: Does the vendor offer a single point of contact for hardware, software, and hypervisor issues? Or will you need to juggle support tickets between hardware vendors and hypervisor providers? Full-stack support streamlines resolution time when things break.
- Determine edge vs. core deployment readiness: If you’re supporting branch offices, retail outlets, or factory floors, the appliance must work in non-data-center environments, compact, low-power units with remote access capabilities. Some vendors build for core-first infrastructure, while others specialize in distributed edge deployments.
- Look for integration with your existing IT ecosystem: Can the appliance plug into your existing monitoring stack (e.g., Prometheus, SolarWinds), identity providers (e.g., Azure AD), and cloud providers (e.g., AWS or Azure)? Interoperability ensures a smoother rollout and reduces disruption.
- Simplify with centralized and automated management: Modern HCI appliances should come with a single, unified management plane for provisioning, monitoring, patching, and scaling. Avoid solutions that require jumping between multiple interfaces or lack full-stack visibility.
Don’t just ask for a demo, simulate your real workload during trials. See how the appliance performs under pressure, how fast it scales, and how intuitive the management tools really are.
To understand this better, here is an overall evaluation checklist that you can refer to before picking the ideal hyperconverged appliance.
Hyperconverged appliance evaluation checklist
- Does the appliance support your primary use case (e.g., VDI, DR, analytics)?
- Is your preferred hypervisor (VMware, Hyper-V, AHV, etc.) supported natively?
- Can you scale compute, storage, or memory independently, or in small increments?
- Are native backup, replication, and snapshot features included out of the box?
- Does the appliance include high availability and automatic failover capabilities?
- Will the vendor serve as a single point of contact for hardware, software, and support?
- Is the appliance designed for both core and edge deployments if needed?
- Can it integrate with your existing monitoring, cloud, and identity tools?
- Does it offer centralized, GUI-based management with full-stack visibility?
- Are licensing terms transparent, flexible, and easy to renew or expand?
If you answered “yes” to 8 or more of these, you’re likely evaluating an enterprise-ready HCI solution. If not, dig deeper into vendor capabilities or reassess your infrastructure requirements.
Hyperconverged appliance: Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is a hyperconverged appliance?
A hyperconverged appliance is a pre-integrated system that combines compute, storage, networking, and virtualization into a single, software-defined unit. It simplifies data center management and enables faster application and workload deployment.
How does HCI differ from traditional infrastructure?
Unlike traditional infrastructure, which separates servers, storage, and networking into siloed components, hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) unifies them into one cohesive system. This reduces complexity, improves scalability, and lowers operational overhead.
What are common use cases for HCI appliances?
HCI appliances are commonly used for virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), disaster recovery, edge computing, and business continuity. Their modular, scalable design makes them ideal for both core data centers and remote office environments
Which vendors offer hyperconverged infrastructure solutions?
Leading HCI vendors include Nutanix, Dell VxRail, VMware (vSAN ReadyNodes), StarWind, and HPE SimpliVity. Each offers unique features, hypervisor options, and management tools tailored to different IT environments.
How do dual-node HCI appliances ensure availability?
Dual-node HCI systems replicate data between two active nodes, allowing instant failover if one node fails or goes offline. This architecture ensures high availability and uninterrupted access to critical applications and data.
What challenges should IT teams expect with HCI deployment?
Common challenges include integration with legacy systems, managing clustered configurations, and upfront capital investment. Teams should also plan for training and ensure proper sizing to avoid under- or over-provisioning.
Middlemen that handle IT chaos
The introduction of HCI has fundamentally changed how organizations design, manage, and scale infrastructure.
By consolidating compute, storage, networking, and virtualization into a unified, software-defined platform, HCI appliances help IT teams cut complexity, improve agility, and future-proof operations. Whether you are supporting mission-critical workloads, enabling remote or edge deployments, or building a scalable private cloud, HCI helps deliver consistent performance to prepare you for future scaling.
Explore the best database software on G2 to learn how to manage and scale growing volumes of unstructured data in the most efficient and cost-effective way.
This article was originally published in 2024. It has been updated with new information.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.
