To help buyers make sense of the data privacy software landscape, I will write several articles on various functions of data privacy software. My aim is to provide our readership with overviews and practical advice when buying data privacy software of all kinds. Our first installment is an overview of data privacy management software.
What is Data Privacy Management Software?
There isn’t a standard that’s developed for Data Privacy Management Software yet, and products are quickly expanding their offerings with loads of recent investment money flowing in to further develop that functionality. For example, in January 2020 alone, two major privacy-software vendors, Securiti.ai and BigID, both separately announced investments of $50 Million each. This is not to mention the flurry of investments that took place in late 2019 prior to the CCPA going into effect, such as start-up DataGrail getting backed as part of Okta’s $50 Million venture fund, nor consolidation in the space with acquisitions like TrustArc’s acquisition of Nymity or OneTrust’s acquisition of the IAPP’s Privacy core eLearning solution.
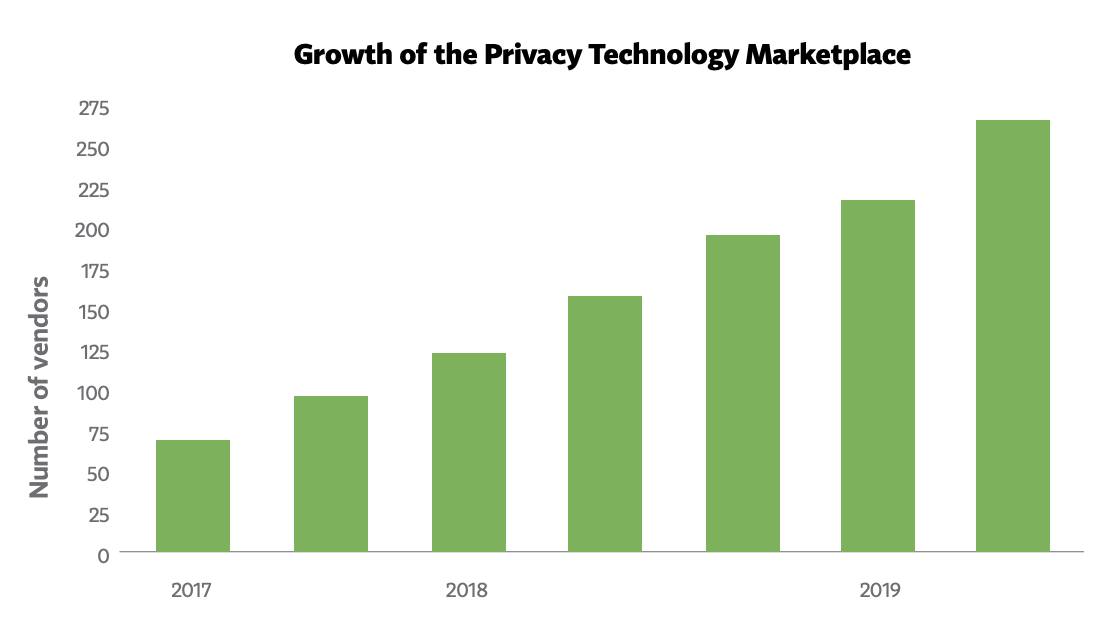 Source: 2019 IAPP Tech Vendor Report
Source: 2019 IAPP Tech Vendor Report
After reviewing slews of software currently available in this dynamic space, however, here’s how we at G2 are defining this category of software, for now.
Data Privacy Management Software:
Data Privacy Management software helps companies manage their privacy programs to comply with global privacy laws such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), among other regulations. The main functionality of Data Privacy Management software includes:
1. Sensitive data discovery and mapping
2. Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) management (or consumer request management) and
3. Consent management platform
These software solutions often provide additional functionality such as (or integrate with other applications, to provide) vendor assessment management, cookie compliance, data breach notification, identity verification, data de-identification or pseudonymity, privacy impact assessments (PIA).
Want to learn more about Data Privacy Management Software? Explore Data Privacy Management products.
Main features of data privacy management software
Let’s take a closer look at the most fundamental features of Data Privacy Management software, which include three main features:
-
- Sensitive data discovery and mapping
- Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) management
- Consent management
General questions to consider when selecting a data privacy management software solution:
-
- Is this software legislation-agnostic? Will it work for GDPR, CCPA, or any number of the multitude of forthcoming privacy laws?
- Does it meet both your and your end users language needs?
- Does this solution meet the needs of your colleagues across departments? Who will primarily use this on the front end? Privacy officers? Legal teams? Who will primarily administer this on the back end? IT teams? InfoSec teams? Are their needs met with this software solution?
Sensitive data discovery and mapping
Can you confidently say that you know where all of your company’s personally identifiable information (PII) and sensitive data reside? What about data in your databases, applications, email platforms, or even endpoints like employee laptops or mobile phones? How about sensitive information stored in old emails? Further questioning, do you know where you got that data from and from whom? And where is the data now going? In order to comply with data privacy laws, companies must know where their sensitive data is located and how it is used.
