Accounting doesn’t excite most business owners.
You love growing your business but dread tasks like calculating assets, liabilities, and equity. While accounting software would simplify the accounting process, you don’t feel ready for that step yet.
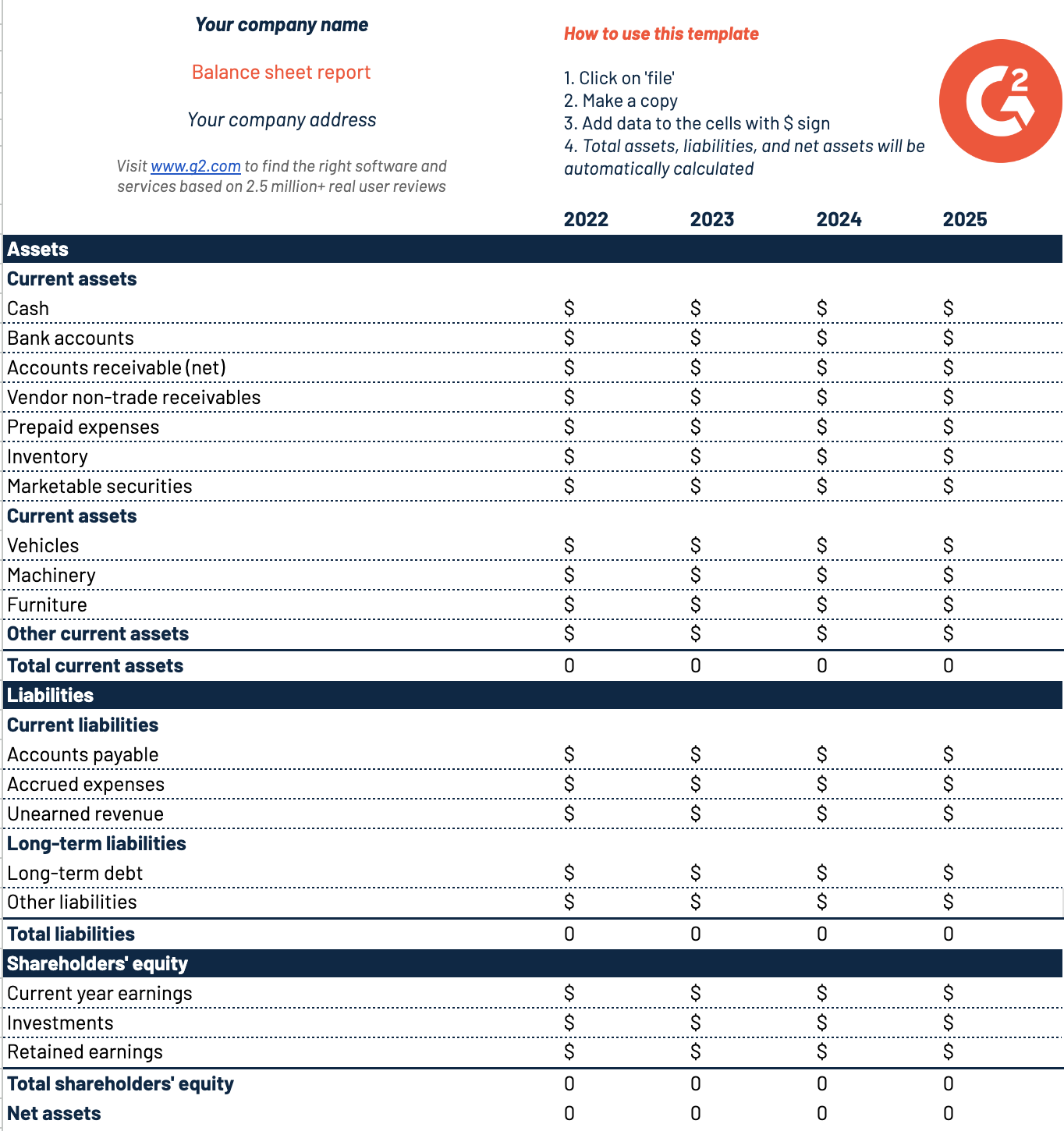
A balance sheet template is exactly what you need. It allows you to calculate all sorts of financial numbers, such as income, expenses, and profitability. To help you get started, we’ve created a free, customizable, and printable balance sheet template that you can use to monitor business finances.
Balance sheet template
Use this balance sheet template to simplify asset, liability, and equity calculations.
How to access this template: Download this Google Sheets balance sheet template, or download this PDF balance sheet template.
A balance sheet is a financial statement that calculates the difference between assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. Companies use it to understand what they own and what they owe. Analysts, investors, and finance managers use income statements and cash flow statements along with balance sheets to assess organizations’ financial health.
Want to learn more about Accounting Software? Explore Accounting products.
Balance sheet formula
The balance sheet formula puts assets on one side and liabilities along with shareholders' equity on the other side to balance them out. Total assets include current assets and non-current assets. Total liabilities consist of current and non-current liabilities. Shareholders’ equity is made up of share capital and retained earnings.
Balance sheet equation:
Assets = liabilities + shareholders' equity
Structure of a balance sheet
A balance sheet has three components: assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Assets are resources you own. They reflect an organization’s cash flow and capital. There are different types of assets, including tangible, intangible, current, non-current, operating, and non-operating. Examples include office buildings, machinery, deposits, and securities.
- Liabilities are financial commitments and obligations you owe to others. There are two types: current and non-current liabilities. Examples include accounts payables, short-term debt, accrued expenses, bonds payable, deferred tax liabilities, and long-term lease obligations.
- Shareholders’ equity is the amount you pay shareholders after liquidating assets and settling debts. Positive equity indicates a company’s ability to pay liabilities with assets, while negative equity indicates that its liabilities exceed its assets.

Sudipto Paul
Sudipto Paul is an SEO content manager at G2. He’s been in SaaS content marketing for over five years, focusing on growing organic traffic through smart, data-driven SEO strategies. He holds an MBA from Liverpool John Moores University. You can find him on LinkedIn and say hi!