Data privacy management software solutions today assist companies with understanding where their sensitive data is in three ways, via:
-
- Manual surveys - This requires colleagues to manually fill out surveys or excel spreadsheets noting where sensitive data is stored. This process can be laborious, so some Data Privacy Management software providers offer pre-built survey templates and workflow tools to administer this tedious task.
- Automated sensitive data discovery - Automated sensitive data discovery tools connect to your databases, applications, and other data repositories and crawl for, identify, and classify sensitive data automatically. Many of these tools offer visual representations of your data so you can see where the overall data is stored geographically, but also create a map of an individual data subject.
- Some combination of both of these methods.
There are advantages and disadvantages to both the survey-based data discovery method and the automated discovery method. For survey-based data discovery, this is not a technological lift, rather one of process. Since employees who manage the data fill out these surveys, user error or incompleteness can be a critical issue. Furthermore, the results of this exercise are static as of when the data was reported. We know new data is made every day, so the information will be outdated from the date it was generated.
For automated data discovery, the benefits are that when implemented, it is an automatic process that does not require employees to find sensitive data and the results are dynamic and up to date. The limits with automated data discovery are that it must be able to connect to not only your cloud storage and cloud applications, but your on-prem databases and legacy applications, as well. Some vendors that provide automated discovery are willing to build custom APIs to connect to legacy stores to address this issue, however.
Questions to consider when selecting an automated data discovery tool:
-
- What pre-built connections does the vendor offer?
- Can their solution find both structured and unstructured data?
- What file formats can their solution find? Do they offer OCR for scanned documents?
- Will they build custom connections for non-standard or legacy data repositories?
- Have your company’s IT teams review the solution to ensure it meets their needs.
For small businesses or businesses with a low amount of sensitive data, survey-based may be sufficient for now. Survey-based sensitive data discovery is also a way to find data that may live on legacy systems or in applications that cannot be discovered using an automated method, such as literal paper files. For large enterprises and companies that have embraced the digital transformation or are digital natives, however, automated discovery would be easy to add to your mix of other SaaS products. From an industry perspective, I have seen a number of investments in automated data discovery, so I do believe long term, this method is the way of the future.
Data subject access request (DSAR) management
So what happens when you get a request from a data subject (a consumer, employee, or other end user) requesting to access, port, or delete their data? How do you manage those requests within the legally defined response timeframes?
| Related:Learn more about process data portability requests, here.→ |
Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) software functionality generally includes providing a DSAR intake form or portal to accept data subject’s request to access, port, or delete their personally identifiable information; identity verification methods; provide a centralized view of all DSARs in process; alerts to administrators when it is getting close the legally mandated response time; provides workflow tools to process DSARs across your organization; and provide reporting tools and logs. Some tools also offer an encrypted communication portal to securely communicate and transfer DSAR data to a data subject.
Questions to ask vendors about their Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) management functionality:
- Do you have template online forms for Data Subject Access Requests (DSAR) to intake requests?
- Do you offer a toll-free phone number to intake DSAR requests via phone, which is required of some companies?
- Can the DSAR forms be branded with the company branding for branding continuity or must it retain the privacy vendor’s branding?
- How do you verify the identity of data subjects? Do you offer identity functionality natively or is this a plug-in to another vendor and hence, another software licence?
- If identity verification is offered, what are the methods of confirming identities? Examples include identification card verification, voice verification, email verification, sms verification, mobile-push, biometric authentication, challenge questions, account-based questions, or other forms of identification and authentication.
- If your data discovery process is manual:
Do you offer workflow tools to manage the process of asking other employees to find, access, or delete the data requested? - If your data discovery process is automated:
After the data is automatically discovered, do you send a report for a privacy administrator to review prior to sending the report to the data subject?
- Do you offer an encrypted communication portal to reply to DSARs?
Consent management
An important feature that is becoming more common in data privacy management software is consent management, as many data privacy regulations require either opt-in or opt-out consent from users before collecting, using, sharing, or selling their user data. Getting user consent right is critical. To adhere to user consent and preferences, companies can employ consent management tools.
With consent management tools, users can consent to a whole host of data usage by companies, including right to data collection, location tracking, contact preferences including sms, email, phone, and more. End users can even set collection and usage permissions for their IoT devices. Employing consent management tools makes adhering to data privacy regulations much easier.
What’s next
This article provides a high-level overview of Data Privacy Management software. My aim is to write more in depth information on the functionality of data privacy management platforms, as well as content about other privacy-related software. Follow my content on G2’s research site for updates. You can also follow me on LinkedIn.
Disclaimer: I am not a lawyer and am not offering legal advice. If you have legal questions, consult a licensed attorney. I also don't give fashion advice, relationship advice, or movie recommendations. Trust me, this is for the best.

Merry Marwig, CIPP/US
Merry Marwig is a senior research analyst at G2 focused on the privacy and data security software markets. Using G2’s dynamic research based on unbiased user reviews, Merry helps companies best understand what privacy and security products and services are available to protect their core businesses, their data, their people, and ultimately their customers, brand, and reputation. Merry's coverage areas include: data privacy platforms, data subject access requests (DSAR), identity verification, identity and access management, multi-factor authentication, risk-based authentication, confidentiality software, data security, email security, and more.
